Abstract
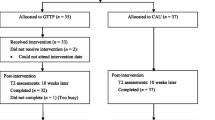
A growing body of literature suggests that parenting practices characterized by careful monitoring, firm and consistent limit setting, and nurturing communication patterns with children are protective against adolescent substance use and other problem behaviors. Family-based prevention programs that promote these behaviors can be an effective way to prevent adolescent substance use. However, low participation rates remain problematic for many such programs, particularly programs that require parents to attend scheduled meetings outside the home. The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of a newly developed substance use prevention program when self-administered at home by parents of middle school students. As part of a randomized trial, 338 parents of middle school students either received the parent prevention program or served as control group participants. Parents completed self-report surveys at home that assessed parenting behaviors at pre-test, post-test, and one-year follow-up time points. A series of mixed model ANCOVAs were conducted, examining the post-test and one-year follow-up means for the parent outcomes, controlling for pre-test levels on these outcomes. Analyses showed that at the post-test assessment, intervention parents reported significant increases relative to controls in appropriate role modeling, disciplinary practices, family communication, and parental monitoring skills. At the one-year follow-up assessment, intervention effects on family communication skills remained significant and effects on parental role modeling were marginally significant. This study shows that a theoretically rich prevention program can be effectively self-administered by parents at home and improve key parenting skills that have been shown to prevent adolescent substance use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, J., & Hops, H. (2010). The role of peers and family as predictors of drug etiology. In L. M. Scheier (Ed.), Handbook of drug use etiology. Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
Botvin, G. J., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., Botvin, E. M., Diaz, T., et al. (1995). Long-term follow-up results of a randomized drug abuse prevention trial in a White middle-class population. Journal of the American Medical Association, 273, 1106–1112.
Brody, G. H., Murry, V. M., Chen, Y., Kogan, S. M., Brown, A. C., et al. (2006). Effects of family risk factors on dosage and efficacy of a family-centered preventive intervention for rural African-Americans. Prevention Science, 7, 281–291.
Cohen, J., & Cohen, P. (1983). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
DiClemente, R. J., Wingood, G. M., Crosby, R., Sionean, C., Cobb, B. K., Harrington, K., et al. (2001). Parental monitoring: Association with adolescents’ risk behaviors. Pediatrics, 107, 1363–1368.
Grube, J. (2010). Environmental approaches to preventing drinking and drinking problems among youth. In L. M. Scheier (Ed.), Handbook of drug use etiology: Theory, methods, and empirical findings (pp. 493–509). Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
Haggerty, K. P., Skinner, M. L., MacKenzie, E. P., & Catalano, R. F. (2007). A randomized trial of parents who care: Effects on key outcomes at 24-month follow-up. Prevention Science, 8, 249–260.
Harakeh, Z., Scholte, R., De Vries, H., & Engels, R. C. (2005). Parental rules and communication: Their association with adolescent smoking. Addiction, 100, 862–870.
Hawkins, J. D., Van Horn, M. L., & Arthur, M. W. (2004). Community variation in risk and protective factors and substance use outcomes. Prevention Science, 5, 213–220.
Hawkins, J. D., & Weis, J. G. (1985). The social development model: An integrated approach to delinquency prevention. Journal of Primary Prevention, 6, 73–97.
Hays, S. P., Hays, C. E., & Mulhall, P. F. (2003). Community risk and protective factors and adolescent substance use. Journal of Primary Prevention, 24, 125–142.
Kumpfer, K. L., Alvarado, R., & Whiteside, H. O. (2003). Family-based interventions for substance use and misuse prevention. Substance Use and Misuse, 38, 1759–1787.
Li, X., Stanton, B., & Feigelman, S. (2000). Impact of perceived parental monitoring on adolescent risk behavior over 4 years. Journal of Adolescent Health, 27, 49–56.
Lochman, J. E., & van-den-Steenhoven, A. (2002). Family-based approaches to substance abuse prevention. Journal of Primary Prevention, 23, 49–114.
Murray, D. M. (1998). Design and analysis of group-randomized trials. New York: Oxford Press.
Newcomb, M. D., & Locke, T. (2005). Health, social, and psychological consequences of drug use and abuse. In Z. Sloboda (Ed.), Epidemiology of drug abuse (pp. 45–59). New York: Springer.
Peterson, C. A., Luze, G. J., Eshbaugh, E. M., Jeon, H., & Kantz, K. R. (2007). Enhancing parent-child interactions through home visiting: Promising practice or unfulfilled promise? Journal of Early Intervention, 29, 119–140.
Scheier, L. M. (2010). Handbook of drug use etiology: Theory, methods, and empirical findings. Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
Spoth, R. L., & Redmond, C. (2000). Research on family engagement in preventive interventions: toward improved use of scientific findings in primary prevention practice. Journal of Primary Prevention, 21, 267–284.
Spoth, R. L., Redmond, C., & Shin, C. (2000). Reducing adolescents’ aggressive and hostile behaviors: Randomized trial effects of a brief family intervention 4 years past baseline. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 154, 1248–1257.
Spoth, R. L., Redmond, C., & Shin, C. (2001). Randomized trial of brief family interventions for general populations: Adolescent substance use outcomes 4 years following baseline. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69, 627–642.
Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration. (2008). Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings (Office of Applied Studies, NSDUH Series H-34, DHHS Publication No. SMA 08–4343). Rockville, MD.
Swadi, H. (1999). Individual risk factors for adolescent substance use. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 55, 209–224.
Wills, T. A., Walker, C., & Resko, J. A. (2005). Longitudinal studies of drug use and abuse. In Z. Sloboda (Ed.), Epidemiology of drug abuse (pp. 177–192). New York: Springer.
Wills, T. A., & Yaeger, A. M. (2003). Family factors and adolescent substance use: Models and mechanisms. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12, 222–226.
Disclosure
Dr. Kenneth Griffin is a paid consultant to National Health Promotion Associates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffin, K.W., Samuolis, J. & Williams, C. Efficacy of a Self-Administered Home-Based Parent Intervention on Parenting Behaviors for Preventing Adolescent Substance Use. J Child Fam Stud 20, 319–325 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-010-9395-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-010-9395-2