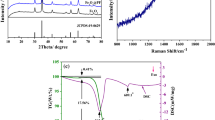
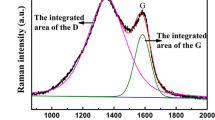
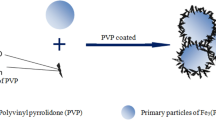
Abstract
Chemical lithiation of amorphous FePO4 with LiI in acetonitrile is performed to form amorphous LiFePO4. The amorphous FePO4·2H2O precursor is synthesized by co-precipitation method from equimolar aqueous solutions of FeSO4·7H2O and NH4H2PO4, using H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) as the oxidizing agent. The nanocrystalline LiFePO4/C is obtained by annealing the amorphous LiFePO4 and in situ carbon coating with sucrose in a reducing atmosphere. The particle size of FePO4·2H2O precursor decreases with increasing reaction temperature. The final LiFePO4/C products completely maintain the shape and size of the precursor even after annealing at 700 °C for 2 h. The excellent electrochemical properties of these nanocrystalline LiFePO4/C composites suggest that to decrease the particle size of LiFePO4 is very effective in enhancing the rate capability and cycle performance. The specific discharge capacities of LiFePO4/C obtained from the FePO4·2H2O precursor synthesized at 75 °C are 151.8 and 133.5 mAh g−1 at 0.1 and 1 C rates, with a low capacity fading of about 0.075 % per cycle over 50 cycles at 0.5 C rate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 144:1188–1194
Ellis B, Herle PS, Rho Y-H, Nazar LF, Dunlap R, Perry LK, Ryan DH (2007) Nanostructured materials for lithium-ion batteries: surface conductivity vs. bulk ion/electron transport. Faraday Discuss 134:119–141
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Masquelier C, Okada S, Goodenough JB (1997) Effect of structure on the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple in iron phosphates. J Electrochem Soc 144:1609–1613
Meethong N, Kao Y-H, Speakman SA, Chiang Y-M (2009) Aliovalent substitutions in olivine lithium iron phosphate and impact on structure and properties. Adv Funct Mater 19:1060–1070
Muraliganth T, Manthiram A (2010) Understanding the shifts in the redox potentials of olivine LiM1−y M y PO4 (M = Fe, Mn, Co, and Mg) solid solution cathodes. J Phys Chem C 114:15530–15540
Sun CS, Zhou Z, Xu ZG, Wang DG, Wei JP, Bian XK, Yan J (2009) Improved high-rate charge/discharge performances of LiFePO4/C via V-doping. J Power Sources 193:841–845
Chang ZR, Lv HJ, Tang HW, Li HJ, Yuan XZ, Wang H (2009) Synthesis and characterization of high-density LiFePO4/C compositions as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 54:4595–4599
Su L, Jing Y, Zhou Z (2011) Li ion battery materials with core–shell nanostructures. Nanoscale 3:3967–3983
Sun CS, Zhang Y, Zhang XJ, Zhou Z (2010) Structural and electrochemical properties of Cl-doped LiFePO4/C. J Power Sources 195:3680–3683
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Zane D, Paspuali M (2002) Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4. Solid State Ion 148:45–51
Zhao B, Jiang Y, Zhang HJ, Tao HH, Zhong MY, Jiao Z (2009) Morphology and electrical properties of carbon LiFePO4 cathode materials. J Power Sources 189:462–466
Ding Y, Jiang Y, Xu F, Yin J, Ren H, Zhuo Q, Long Z, Zhang P (2010) Preparation of nano-structured LiFePO4/graphene composites by co-precipitation method. Electrochem Commun 12:10–13
Lim S, Yoon CS, Cho J (2008) Synthesis of nanowire and hollow LiFePO4 cathodes for high-performance lithium batteries. Chem Mater 20:4560–4564
Dominko R, Bele M, Gaberscek M, Remskar M, Hanzel D, Pejovnik S, Jamnik J (2005) Impact of the carbon coating thickness on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C composites. J Electrochem Soc 152:A607–A610
Wang XJ, Ren JX, Li YZ, Wei JP, Gao XP, Yan J (2005) Synthesis of cathode material “carbon-included” LiFePO4 by microwave heating. J Inorg Chem 21:249–252
Wang M, Yang Y, Zhang YX (2011) Synthesis of micro-nano hierarchical structured LiFePO4/C composite with both superior high-rate performance and high tap density. Nanoscale 3:4434–4439
Mi CH, Zhao XB, Cao GS, Tu JP (2005) In situ synthesis and properties of carbon-coated LiFePO4 as Li-ion battery cathodes. J Electrochem Soc 152:A483–A487
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Scaccia S, Carewska M, Cardellini F, Pasquali M (2002) Synthesis and characterization of amorphous hydrated FePO4 and its electrode performance in lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 149:A297–A301
Andersson AS, Thomas JO (2001) The source of first-cycle capacity loss in LiFePO4. J Power Sources 97–98:498–502
Wang GX, Liu H, Liu J, Qiao S, Lu GM, Munroe P, Ahn H (2010) Mesoporous LiFePO4/C nanocomposite cathode materials for high power lithium ion batteries with superior performance. Adv Mater 22:4944–4948
Wang YG, Wang YR, Hosono E, Wang KX, Zhou HS (2008) The design of a LiFePO4/carbon nanocomposite with a core-shell structure and its synthesis by an in situ polymerization restriction method. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:7461–7465
Huang YH, Ren HB, Peng ZH, Zhou YH (2009) Synthesis of LiFePO4/carbon composite from nano-FePO4 by a novel stearic acid assisted rheological phase method. Electrochim Acta 55:311–315
Nien YH, Carey JR, Chen JS (2009) Physical and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C composite cathode prepared from various polymer-containing precursors. J Power Sources 193:822–827
Luo JY, Li XL, Xia YY (2007) Synthesis of highly crystalline spinel LiMn2O4 by a soft chemical route and its electrochemical performance. Electrochim Acta 52:4525–4531
Hwang SJ, Park DH, Kwon CW, Campet G, Choy JH (2004) Effect of reaction media on electrochemical performance of nanocrystalline manganese oxyiodides prepared by chimie douce route. J Power Sources 125:119–123
Kuo HT, Chan TS, Bagkar NC, Liu RS, Shen CH, Shy DS, Xing XK, Lee JF (2009) Effect of LiI amount to enhance the electrochemical performance of carbon-coated LiFePO4. Electrochem Solid State Lett 12:A111–A114
Scaccia S, Carewska M, Bartolomeo AD, Prosini PP (2002) Thermoanalytical investigation of iron phosphate obtained by spontaneous precipitation from aqueous solutions. Thermochim Acta 383:145–152
Rajic N, Gabrovsek R, Kaucic V (2000) Thermal investigation of two FePO materials prepared in the presence of 1,2-diaminoethane. Thermochim Acta 359:119–122
Wang DY, Li H, Wang ZX, Wu XD, Sun YC, Huang XJ, Chen LQ (2004) New solid-state synthesis routine and mechanism for LiFePO4 using LiF as lithium precursor. J Solid State Chem 177:4582–4587
Wang L, Huang Y, Jiang R, Jia D (2007) Preparation and characterization of nano-sized LiFePO4 by low heating solid-state coordination method and microwave heating. Electrochim Acta 52:6778–6783
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (11275121, 21241002), Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai (11DZ110020, 10ZR1411300), and Shanghai Leading Academic Disciplines Project (S30109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Zhuang, H., Pan, D. et al. Chemical lithiation route to size-controllable LiFePO4/C nanocomposite. J Appl Electrochem 43, 611–617 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-013-0542-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-013-0542-5