Abstract
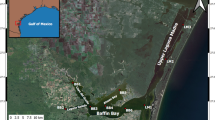
Myall Lakes is a large brackish coastal lake on the east coast of Australia that was considered pristine until the occurrence of blue-green algal blooms in 1999. The temporal and spatial extent of chemical and biological changes to the water column of Myall Lakes was studied intensively after a rain event in 2002. Water quality profiles (T, EC, pH, DO), turbidity (secchi), nutrients (TN, NO x , NH4 +, DON, TP, FRP, DOP, Si), and phytoplankton (chl a and cell counts) were measured at nine sites on eight occasions immediately after the rain event. Freshwater inflows affected a large area of the lake. Greatest changes were seen in areas close to the mouth of the upper Myall River which is the largest freshwater input to the lakes. Here, greatly elevated concentrations of NO x , TP, and FRP (up to two orders of magnitude higher than background) were recorded immediately after the rain event but persisted for only 2 to 8 days. Slightly elevated concentrations of TP and NO x were seen in inflows from the smaller Boolambayte Creek. Stratification was associated with bottom water anoxia and release of ammonia from the sediments. Identification of the sources of nutrient species delivered from different parts of the catchment, combined with studies of nutrient loads can assist managers to develop effective nutrient reduction strategies to reduce the incidence of blue-green algal blooms in Myall Lakes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, F. E., 1973. Soil Organic Matter and its Role in Crop Production. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Anderson, D. M., P. M. Glibert & J. M. Burkholder, 2002. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition and consequences. Estuaries 25: 704–726.
APHA, 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, AWWA-WPCF.
Atkinson, G., P. Hutchings, M. Johnson, W. Johnson & M. Melville, 1981. An ecological investigation of the Myall Lakes region. Australian Journal of Ecology 6: 299–327.
Chessman, B. C., 1986. Impact of the 1983 wildfires on river water quality in East Gippsland, Victoria. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 37: 399–420.
CSIRO, 2001. Gippsland Lakes Environmental Study; Assessing Options for Improving Water Quality and Ecological Function. Report prepared for the Gippsland Coastal Board.
CSIRO, 2004. Climate Change in NSW: Part 2 Projected Changes in Climate Extremes. Consultancy report for NSW Greenhouse Office.
Davis, J. R. & K. Koop, 2006. Eutrophication in Australian rivers, reserviours and estuaries – a southern hemisphere perspective on the science and its implications. Hydrobiologia 559: 23–76.
DIPNR, 2004. Understanding blue green algal blooms in Myall Lakes. Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Donohue, R., W. A. Davidson, N. E. Peters, S. Nelson & B. Jakowyna, 2001. Trends in total phosphorus and total nitrogen concentrations of tributaries to the Swan-Canning Estuary, 1987–1998. Hydrological Processes 15: 2411–2434.
Eyre, B. & C. Twigg, 1997. Nutrient behaviour during post-flood recovery of the Richmond River estuary northern NSW, Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 44: 311–326.
Ferguson, A., B. Eyre & J. Gay, 2004. Nutrient cycling in the sub-tropical Brunswick Estuary, Australia. Estuaries 27: 1–17.
Haines, P., 2006. Physical and Chemical Behaviour and Management of Intermittently Closed and Open Lakes and Lagoons (ICOLLs) in NSW. PhD Thesis Griffith University, Queensland, Australia: 390 pp.
Harris, G. P., 1999. Comparison of the biogeochemistry of lakes and estuaries: ecosystem processes, functional groups, hysteresis effects and interactions between macro- and microbiology. Marine and Freshwater Research 50: 791–811.
Harris, G. P., 2001. Biogeochemistry of nitrogen and phosphorus in Australian catchments, rivers and estuaries: effects of land use and flow regulation and comparisons with global patterns. Marine Freshwater Research 52: 139–149.
Henriksen, K. & W. M. Kemp, 1988. Nitrification in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. In Blackburn, T. H. & J. Sørensen (eds), Nitrogen Cycling in Coastal Marine Environments. John Wiley & Sons, Chickester: 207–249.
Hosomi, M. & R. Sudo, 1986. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in freshwater samples using persulfate digestion. International Journal of Environmental Studies 27: 267–275.
Hubertz, E. D. & L. B. Cahoon, 1999. Short-term variability of water quality parameters in two shallow estuaries of North Carolina. Estuaries 22: 814–823.
Livingston, R. J., 2001. Eutrophication Processes in Coastal Systems: Origin and Succession of Plankton Blooms and Effects on Secondary Production in Gulf Coast Estuaries. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 327 pp.
McComb, A. J., 1995. Eutrophic Shallow Estuaries and Lagoons. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 240 pp.
McKee, L., B. Eyre & S. Hossain, 2000a. Intra- and interannual export of nitrogen and phosphorus in the subtropical Richmond River catchment, Australia. Hydrological Processes 14: 1787–1809.
McKee, L. J., B. D. Eyre & S. Hossain, 2000b. Transport and retention of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sub-tropical Richmond River estuary, Australia – a budget approach. Biogeochemistry 50: 241–278.
Moore, S. K., M. E. Baird & I. M. Suthers, 2006. Relative effects of physical and biological processes on nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics in a shallow estuary after a storm event. Estuaries and Coasts 29: 81–95.
Peters, N. E. & R. Donohue, 2001. Nutrient transport to the Swan-Canning estuary, Western Australia. Hydrological Processes 15: 2555–2578.
Ringuet, S. & F. T. Mackenzie, 2005. Controls on nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics during normal flow and storm runoff conditions, southern Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Estuaries 28: 327–337.
Ryan, N. J., S. M. Mitrovic & L. C. Bowling, 2008. Temporal and spatial variability in the phytoplankton community of Myall Lakes, Australia, and influences of salinity. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9375-3.
Sanderson, B. G., 2008. Circulation and the nutrient budget in Myall Lakes. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9380-6.
Sauer, T. J., R. B. Alexander, J. V. Brahana & R. A. Smith, 2001. The importance and role of watersheds in the transport of nitrogen. In Follett, R. F. & J. L. Hatfield (eds), Nitrogen in the Environment: Sources, Problems, and Management. Elsevier Science B. V., Amsterdam: 147–181.
Strong, W. M. & M. G. Mason, 1999. Nitrogen. In Peverill, K. I., L. A. Sparrow & D. J. Reuter (eds), Soil Analysis – An Interpretation Manual. CSIRO, Collingwood.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. E. Likens, 2000. Limnological Analyses. Springer Verlag, New York.
Young, W. J., F. M. Marston & J. R. Davis, 1996. Nutrient exports and land use in Australian catchments. Journal of Environmental Management 47: 165–183.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded and supported by the NSW Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources (now NSW Department of Natural Resources). The authors would like to thank many colleagues who assisted with field collections at short notice. Interpretation of these results was greatly improved by discussions with Dr Lee Bowling, Dr Dave Rissik, and Peter Evans and comments by two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: J. Wilson, L. Bowling & J. Tibby
The Myall Lakes: patterns and processes in an unusual coastal lake system in eastern Australia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, J. Nutrient and phytoplankton responses to a flood event in a series of interconnected coastal lakes: Myall Lakes Australia. Hydrobiologia 608, 21–34 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9377-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9377-1