Abstract
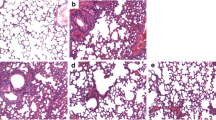
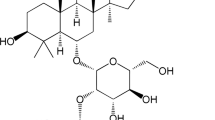
Arctiin is a lignin isolated from Arctium lappa which has been known to have anti-viral and anti-inflammatory effects. The aim of this study is to explore the protective effect of arctiin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in acute lung injury (ALI) model of mice. Male BALB/c mice were pretreated with commercial arctiin (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) 1 h prior to LPS challenge. Twelve hours later, airway inflammation was assessed. We assessed the effects of arctiin on the LPS-induced production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). The lung wet-to-dry weight ratio, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, and inflammatory signaling pathway were also detected. Our results showed that arctiin not only significantly ameliorated LPS-stimulated lung histopathological changes but also reduced the lung MPO activity. Arctiin also dramatically decreased the production of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the BALF. In addition, arctiin significantly inhibited LPS-induced PI3K/Akt phosphorylation as well as NF-κB activation. In conclusion, our results suggested that arctiin protected against LPS-induced ALI through inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matuschak, G.M., and A.J. Lechner. 2010. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: pathophysiology and treatment. Missouri Medicine 107: 252–258.
Brun-Buisson, C., C. Minelli, G. Bertolini, L. Brazzi, J. Pimentel, K. Lewandowski, J. Bion, J.A. Romand, J. Villar, A. Thorsteinsson, P. Damas, A. Armaganidis, F. Lemaire, and ALIVE Study Group. 2004. Epidemiology and outcome of acute lung injury in European intensive care units. Results from the ALIVE study. Intensive Care Medicine 30: 51–61.
Baumgarten, G., P. Knuefermann, H. Wrigge, C. Putensen, H. Stapel, K. Fink, R. Meyer, A. Hoeft, and C. Grohe. 2006. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 for the pathogenesis of acute lung injury in Gram-negative sepsis. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 23: 1041–1048.
Kabir, K., J.P. Gelinas, M. Chen, D. Chen, D. Zhang, X. Luo, J.H. Yang, D. Carter, and R. Rabinovici. 2002. Characterization of a murine model of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Shock 17: 300–303.
Bhatia, M., and S. Moochhala. 2004. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Journal of Pathology 202: 145–156.
Flori, H.R., D.V. Glidden, G.W. Rutherford, and M.A. Matthay. 2005. Pediatric acute lung injury: prospective evaluation of risk factors associated with mortality. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 171: 995–1001.
Lee, S., S. Shin, H. Kim, S. Han, K. Kim, J. Kwon, J.H. Kwak, C.K. Lee, N.J. Ha, D. Yim, and K. Kim. 2011. Anti-inflammatory function of arctiin by inhibiting COX-2 expression via NF-kappaB pathways. J Inflamm (Lond) 8: 16.
Wu, J.G., J.Z. Wu, L.N. Sun, T. Han, J. Du, Q. Ye, H. Zhang, and Y.G. Zhang. 2009. Ameliorative effects of arctiin from Arctium lappa on experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. Phytomedicine 16: 1033–1041.
Li, J., Y.P. Yuan, S.C. Xu, N. Zhang, C.R. Xu, C.X. Wan, J. Ren, X.F. Zeng, and Q.Z. Tang. 2017. Arctiin protects against cardiac hypertrophy through inhibiting MAPKs and AKT signaling pathways. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 135: 97–104.
Min, B., H. Lee, J.H. Song, M.J. Han, and J. Chung. 2014. Arctiin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and decreases adiposity and body weight in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutr Res Pract 8: 655–661.
Grommes, J., and O. Soehnlein. 2011. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Molecular Medicine 17: 293–307.
Matheson, N.R., P.S. Wong, and J. Travis. 1979. Enzymatic inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by neutrophil myeloperoxidase. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 88: 402–409.
Meduri, G.U., S. Headley, G. Kohler, F. Stentz, E. Tolley, R. Umberger, and K. Leeper. 1995. Persistent elevation of inflammatory cytokines predicts a poor outcome in ARDS. Plasma IL-1 beta and IL-6 levels are consistent and efficient predictors of outcome over time. Chest 107: 1062–1073.
Meduri, G.U., G. Kohler, S. Headley, E. Tolley, F. Stentz, and A. Postlethwaite. 1995. Inflammatory cytokines in the BAL of patients with ARDS. Persistent elevation over time predicts poor outcome. Chest 108: 1303–1314.
Tak, P.P., and G.S. Firestein. 2001. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 107: 7–11.
Li, Q., and I.M. Verma. 2002. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nature Reviews. Immunology 2: 725–734.
Everhart, M.B., W. Han, T.P. Sherrill, M. Arutiunov, V.V. Polosukhin, J.R. Burke, R.T. Sadikot, J.W. Christman, F.E. Yull, and T.S. Blackwell. 2006. Duration and intensity of NF-kappaB activity determine the severity of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Journal of Immunology 176: 4995–5005.
Jing, W., M. Chunhua, and W. Shumin. 2015. Effects of acteoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via regulation of NF-kappaB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 285: 128–135.
Liu, Y., H. Wu, Y.C. Nie, J.L. Chen, W.W. Su, and P.B. Li. 2011. Naringin attenuates acute lung injury in LPS-treated mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. International Immunopharmacology 11: 1606–1612.
Yang, R., L. Yang, X. Shen, W. Cheng, B. Zhao, K.H. Ali, Z. Qian, and H. Ji. 2012. Suppression of NF-kappaB pathway by crocetin contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 674: 391–396.
Huang, C.Y., Y.C. Fong, C.Y. Lee, M.Y. Chen, H.C. Tsai, H.C. Hsu, and C.H. Tang. 2009. CCL5 increases lung cancer migration via PI3K, Akt and NF-kappaB pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology 77: 794–803.
Qi, S., Y. Xin, Y. Guo, Y. Diao, X. Kou, L. Luo, and Z. Yin. 2012. Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. International Immunopharmacology 12: 278–287.
Xu, C.Q., B.J. Liu, J.F. Wu, Y.C. Xu, X.H. Duan, Y.X. Cao, and J.C. Dong. 2010. Icariin attenuates LPS-induced acute inflammatory responses: involvement of PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology 642: 146–153.
Moynagh, P.N. 2005. TLR signalling and activation of IRFs: revisiting old friends from the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends in Immunology 26: 469–476.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.Z. and F.D. contributed to the conception and design. B. Z., G.W., Z.H., and T.L. did the analysis and interpretation. T.L. did the data collection. B.Z. and F.D. wrote the article and did the critical revision of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, B., Weng, G., Huang, Z. et al. Arctiin Prevents LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Inhibition of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Mice. Inflammation 41, 2129–2135 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0856-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0856-x