Abstract
Writing is recognized as a critical skill in science, technology, engineering, and mathematical fields, as it provides opportunities for individuals to think critically about learned information, integrate knowledge, communicate understanding, and contribute new information to the field. Requirements for applying mathematical knowledge to writing require a seamless blend of content-specific knowledge, domain-specific vocabulary, and an understanding of written expression. Relatively, little is known about how mathematics writing is currently being assessed in K-12 classrooms to promote the acquisition and growth of students’ writing. This exploratory survey research sought to evaluate how undergraduate students across various career majors, at a large university in the USA, perceive the writing quality of elementary mathematics writing samples. Research determined that respondents valued accuracy of the mathematics, logical explanation, effort of the response, as well as organization/mechanics of the writing. The extremes of mathematical writing had the most reliable scores, bringing attention to the need to develop quality assessments (e.g., rubrics) that address subjectivity of writing quality indicators and explicitly communicate expectations of mathematics writing. Implications for practice and future research are presented.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrose, R., Clement, L., Philipp, R., & Chauvot, J. (2004). Assessing prospective elementary school teachers’ beliefs about mathematics and mathematics learning: Rationale and development of a constructed-response-format beliefs survey. School Science and Mathematics, 104, 56–69.
Bagley, T., & Gallenberger, C. (1992). Assessing students’ dispositions: Using journal to improve students’ performance. Mathematics Teacher, 85, 660–663.
Baxter, J. A., Woodward, J., & Olson, D. (2005). Writing in mathematics: An alternative form of communication for academically low achieving students. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 20, 119–135.
Bicer, A., Capraro, R. M., & Capraro, M. M. (2013). Integrating writing into mathematics classroom to increase students’ problem-solving skills. International Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 5, 361–369.
Borasi, R., & Rose, B. J. (1989). Journal writing and mathematics instruction. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 20, 347–365.
Brantlinger, E., Jimenez, R., Klingner, J., Pugach, M., & Richardson, V. (2005). Qualitative studies in special education. Exceptional Children, 71, 195–207.
Burns, M. (2004). Writing in math. Educational Leadership, 62(2), 30–33.
Casa, T. M., Firmender, J. M., Cahill, J., Cardetti, F., Choppin, J. M., Cohen, J. & Zawodniak, R. (2016). Types of and purposes for elementary mathematical writing: Task force recommendations. Retrieved from http://mathwriting.eduation.uconn.edu
Cohen, H. A., Miller, H. C., Casa, T. M., & Firmender, J. M. (2015). Characteristics of second graders’ mathematical writing. School Science and Mathematics, 115, 344–355.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155–159.
Common Core State Standards. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.corestandards.org/ELA-Literacy/introduction/students-who-are-college-and-career-ready-in-reading-writing-speaking-listening-language/
Danielson, C. (2010). Writing papers in math class: A tool for encouraging mathematical exploration by preservice elementary teachers. School Science and Mathematics, 110(8), 374-381.
Flesch, R. (1948). A new readability yardstick. Journal of Applied Psychology, 32, 221–233.
Freeman, B., Higgins, K. N., & Horney, M. (2016). How students communicate mathematical ideas: An examination of multimodal writing using digital technologies. Contemporary Educational Technology, 7, 281–313.
Gigante, M. E. (2016). Navigating the next generation science standards: Implications and implementations for faculty in writing and the sciences. Teaching/Writing: The Journal of Writing Teacher Education, 5(1), 6. Available at http://scholarworks.wmich.edu/wte/vol5/iss1/6.
Hebert, M. A., & Powell, S. R. (2016). Examining fourth-grade mathematics writing: Features of organization, mathematics vocabulary, and mathematical representations. Reading and Writing, 29, 1511–1537.
Hoyles, C., & Küchemann, D. (2002). Students’ understandings of logical implication. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 51, 193–223.
Jackson, A., & Kiersz, A. (2016). The latest ranking of top countries in math, reading, and science is out—and the US didn't crack the top 10. Retrieved from http://www.businessinsider.com/pisa-worldwide-ranking-of-math-science-reading-skills-2016-12.
Kline, S. L., & Ishii, D. K. (2008). Procedural explanations in mathematics writing: A framework for understanding college students’ effective communication practices. Written Communication, 25, 441–461.
Knox, H. (2017). Using writing strategies in math to increase metacognitive skills for the gifted learner. Gifted Child Today, 40, 43–47.
Kostos, K., & Shin, E. K. (2010). Using math journals to enhance second graders’ communication of mathematical thinking. Early Childhood Education Journal, 38, 223–231.
Langdon, D., McKittrick, G., Beede, D., Khan, B. & Doms, M. (2011, July). STEM: Good jobs now and for the future. ESA issue brief# 03–11. Washington, DC: US Department of Commerce. Retrieved on May 23, 2018 from https://www.commerce.gov/file/stem-good-jobs-now-and-future
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. (1991). Professional standards for teaching mathematics. Reston, VA: Author.
National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. (2000). Principles and standards for school mathematics. Reston, VA: Author.
National Governors Association Center for Best Practices & Council of Chief State School Officers. (2010). Common core state standards for mathematics. Washington, DC: Author.
Onwuegbuzie, A., & Teddlie, C. (2003). A framework for analyzing data in mixed methods research. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods research (pp. 351–384). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Powell, S. R., Hebert, M. A., Cohen, J. A., Casa, T. M., & Firmender, J. M. (2017). Synthesis of mathematics writing: Assessments, interventions, and surveys. Journal of Writing Research, 8, 493–526.
Pugalee, D. K. (2005). Writing to develop mathematical understanding. Norwood, MA: Christopher-Gordon Publishers, Inc.
Ryan, G. W., & Bernard, H. R. (2003). Techniques to identify themes. Field Methods, 15, 85–109.
Saldaña, J. (2009). The coding manual for qualitative researchers. Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Smith, K. S., Rook, J. E., & Smith, T. W. (2007). Increasing student engagement using effective and metacognitive writing strategies in content areas. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 51, 43–48.
Stonewater, J. K. (2002). The mathematics writer's checklist: The development of a preliminary assessment tool for writing in mathematics. School Science and Mathematics, 102, 324–334.
Tebeaux, E. (2017). Whatever happened to technical writing? Journal of Technical Writing and Communication, 47, 3–21.
U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). (2011). Writing assessment. Retrieved on March 22, 2018 from https://www.nationsreportcard.gov/writing_2011/.
Vivaldi, F. (2014). Mathematical writing. London, England: Springer undergraduate mathematics series. Retrieved fromhttps://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-6527-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Word Problems Used
Kelly and Nick each ordered a medium pizza. Kelly ate 3/8 of her pizza. Nick ate 3/4 of his pizza. They were wondering if they could combine both pizzas into one box to store in the fridge. Can they store all of the pizza in one box without any of the pizza overlapping? Explain your response. | |
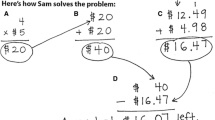
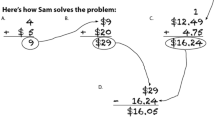
You are on a road trip traveling from New York City to State College. You need to add 12.5 gallons of gas to your car to make it back to State College safely. Last time you filled up you used 15 gallons of gas. You pull into a gas station where gas costs $2.35. How much will it cost you to fill up your tank? |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hughes, E.M., Markelz, A.M. & Cozad, L.E. Evaluating Various Undergraduate Perspectives of Elementary-Level Mathematical Writing. Int J of Sci and Math Educ 17, 1031–1048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-018-9903-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-018-9903-1