Abstract
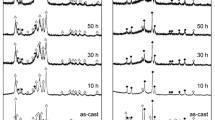
Surface modification of Zr0.9Ti0.1Ni1.1Co0.1Mn0.5V0.2Cr0.1 alloy was accomplished by mechanical grinding (MG). The decrepitation of alloy particles gave rise to a new surface. The effect of MG was systematically studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), pressure-composition (PC) isotherms and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Initial activation and rate capability of a negative electrode made from this alloy were significantly improved by MG treatment at 300 rpm for 0.5–1 h, but prolonged MG treatment (10 h) reduced the nominal discharge capacity from 350 mAh g−1 to 180 mAh g−1. Under these conditions the alloy particles disintegrate and become nanocrystalline, which reduces the discharge capacity owing to the change in the stereology of tetrahedral interstices available for hydrogen storage. The data based on PC isotherms and hydriding kinetics indicates that the equilibrium hydrogen pressure increases and the hydriding rate and storage capacity are significantly reduced by prolonged MG treatment. EIS data reveal that the improved rate capability can be ascribed to an enhanced charge-transfer reaction which is the rate-determining step in the hydriding and dehydriding reactions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohno T, Yoshida H, Kawashima F, Inaba T, Sakai I, Yamamoto M, Kanda M (2000) J Alloys Comp 311:L5–L7
Liu Y, Pan H, Gao M, Zhu Y, Lei Y, Wang Q (2004) Int J Hydrogen Energy 29:297–305
Wang Y, Gao XP, Lu ZW, Hu WK, Zhou Z, Qu JQ, Shen PW (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:2187–2191
Yasuoka S, Magari Y, Murata T, Tanaka T, Ishida J, Nakamura H, Nohma T, Kihara M, Baba Y, Teraoka H (2006) J Power Sources 156:662–666
Fetcenko MA, Venkatesan S (1990) Prog Batter Sol Cells 9:259–264
Moriwaki Y, Gamo T, Shintani A, Iwaki T (1989) Denki Kagaku 57:488–491
Sawa H, Wakao S, Furukawa J (1990) Denki Kagaku 58:862–867
Wakao S, Sawa H, Furukawa J (1991) Denki Kagaku 59:945–949
Zuttel A, Mail F, Schlapbach L (1994) J Alloys Compd 209:99–105
Yan D, Sandrock G, Suda S (1994) J Alloys Compd 216:237–242
Iwakura C, Choi WK, Zhang SG, Inoue H (1999) Electrochim Acta 44:1677–1679
Gao XP, Zhang W, Yang HB, Song DY, Zhang YS, Zhou ZX, Shen PW (1996) J Alloys Compd 235:225–231
Li ZP, Higuchi E, Liu BH, Suda S (1999) J Alloys Compd 293–295:593–600
Sun D, Latroche M, Percheron-Guegan A (1997) J Alloys Compd 257:302–305
Lee S-M, Kim S-H, Lee J-Y (2002) J Alloys Compd 330–332:796–801
Hesabi ZR, Simchi A, Reihani SMS (2006) Mater Sci Eng A428:159–168
Ikeya T, Kumai K, Iwahori T (1993) J Electrochem Soc 140:3082–3086
Burgio N, Iasonna A, Magini M, Martelli S, Padella F (1991) Il Nuovo Cimento 13D:459–476
Ivey DG, Northwood DO (1986) Ziet Phys Chem NF 147:191–209
Kirchheim R (1982) Acta Metall 30:1069–1107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuoka, M., Tamura, K. Effects of mechanical grinding on initial activation and rate capability of Zr–Ti based Laves phase alloy electrode. J Appl Electrochem 37, 759–764 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-007-9311-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-007-9311-7