Abstract
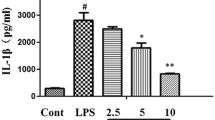
Nobiletin (NOB), a citrus polymethoxy flavonoid, has been reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-insulin resistance activities. Although the anti-inflammatory activity of NOB already reported, its involvement in lung protection has not been reported. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory response of NOB in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated A549 cells and LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice. The animals were pre-treated with NOB (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg) or DEX (5 mg/kg) at 12 and 1 h before intranasal instillation of LPS. The severity of pulmonary injury was evaluated 6 h after LPS administration. Results suggested that treatment with NOB dramatically attenuated lung histopathological changes, wet-to-dry (W/D) ratio, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, the numbers of inflammatory cells, and TNF-α, IL-6, and NO in BALF induced by LPS. Furthermore, NOB also significantly inhibited the expression of iNOS and the phosphorylation of NF-κBp65 and IκBα. In vitro, NOB inhibited NF-κB activation and TNF-α, IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated A549 cells. Taken together, these results indicated that NOB exhibited a protective effect on ALI, and the possible mechanism is involved in inhibiting NF-κB activation, subsequently inhibiting LPS-induced inflammatory response.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, J., Y. Wang, X. Wei, X. Wu, G. Chen, G. Cao, X. Shen, X. Zhang, Q. Tang, G. Liang, and X. Li. 2013. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel thiazolidinone derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 64 (6): 292–301.
Tilg, H., and A.R. Moschen. 2006. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nature Reviews. Immunology 6 (10): 772–783.
Rubenfeld, G.D., and M.S. Herridge. 2007. Epidemiology and outcomes of acute lung injury. Chest 131 (2): 554–562.
Roch, A., S. Hraiech, E. Masson, D. Grisoli, J.M. Forel, M. Boucekine, P. Morera, C. Guervilly, M. Adda, S. Dizier, R. Toesca, F. Collart, and L. Papazian. 2014. Outcome of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and brought to a referral center. Intensive Care Medicine 40 (1): 74–83.
Reutershan, J., A. Basit, E.V. Galkina, and K. Ley. 2005. Sequential recruitment of neutrophils into lung and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in LPS-induced acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 289 (5): L807–L815.
Conti, G., S. Tambalo, G. Villetti, S. Catinella, C. Carnini, F. Bassani, N. Sonato, A. Sbarbati, and P. Marzola. 2010. Evaluation of lung inflammation induced by intratracheal administration of LPS in mice: comparison between MRI and histology. Magma 23 (2): 93–101.
Bhatia, M., and S. Moochhala. 2004. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Journal of Pathology 202 (2): 145–156.
Baeuerle, P.A., and T. Henkel. 1994. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annual Review of Immunology 33 (2): 141–179.
Li, Y.C., C.H. Yeh, M.L. Yang, and Y.H. Kuan. 2012. Luteolin suppresses inflammatory mediator expression by blocking the Akt/NFkappaB pathway in acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012: 383608.
Niu, X., H. Hu, W. Li, Y. Li, H. Huang, Q. Mu, H. Yao, and H. Li. 2014. Protective effect of total alkaloids on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. The Journal of Surgical Research 189 (1): 126–134.
Lin, N., T. Sato, Y. Takayama, Y. Mimaki, Y. Sashida, M. Yano, and A. Ito. 2003. Novel anti-inflammatory actions of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxy flavonoid, on human synovial fibroblasts and mouse macrophages. Biochemical Pharmacology 65 (12): 2065–2071.
Murakami, A., T. Shigemori, and H. Ohigashi. 2005. Zingiberaceous and citrus constituents, 1′-acetoxychavicol acetate, zerumbone, auraptene, and nobiletin, suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW264.7 murine macrophages through different modes of action. The Journal of Nutrition 135 (12 Suppl): 2987S–2992S.
Kunimasa, K., M. Ikekita, M. Sato, T. Ohta, Y. Yamori, M. Ikeda, S. Kuranuki, and T. Oikawa. 2010. Nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxyflavonoid, suppresses multiple angiogenesis-related endothelial cell functions and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Science 101 (11): 2462–2469.
Li, S., M.-H. Pan, C.-Y. Lo, D. Tan, Y. Wang, F. Shahidi, and C.-T. Ho. 2009. Chemistry and health effects of polymethoxyflavones and hydroxylated polymethoxyflavones. Journal of Functional Foods 1 (1): 2–12.
Lee, Y.S., B.Y. Cha, K. Saito, H. Yamakawa, S.S. Choi, K. Yamaguchi, T. Yonezawa, T. Teruya, K. Nagai, and J.T. Woo. 2010. Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochemical Pharmacology 79 (11): 1674–1683.
Xiong, Y., D. Chen, C. Yu, B. Lv, J. Peng, J. Wang, and Y. Lin. 2015. Citrus nobiletin ameliorates experimental colitis by reducing inflammation and restoring impaired intestinal barrier function. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 59 (5): 829–842.
Shibayama, T., M. Tachibana, H. Tazaki, and K. Nakamura. 1991. Studies on anti-tumor activity of tumor necrosis factor alpha against human renal cell carcinoma cells heterotransplanted into nude mice. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 82 (10): 1611–1619.
Rubenfeld, G.D., E. Caldwell, E. Peabody, J. Weaver, D.P. Martin, M. Neff, E.J. Stern, and L.D. Hudson. 2005. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. The New England Journal of Medicine 353 (16): 1685–1693.
Hernandez, M.L., M. Herbst, J.C. Lay, N.E. Alexis, W.J. Brickey, J.P. Ting, H. Zhou, and D.B. Peden. 2012. Atopic asthmatic patients have reduced airway inflammatory cell recruitment after inhaled endotoxin challenge compared with healthy volunteers. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 130 (4): 869–876.
Martin, T.R. 2000. Recognition of bacterial endotoxin in the lungs. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 23 (2): 128–132.
Suda, K., M. Tsuruta, J. Eom, C. Or, T. Mui, J.E. Jaw, Y. Li, N. Bai, J. Kim, J. Man, D. Ngan, J. Lee, S. Hansen, S.W. Lee, S. Tam, S.P. Man, S. Van Eeden, and D.D. Sin. 2011. Acute lung injury induces cardiovascular dysfunction: effects of IL-6 and budesonide/formoterol. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 45 (3): 510–516.
Soromou, L.W., N. Chen, L. Jiang, M. Huo, M. Wei, X. Chu, F.M. Millimouno, H. Feng, Y. Sidime, and X. Deng. 2012. Astragalin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by down-regulating NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 419 (2): 256–261.
Ware, L.B., and M.A. Matthay. 2000. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine 342 (18): 1334–1349.
Niu, X., Y. Wang, W. Li, Q. Mu, H. Li, H. Yao, and H. Zhang. 2015. Protective effects of Isofraxidin against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. International Immunopharmacology 24 (2): 432–439.
Zhong, W.T., L.X. Jiang, J.Y. Wei, A.N. Qiao, M.M. Wei, L.W. Soromou, X.X. Xie, X. Zhou, X.X. Ci, and D.C. Wang. 2013. Protective effect of esculentoside A on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. The Journal of Surgical Research 185 (1): 364–372.
Pereira, M.M., T.P. Santos, R. Aras, R.D. Couto, M.L. Atta, and A.M. Atta. 2014. Serum levels of cytokines and chemokines associated with cardiovascular disease in Brazilian patients treated with statins for dyslipidemia. International Immunopharmacology 18 (1): 66–70.
Shin, N.R., I.S. Shin, H.H. Song, J.M. Hong, O.K. Kwon, C.M. Jeon, J.H. Kim, S.W. Lee, J.K. Lee, H. Jin, W.Y. Li, S.R. Oh, K.W. Hahn, and K.S. Ahn. 2015. Callicarpa Japonica Thunb. reduces inflammatory responses: a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. International Immunopharmacology 26 (1): 174–180.
Zhang, Y.M., S.K. Zhang, and N.Q. Cui. 2014. Intravenous infusion of mesenteric lymph from severe intraperitoneal infection rats causes lung injury in healthy rats. World Journal of Gastroenterology 20 (16): 4771–4777.
Kristof, A.S., P. Goldberg, V. Laubach, and S.N. Hussain. 1998. Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 158 (6): 1883–1889.
Goldring, S. R., M. B. Goldring. 2004. The role of cytokines in cartilage matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 427 Suppl): S27-36.
Forstermann, U., and W.C. Sessa. 2012. Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. European Heart Journal 33 (7): 829–837.
Andy, S. N., C. K. Chan, H. A. Kadir. 2017. Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber modulates neuroinflammatory response through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt-dependent NF-κB signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. J Funct Foods 38 (Part A): 221-231.
Fukao, T., and S. Koyasu. 2003. PI3K and negative regulation of TLR signaling. Trends in Immunology 24 (7): 358–363.
Ma, S.F., D.N. Grigoryev, A.D. Taylor, S. Nonas, S. Sammani, S.Q. Ye, and J.G.N. Garcia. 2005. Bioinformatic identification of novel early stress response genes in rodent models of lung injury. American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular & Molecular Physiology 289 (3): 468–477.
Surh, Y.J., K.S. Chun, H.H. Cha, S.S. Han, Y.S. Keum, K.K. Park, and S.S. Lee. 2001. Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutation Research 480-481.
Lawrence, T., D.W. Gilroy, P.R. Colville-Nash, and D.A. Willoughby. 2001. Possible new role for NF-kappaB in the resolution of inflammation. Nature Medicine 7 (12): 1291–1297.
Schwartz, M.D., E.E. Moore, F.A. Moore, R. Shenkar, P. Moine, J.B. Haenel, and E. Abraham. 1996. Nuclear factor-kappa B is activated in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 24 (8): 1285–1292.
Funding
This work was supported by a research grant (no.: 2013KW26-02) from the Natural Science Foundation of International Cooperation Projects (Shaanxi Province, PR China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhao, R., Wang, X. et al. Nobiletin-Ameliorated Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Acute Lung Injury by Suppression of NF-κB Pathway In Vivo and Vitro. Inflammation 41, 996–1007 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0753-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0753-3