Abstract
Purpose
Elevated red blood cell distribution width (RDW) has been associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) in cross-sectional and prospective studies. In this study, we aim to evaluate the relation of preablation RDW levels to late AF recurrence following cryoablation.
Methods
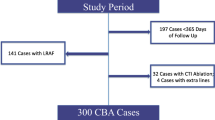
A total of 299 patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AF despite ≥1 antiarrhythmic drug(s) who were scheduled for cryoballoon-based AF ablation were enrolled in this prospective study.
Results
A total of 299 patients (55.40 ± 10.60years, 49.20 % male) were involved and followed up at a median time of 24 (6–44) months. Patients with late AF recurrence had higher RDW levels (14.30 ± 0.93 vs. 13.52 ± 0.93 %, p < 0.001). Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis showed that RDW level was an independent predictor for late AF recurrence (HR 1.88, 95 % CI 1.41–2.50, p < 0.001) along with left atrial (LA) diameter (HR 3.09, 95 % CI 1.81–5.27, p < 0.001), duration of AF (HR 1.04, 95 % CI 1.01–1.07, p = 0.02), and early AF recurrence (HR 6.39, 95 % CI 3.41–11.97, p < 0.001). A cut-off level of 13.75 % for RDW predicted late AF recurrence following cryoballoon-based pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) with a sensitivity and specificity of 78.00 and 70.00 %, respectively.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that elevated RDW may be a predictor of late recurrence following cryoballoon-based AF ablation. Further studies are needed to establish its exact pathophysiologic and prognostic roles.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makhoul, B. F., Khourieh, A., Kaplan, M., Bahouth, F., Aronson, D., & Azzam, Z. S. (2013). Relation between changes in red cell distribution width and clinical outcomes in acute decompensated heart failure. International Journal of Cardiology, 167(4), 1412–1416.
Jung, C., Fujita, B., Lauten, A., Kiehntopf, M., Kuthe, F., Ferrari, M., & Figulla, H. R. (2011). Red blood cell distribution width as useful tool to predict long-term mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. International Journal of Cardiology, 152(3), 417–418.
Tonelli, M., Sacks, F., Arnold, M., Moye, L., Davis, B., Pfeffer, M., & for the C, Recurrent Events Trial I. (2008). Relation between red blood cell distribution width and cardiovascular event rate in people with coronary disease. Circulation, 117(2), 163–168.
Zalawadiya, S. K., Veeranna, V., Niraj, A., Pradhan, J., & Afonso, L. (2010). Red cell distribution width and risk of coronary heart disease events. The American Journal of Cardiology, 106(7), 988–993.
Dabbah, S., Hammerman, H., Markiewicz, W., & Aronson, D. (2010). Relation between red cell distribution width and clinical outcomes after acute myocardial infarction. The American Journal of Cardiology, 105(3), 312–317.
Adamsson Eryd, S., Borne, Y., Melander, O., Persson, M., Smith, J. G., Hedblad, B., & Engstrom, G. (2014). Red blood cell distribution width is associated with incidence of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Internal Medicine, 275(1), 84–92.
Liu, T., Shao, Q., Miao, S., Liu, E., Xu, G., Yuan, R., & Li, G. (2014). Red cell distribution width as a novel, inexpensive marker for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. International Journal of Cardiology, 171(2), e52–e53.
Calkins, H., Kuck, K.H., Cappato, R., Brugada, J., Camm, A.J., Chen, S.A., Crijns, H.J., Damiano, R.J., Jr., Davies, D.W., DiMarco, J., Edgerton, J., Ellenbogen, K., Ezekowitz, M.D., Haines, D.E., Haissaguerre, M., Hindricks, G., Iesaka, Y., Jackman, W., Jalife, J., Jais, P., Kalman, J., Keane, D., Kim, Y.H., Kirchh, P., Klein, G., Kottkamp, H., Kumagai, K., Lindsay, B.D., Mansour, M., Marchlinski, F.E., McCarthy, P.M., Mont, J.L., Morady, F., Nademanee, K., Nakagawa, H., Natale, A., Nattel, S., Packer, D.L., Pappone, C., Prystowsky, E., Raviele, A., Reddy, V., Ruskin, J.N., Shemin, R.J., Tsao, H.M., Wilber, D. (2012). 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 33(2), 171–257.
European Heart Rhythm A, European Association for Cardio-Thoracic S, Camm, A. J., Kirchhof, P., Lip, G. Y., Schotten, U., Savelieva, I., Ernst, S., Van Gelder, I. C., Al-Attar, N., Hindricks, G., Prendergast, B., Heidbuchel, H., Alfieri, O., Angelini, A., Atar, D., Colonna, P., De Caterina, R., De Sutter, J., Goette, A., Gorenek, B., Heldal, M., Hohloser, S. H., Kolh, P., Le Heuzey, J. Y., Ponikowski, P., Rutten, F. H., & Guidelines ESCCfP. (2010). Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the task force for the management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Europace, 12(10), 1360–1420.
Camm, A. J., Lip, G. Y., De Caterina, R., Savelieva, I., Atar, D., Hohnloser, S. H., Hindricks, G., Kirchhof, P., Guidelines-CPG ESCCfP, & Document R. (2012). 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation—developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace, 14, 1385–1413.
Akoum, N., Daccarett, M., McGann, C., Segerson, N., Vergara, G., Kuppahally, S., Badger, T., Burgon, N., Haslam, T., Kholmovski, E., Macleod, R., & Marrouche, N. (2011). Atrial fibrosis helps select the appropriate patient and strategy in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a DE-MRI guided approach. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(1), 16–22.
Arya, A., Hindricks, G., Sommer, P., Huo, Y., Bollmann, A., Gaspar, T., Bode, K., Husser, D., Kottkamp, H., & Piorkowski, C. (2010). Long-term results and the predictors of outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using steerable sheath catheter navigation after single procedure in 674 patients. Europace, 12(2), 173–180.
Aytemir, K., Oto, A., Canpolat, U., Sunman, H., Yorgun, H., Sahiner, L., & Kaya, E. B. (2013). Immediate and medium-term outcomes of cryoballoon-based pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation: single-centre experience. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 38(3), 187–195.
Lin, Y. J., Tsao, H. M., Chang, S. L., Lo, L. W., Tuan, T. C., Hu, Y. F., Udyavar, A. R., Tsai, W. C., Chang, C. J., Tai, C. T., Lee, P. C., Suenari, K., Huang, S. Y., Nguyen, H. T., & Chen, S. A. (2010). Prognostic implications of the high-sensitive C-reactive protein in the catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. The American Journal of Cardiology, 105(4), 495–501.
Patel, K. V., Semba, R. D., Ferrucci, L., Newman, A. B., Fried, L. P., Wallace, R. B., Bandinelli, S., Phillips, C. S., Yu, B., Connelly, S., Shlipak, M. G., Chaves, P. H., Launer, L. J., Ershler, W. B., Harris, T. B., Longo, D. L., & Guralnik, J. M. (2010). Red cell distribution width and mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 65(3), 258–265.
Weiss, G., & Goodnough, L. T. (2005). Anemia of chronic disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, 352(10), 1011–1023.
Guo, Y., Lip, G. Y., & Apostolakis, S. (2012). Inflammation in atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 60(22), 2263–2270.
Aviles, R. J., Martin, D. O., Apperson-Hansen, C., Houghtaling, P. L., Rautaharju, P., Kronmal, R. A., Tracy, R. P., Van Wagoner, D. R., Psaty, B. M., Lauer, M. S., & Chung, M. K. (2003). Inflammation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 108(24), 3006–3010.
Issac, T. T., Dokainish, H., & Lakkis, N. M. (2007). Role of inflammation in initiation and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review of the published data. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50(21), 2021–2028.
Koroglu, S., Tuncer, C., Acar, G., Akcay, A., Sokmen, G., Yalcintas, S., Nacar, A., Altun, B., & Sokmen, A. (2012). Relation of inflammatory and oxidative markers to the occurrence and recurrence of persistent atrial fibrillation. Turk Kardiyoloji Dernegi arsivi : Turk Kardiyoloji Derneginin yayin organidir, 40(6), 499–504.
Zhao, Z., Liu, T., Li, J., Yang, W., Liu, E., & Li, G. (2014). Elevated red cell distribution width level is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in a canine model of rapid atrial pacing. International Journal of Cardiology, 174(1), 174–176.
Wan, J., Ristenpart, W. D., & Stone, H. A. (2008). Dynamics of shear-induced ATP release from red blood cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(43), 16432–16437.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurses, K.M., Yalcin, M.U., Kocyigit, D. et al. Red blood cell distribution width predicts outcome of cryoballoon-based atrial fibrillation ablation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 42, 51–58 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9959-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9959-y