Abstract
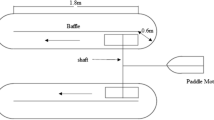
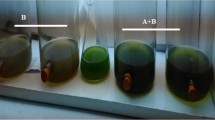
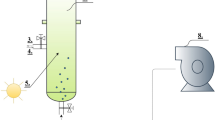
Five species of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus quadricauda, Euglena gracilis, Ankistrodesmus convolutus and Chlorococcum oviforme, were screened for their ability to grow in treated landfill leachate (TL) using shake flask cultures. The treated leachate had undergone previous treatment through mechanical aeration in treatment ponds at the landfill site. The five algae, except for C. oviforme, were able to grow in medium containing up to 50% TL. Two high-rate algal ponds (HRAP) equipped with paddlewheel were used for the semi-continuous cultures. A mixture of the five algae was used to inoculate one of two HRAPs for secondary treatment of TL. The other HRAP was filled with natural lake water containing mixed populations of algae. A volume of 400 mL (1%) from both ponds were removed daily and replaced with TL. The leachate loading rate was increased to 2% (0.8 L day−1) on day 197 and then to 4% (1.6 L day−1) on day 309, providing hydraulic retention time of 100, 50 and 25 days, respectively. Although higher biomass was obtained in the HRAP containing the consortium of five algae, there was no significant difference in reduction of pollutants between the two ponds. The HRAPs produced algal biomass ranging from 2.00 to 5.54 g dry weight L−1 with significant reduction in chemical oxygen demand (91.0%), ammoniacal nitrogen (99.9%) and orthophosphate (86.0%) contents. The HRAP offers a potential treatment system for TL which is simple, low cost, flexible in use and requiring low maintenance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agamuthu P (1999) Characteristics of municipal solid waste and leachate from selected landfills in Malaysia. Malaysian J Sci 18:99–103
APHA (American Public Health Association, American Waterworks Association, Water Pollution Control Federation) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. Diaz de Santos, Madrid
ASTM (1993) Standard guide for conducting renewal rife-cycle toxicity test with Daphnia magna. Method E1193-87. In: Selected ASTM standards related to algae studies 1, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Chiemchaisri C, Chiemchaisri W, Junsod J, Threedeach S, Wicranarachchi PN (2009) Leachate treatment and greenhouse gas emission in sub-surface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol 100:3808–3814
Chu WL, See YC, Phang SM (2009) Use of immobilised Chlorella vulgaris for the removal of colour from textile dyes. J Appl Phycol 21:641–648
Department of Environment Malaysia (DOE), Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment Malaysia (2009) Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 2008. Publication Section, Strategic Communications Division, Department of Environment Malaysia
Di Iaconi C, Pagano M, Ramadori R, Lopez A (2010) Nitrogen recovery from a stabilized municipal landfill leachate. Bioresour Technol 101:1732–1736
Garcia J, Mujeriego R, Hernandez-Marine M (2000) High rate algal Pond operating strategies for urban wastewater nitrogen removal. J Appl Phycol 12:331–339
Guillart RRL (1973) Division rate. In: Stein J (ed) Handbook of phycological methods: culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 289–311
Han X, Wong YS, Wong MH, Tam NFY (2007) Biosorption and bioreduction of Cr (VI) by a microalgal isolate Chlorella miniata. J Hazard Mater 146:65–72
Hashim MA, Chu KH, Phang SM, Ong GS (1997) Adsorption equilibria of cadmium on algae biomass. Adsorp Sci Technol 15:445–453
Hernandez AJ, Adarve MJ, Gil A, Pastor J (1999) Soil salination from landfill leachates: effects on the macronutrient content and plant growth of four grassland species. Chemosphere 38:1693–1711
Kim DJ, Lee DI, Keller J (2006) Effect of temperature and free ammonia on nitrification and nitrite accumulation in landfill leachate and analysis of its nitrifying bacterial community by FISH. Bioresour Technol 97:459–468
Kortegast AP, Eledridge SF, Richards BA, Yong S, Chock ET, Bryce A, Robinson H, Carville M (2007) Leachate generation and treatment at the Bukit Tagar Landfill, Malaysia. Presented at Sardinia 2007, 11th International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Sardinia, Italy. Available at: http//www.leachate.co.uk/sardine2007-Bukit-Tagar.pdf. Accessed 21 April 2010
Lim SL, Chu WL, Phang SM (2010) Use of Chlorella vulgaris for bioremediation of textile wastewater. Bioresour Technol 101:7314–7322
Lin L, Chan GYS, Jiang BL, Lan CY (2007) Use of ammoniacal nitrogen tolerant microalgae in landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manage 27:1376–1382
Mustafa EM (2003) Treatment of landfill leachate using a high rate algal pond system. M Tech (Env. Mgt) thesis, Institute of Postgraduate Studies, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia
Nichols HW, Bold HC (1965) Trichorsarcina polymorpha gen.et sp. nov. J Phycol 1:34–38
Norberg-King TJ (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity : the inhibition concentration (ICP) approach (Version 2.0). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Research Laboratory, Duluth, MN. Technical report 03-93 of the National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center 39
Phang SM, Ong KC (1988) Algal biomass production in digested palm oil mill effluent. Biol Waste 25:177–191
Phang SM, Miah MS, Yeoh BG, Hashim MA (2000) Spirulina cultivation in digested sago starch factory wastewater. J Appl Phycol 12:395–400
Phang SM, Chui YY, Geetha K, Susila J, Hashim MA (2001) High Rate Algal Ponds for treatment of wastewater—a case study for the rubber industry. In: Kojima H, Lee YK (eds) Photosynthetic microorganisms in environmental biotechnology. Springer, Hong Kong, pp 51–76
Read AD, Hudgins M, Harper S, Phillips P, Morris J (2001) The successful demonstration of aerobic landfilling: the potential for a more sustainable solid waste management approach. J Res Conserv Recycl 32:115–146
Reinhart DR, Townsend TG (1998) Landfill bioreactor design & operation. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Renou S, Givaudan JG, Poulain S, Dirassouyan F, Moulin P (2008) Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity. J Hazard Mater 150:468–493
Strickland JD, Parsons TR (1968) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull no. 167, Fisheries Research Board, Canada
Wang YQ, Liu SJ, Xu Z, Han TW, Chuan S, Zhu T (2006) Ammonia removal from leachate solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. J Hazard Mater B136:735–740
Acknowledgements
This project (project no. 08-01-01-T0002) was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technology & Innovation (MOSTI) through the Environmental/Industrial Biotechnology, Biotechnology Cooperative Centre of the National Biotechnology Directorate. The Vote F (F0140/2002B) grant from the University of Malaya was awarded to the first author. The authors also wish to thank Worldwide Landfills Ltd. for providing the leachate samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, EM., Phang, SM. & Chu, WL. Use of an algal consortium of five algae in the treatment of landfill leachate using the high-rate algal pond system. J Appl Phycol 24, 953–963 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9716-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9716-x