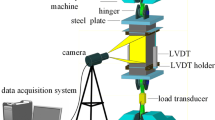
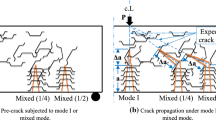
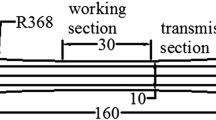
Abstract
Mixed-mode fracture experiments were conducted on aligned steel fibre reinforced cementitious composite (ASFRC) and ordinary steel fibre reinforced cementitious composite (SFRC) three-point bending beams. Mixed-mode fracture performances of the ASFRC and SFRC specimens were studied by changing the crack offset distance. The fracture processes of the ASFRC and SFRC specimens were simulated using the extended finite element method. A good agreement was found when the simulation results were compared with the experimental ones. The alignment of steel fibres significantly improved mixed-mode fracture properties. The peak load \(P_{\mathrm {max}}\) and crack initiation angle of the ASFRC specimen were obviously greater than those of the SFRC specimen because more steel fibres bridged the crack. Compared to the SFRC, the \(P_{\mathrm {max}}\) of the ASFRC increased by 58%, 49% and 38% with the crack offset distances of 0, 50 and 100 mm, respectively. The crack initiation angle of the ASFRC increased by 11% and 17% with the crack offset distances of 50 and 100 mm, respectively. In addition, the influences of the initial crack length to depth ratios a/D and the steel fibre volume fraction \(V_{\mathrm {f}}\) on the ASFRC specimens were simulated. The \(P_{\mathrm {max}}\) significantly increased with \(V_{\mathrm {f}}\) and decreased with a/D
























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Initial crack length
- \(B_{\mathrm {}}\) :
-
Width of specimen
- CMOD :
-
Crack mouth opening displacement
- CMOD \(_{\mathrm {c}}\) :
-
Critical crack mouth opening displacement
- d :
-
Crack offset distance
- D :
-
Depth of specimen
- \(D_{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Diameter of the steel fibre
- F :
-
Draft load of single steel fibre
- L :
-
Length of specimen
- \(L_{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Length of the steel fibre
- S :
-
Span of specimen
- \(S_{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Slip length of the steel fibre
- \(V_{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Steel fibre volume fraction
- \(\sigma _{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Stress of steel fibre
- \(\varepsilon _{\mathrm {f}}\) :
-
Strain of steel fibre
References
Abrishambaf A, Barros JAO, Cunha VMCF (2013) Relation between fibre distribution and post-cracking behaviour in steel fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete panels. Cem Concr Res 51:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.04.009
Abrishambaf A, Barros JAO, Cunha VMCF (2015) Tensile stress-crack width law for steel fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete obtained from indirect (splitting) tensile tests. Cem Concr Compos 57:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.12.010
Abrishambaf A, Cunha VMCF, Barros JAO (2016) A two-phase material approach to model steel fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete in panels. Eng Fract Mech 162:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.04.043
Al-Mattarneh H (2014) Electromagnetic quality control of steel fiber concrete. Constr Build Mater 73:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.101
Altun F, Haktanir T, Ari K (2007) Effects of steel fiber addition on mechanical properties of concrete and RC beams. Constr Build Mater 21:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.12.006
Arman E, Kai N (1999) Building material, especially concrete or mortar, contains magnetically or electrically aligned parallel fibres. DE19750746
Barragán BE, Gettu R, Martín MA, Zerbino RL (2003) Uniaxial tension test for steel fibre reinforced concrete—a parametric study. Cem Concr Compos 25:767–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00096-3
Belytschko T, Black T (1999) Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing. Int J Numer Methods Eng 45:601–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19990620)45:5%3c601::AID-NME598%3e3.0.CO;2-S
Brandt AM (1985) On the optimal direction of short metal fibres in brittle matrix composites. J Mater Sci 20:3831–3841. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00552371
Carpinteri A (1988) Interaction between tensile strength failure and mixed mode crack propagation in concrete. Mater Struct 21:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472319
Cunha VMCF, Barros JAO, Sena-Cruz JM (2012) A finite element model with discrete embedded elements for fibre reinforced composites. Comput Struct 94–95:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2011.12.005
Dupont D, Vandewalle L (2005) Distribution of steel fibres in rectangular sections. Cem Concr Compos 27:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2004.03.005
Gal E, Kryvoruk R (2011) Meso-scale analysis of FRC using a two-step homogenization approach. Comput Struct 89:921–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2011.02.006
Gettu R, Gardner DR, Saldívar H, Barragán BE (2005) Study of the distribution and orientation of fibers in SFRC specimens. Mater Struct Constr 38:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1617/14021
Hillerborg A, Modéer M, Petersson P-E (1976) Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements. Cem Concr Res 6:773–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(76)90007-7
Jenq YS, Shah SP (1988) Mixed-mode fracture of concrete. Int J Fract 38:123–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00033002
Kang ST, Kim JK (2011) The relation between fiber orientation and tensile behavior in an ultra high performance fiber reinforced cementitious composites (UHPFRCC). Cem Concr Res 41:1001–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.05.009
Karihaloo BL, Xiao QZ (2003) Modelling of stationary and growing cracks in FE framework without remeshing: a state-of-the-art review. Comput Struct 81:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(02)00431-5
Lee C, Kim H (2010) Orientation factor and number of fibers at failure plane in ring-type steel fiber reinforced concrete. Cem Concr Res 40:810–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.11.009
Mu R, Li H, Qing LB et al (2017) Aligning steel fibers in cement mortar using electro-magnetic field. Constr Build Mater 131:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.081
Mu R, Wei LS, Wang XW et al (2018) Preparation of aligned steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite and its flexural behavior. J Vis Exp 136:e56307. https://doi.org/10.3791/56307
Mu R, Xing P, Yu JX et al (2019) Investigation on reinforcement of aligned steel fiber on flexural behavior of cement-based composites using acoustic emission signal analysis. Constr Build Mater 201:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.084
Mu R, Diao CR, Liu H et al (2021) Design, preparation and mechanical properties of full-field aligned steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite. Constr Build Mater 272:121631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121631
Pirmohammad S, Hojjati Mengharpey M (2018) A new mixed mode I/II fracture test specimen: numerical and experimental studies. Theor Appl Fract Mech 97:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2018.08.012
Prashanth MH, J.M. Chandra Kishen (2016) An acoustic emission study of mixed mode crack propagation in reinforced concrete beams. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures. https://doi.org/10.21012/FC9.077
Qing LB, Yu KL, Mu R, Ge ZM (2018) Meso-scale simulation of tension properties for aligned steel fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao/Journal Build Mater (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.04.006
Qing LB, Cheng YH, Mu R (2019) Toughness enhancement and equivalent initial fracture toughness of cementitious composite reinforced with aligned steel fibres. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 42:2533–2543. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13102
Qing LB, Shi XY, Mu R et al (2019) An analytical non-linear hinge model for predicting the fracture processes of cementitious composites. Theor Appl Fract Mech 104:102387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102387
Ren XD, Li J (2013) Multi-scale based fracture and damage analysis of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Eng Fail Anal 35:253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2013.01.029
RILEM Committee FMT89 (1990) Determination of fracture parameters (\(K_{\rm IC\rm ^{\rm s}}\) and CTOD\(_{\rm c})\) of plain concrete using three-point bend tests. Mater. Struct. 23 (6):457–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472029
Rotondo PL, Weiner KH (1986) Aligned steel fibres in concrete poles. Concr Int 8:22–27
Ruiz G, de la Rosa A, Almeida LC et al (2019) Dynamic mixed-mode fracture in SCC reinforced with steel fibers: an experimental study. Int J Impact Eng 129:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.03.003
Sebaibi N, Benzerzour M, Abriak NE (2014) Influence of the distribution and orientation of fibres in a reinforced concrete with waste fibres and powders. Constr Build Mater 65:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.134
Soetens T, Matthys S (2014) Different methods to model the post-cracking behaviour of hooked-end steel fibre reinforced concrete. Constr Build Mater 73:458–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.093
Soroushian P, Elyamany H, Tlili A, Ostowari K (1998) Mixed-mode fracture properties of concrete reinforced with low volume fractions of steel and polypropylene fibers. Cem Concr Compos 20:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(97)87390-8
Stolarska M, Chopp DL, Moës N, Belytschko T (2001) Modelling crack growth by level sets in the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 51:943–960. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.201
Sukumar N, Prévost J-H (2003) Modeling quasi-static crack growth with the extended finite element method Part I: computer implementation. Int J Solids Struct 40:7513–7537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2003.08.002
Sukumar N, Srolovitz DJ, Baker TJ, Prévost JH (2003) Brittle fracture in polycrystalline microstructures with the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.653
Yu RC, Cifuentes H, Rivero I et al (2016) Dynamic fracture behaviour in fibre-reinforced cementitious composites. J Mech Phys Solids 93:135–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2015.12.025
Zerbino R, Tobes JM, Bossio ME, Giaccio G (2012) On the orientation of fibres in structural members fabricated with self-compacting fibre reinforced concrete. Cem Concr Compos 34:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.09.005
Acknowledgements
The work presented in the paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51779069, 51878239, 52022027) the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No. E2020202151), and the Key Project of University Science and Technology Research of Hebei Province (No. ZD2019072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qing, L., Li, Y., Wang, X. et al. Investigation of mixed-mode fracture of aligned steel fibre reinforced cementitious composites. Int J Fract 228, 159–178 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-021-00527-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-021-00527-w