Abstract
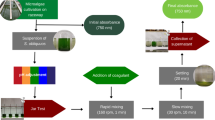
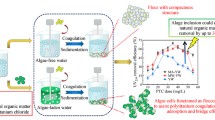
Coagulation is an important step in the harvesting of algal biomass. This paper presents experimental results for a variety of prospective marine microalgal species using several inorganic and organic coagulants. Tetraselmis suecica and Chlorococcum sp. are readily coagulated using alum or iron(III) sulphate without any pH adjustment; doses of 3–5 mg L−1 or 0.2 mmol m−2 of Al3+ or Fe3+ yielding cell recoveries above 90 % after only 5-min settling. Nannochloropsis salina, Dunaliella tertiolecta and Isochrysis galbana are harder to coagulate and require at least two times more coagulant to achieve similar recoveries. Several cationic polyacrylamides were investigated but were less effective than Al3+ or Fe3+. Addition of NaOH to control pH improved the coagulation efficiency of N. salina but not of D. tertiolecta. The high coagulant demand of N. salina is due in part to its small size and large surface area, while that of D. tertiolecta may be attributable to its high production of extracellular polymer. The implications of cell surface properties for coagulation efficiency are discussed. At the coagulant doses used herein, settled cells remain viable. Resuspension is a potential problem with some species, arising either from cell motility or from flotation of flocs by oxygen bubbles generated by photosynthesis. These effects can be eliminated by small additions of chlorine or by settling the algae in the dark.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhardt H, Clasen J (1991) Flocculation of micro-organisms. J Water Supply Res Technol 40(2):76–87
Bhaskar PV, Bhosle NB (2005) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in marine biogeochemical processes. Curr Sci India 88:45–53
Bilanovic D, Shelef G, Sukenik A (1988) Flocculation of microalgae with cationic polymers—effects of medium salinity. Biomass 17:65–76
Bolto B, Gregory J (2007) Organic polyelectrolytes in water treatment. Water Res 41:2301–2324
Borowitzka MA, Siva CJ (2007) The taxonomy of the genus Dunaliella (Chlorophyta) with emphasis on the marine and halophilic species. J Appl Phycol 19:567–590
Boussiba S, Sandbank E, Shelef G, Cohen Z, Vonshak A, Ben-Amotz A, Arad S, Richmond A (1988) Outdoor cultivation of the marine microalga Isochrysis galbana in open reactors. Aquaculture 72:247–253
Duan J, Gregory J (2003) Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 100:475–502
Gelin F, Boogers L, Noordeloos AAM, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Riegman R, De Leeuw JW (1996) Resistant biomacromolecules in marine microalgae of the classes Eustigmatophyceae and Chlorophyceae: geochemical implications. Org Ceochem 26:659–675
Gelin F, Volkman JK, Largeau C, Derenne S, Sinninghe Damsté JS, De Leeuw JW (1999) Distribution of aliphatic, nonhydrolyzable biopolymers in marine microalgae. Org Geochem 30:147–159
Green JC, Pienaar RN (1977) The taxonomy of the order Isochrysidales (Prymnesiophyceae) with special reference to the genera Isochrysis Parke, Dicrateria Parke and Imantonia Reynolds. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 57:7–17
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve). Gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Guillard RRL, Wangersky PJ (1958) The production of extracellular carbohydrates by some marine flagellates. Limnol Oceanogr 3:449–454
Hellebust JA (1965) Excretion of some organic compounds by marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 10:192–206
Henderson RK, Parsons SA, Jefferson B (2008) Surfactant as bubble surface modifiers in the flotation of algae: dissolved air flotation that utilizes a chemically modified bubble surface. Environ Sci Technol 42:4883–4888
Hibberd DJ, Leedale GF (1971) A new algal class—the Eustigmatophyceae. Taxon 20:523–525
Hunter RJ (2001) Foundations of colloid science. Oxford University Press, New York, p 616
Huntsman SA (1972) Organic excretion by Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Phycol 8:59–63
Ives K (1959) The significance of surface electric charge on algae in water purification. J Biochem Microbiol Technol Eng 1:37–47
Kiørboe T, Hansen JLS (1993) Phytoplankton aggregate formation: observations of patterns and mechanisms of cell sticking and the significance of exopolymeric material. J Plankton Res 15:993–1018
Knuckey R, Brown M, Robert R, Frampton D (2006) Production of microalgal concentrates by flocculation and their assessment as aquaculture feeds. Aquacult Eng 35:300–313
Kormas KA (2005) Bacterioplankton growth on extracellular organic carbon from marine microalgal cultures. Biol Mar 46:241–251
Levy N, Magdassi S, Bar-Or Y (1992) Physico-chemical aspects in flocculation of bentonite suspensions by a cyanobacterial bioflocculant. Water Res 26:249–254
Lubián LM (1989) Concentrating cultured marine microalgae with chitosan. Aquacult Eng 8:257–265
Ma J, Liu W (2002) Effectiveness and mechanism of potassium ferrate(VI) preoxidation for algae removal by coagulation. Water Res 36:871–878
Marker AFH (1965) Extracellular carbohycrates liberation in the flagellates Isochrysis galbana and Prymnesium parvum. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 45:755–772
McGarry M (1970) Algal flocculation with aluminum sulfate and polyelectrolytes. Res J Water Pollut C 42:191–201
Miller DH (2006) Cell wall chemistry and ultrastructure of Chlorococcum oleofaciens (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 14:189–194
Morales J, de la Noüe J, Picard G (1985) Harvesting marine microalgae species by chitosan flocculation. Aquacult Eng 4:257–270
Oliveira L, Bisalputra T, Antia NJ (1980) Ultrastructural observation of the surface coat of Dunaliella tertiolecta from staining with cationic dyes and enzyme treatments. New Phytol 85:385–392
Palmer DA, Bell JLS (1994) Aluminum speciation and equilibria in aqueous solution: IV. A potentiometric study of aluminum acetate complexation in acidic NaCl brines to 150°C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:65 l–659
Parke M (1949) Studies on marine flagellates. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 28:255–288
Passow U, Alldredge AL, Logan BE (1994) The role of particulate carbohydrate exudates in the flocculation of diatom blooms. Deep-Sea Res 41:335–357
Pieterse AJH, Cloot A (1997) Algal cells and coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation processes. Water Sci Technol 36:111–118
Plummer JD, Edzwald JK (2001) Effect of ozone on algae as precursors for trihalomethane and haloacetic acid production. Environ Sci Technol 35:3661–3668
Plummer JD, Edzwald JK (2002) Effects of chlorine and ozone on algal cell properties and removal of algae by coagulation. J Water Supply Res Technol 51:307–318
Pushparaj B, Pelosi E, Torzillo G, Materassi R (1993) Microbial biomass recovery using a synthetic cationic polymer. Bioresour Technol 43:59–62
Romanovicz DK (1981) Scale formation in flagellates. In: Kiermayer O (ed) Cytomorphogenesis in plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 27–62
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati SA (2001) Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants—recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol Adv 19:371–385
Schenk PM, Thomas-Hall SR, Stephens E, Marx UC, Mussgnug JH, Posten C, Kruse O, Hankamer B (2008) Second generation biofuels: high-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production. Bioenerg Res 1:20–43
Sukenik A, Teltch B, Wachs AW, Shelef G, Nir I, Levanon D (1987) Effect of oxidants on microalgal flocculation. Water Res 21:533–539
Sukenik A, Bilanovic D, Shelef G (1988) Flocculation of microalgae in brackish and sea waters. Biomass 15:187–199
Tenney M, Echelberger W, Schuessler R, Pavoni J (1969) Algal flocculation with synthetic organic polyelectrolytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 18:965–971
Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ (2010) An outlook on microalgal biofuels. Science 329:796
Williams PJB, Laurens LML (2010) Microalgae as biodiesel & biomass feedstocks: review & analysis of the biochemistry, energetics & economics. Energy Environ Sci 3:554–590
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by an ARC linkage grant with financial support from Biofuels Pty Ltd. We thank Tina Hines and Kerrie Browne at Water Studies Centre for DOC and Fe analyses. Al analyses were performed by ALS Laboratory Group, Springvale, Victoria, Australia. The authors also thank Sherrie Caarels for her monitoring work and maintenance of the algal cultures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldridge, R.J., Hill, D.R.A. & Gladman, B.R. A comparative study of the coagulation behaviour of marine microalgae. J Appl Phycol 24, 1667–1679 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9830-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9830-4