Abstract
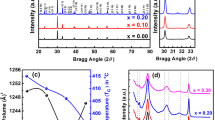
The objective of this study is to investigate the influence of silver ions on a.c. conductivity and dielectric properties of lead arsenate glass ceramics. PbO–As2O3 glasses mixed with different concentrations of Ag2O were prepared by conventional melt quenching technique and later were ceramicized by heat treatment at crystallization temperature for about 72 h. The prepared samples were characterized by XRD, SEM and DSC techniques. The SEM studies have indicated the samples are embedded with different crystal phases of varying sizes from 0.2 to 1.0 µm and the fraction of crystal phases as well as the size of the crystallites increased with increase of Ag2O concentration. The X–ray diffraction studies have revealed that the samples composed of different crystal phases viz., Ag3AsO4, AgPb4(AsO4)3, Pb2As2O5 and PbAs2O4 entrenched in the residual amorphous phase. The spectroscopic studies viz., optical absorption and IR spectroscopic studies have revealed a gradual increase in the degree of depolymerization of the glass network with increase in the concentration of Ag2O. Photoluminescence studies have indicated that the investigated glass ceramics contain silver ion clusters; the concentration of such clusters is predicted to be higher in the samples containing higher content of Ag2O. Finally, we have carried out extensive studies on dielectric properties viz., dielectric constant, loss, electric moduli, impedance spectra and a.c. conductivity over broad ranges of continuous frequencies (3–100 kHz) and temperatures (298–600 K). The obtained results were quantitatively analyzed in terms of different polarization mechanisms. The relaxation effects exhibited by the electric moduli were analyzed in a detailed way by different methods. Spreading of relaxation times for dipoles was established and the possible dipoles responsible for such relaxation effects were suggested. The observed increase of a.c. conductivity with the concentration of Ag2O is attributed to the contribution of both polaronic and ionic transport. Finally, it is concluded that the samples crystallized with higher content of Ag2O exhibit predominantly ionic conductivity and hence such glass ceramics may be useful as solid electrolytes for solid state batteries.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, S. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 28, 6456 (2017)
P. Naresh, G. Naga Raju, M. Srinivas Reddy, T. Venkatappa Rao, I.V. Kityk, N. Veeraiah, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 4902 (2014)
A.K. Yadav, C.R. Gautam, P. Singh, J. Mater. 26, 5001 (2015)
A. Subba Rao, J. Ashok, B. Suresh, G. Naga Raju, N. Venkatramaiah, V. Ravi Kumar, I.V. Kityk, N. Veeraiah, J. Alloys Compd. 712, 672 (2017)
Y. Gandhi, N. Krishna Mohan, N. Veeraiah, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357, 1193 (2011)
Q. Mei, R.T. Hart, C.J. Benmore, S. Amin, K. Leinenweber, J.L. Yarger, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 353, 1755 (2007)
G. Srinivasarao, N. Veeraiah, J. Solid State Chem 166, 104 (2002)
K. Nassau, Bell Syst. Tech. J. 60, 327 (1981)
C.J. Jeon, E.S. Kim, J.H. Cho, Mater. Res. Bull. 96, 54 (2017)
A. Siva Sesha Reddy, A. Ingram, M.G. Brik, M. Kostrzewa, P. Bragiel, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 10, 4066 (2017)
H.J. Wang, B.T. Li, H.X. Lin, L. Luo, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 2860 (2016)
G. Murali Krishna, B. Anila Kumari, M. Srinivasa Reddy, N. Veeraiah, J.Solid State Chem. 180, 2747 (2007)
N. Isaka, K. Ohkawa, H. Kiyono, H. Itoh, Junichi Takahashi, J. Mater. Sci. 19, 1233 (2008)
P. Naresh, G. Nagaraju, Y. Gandhi, M. Piasecki, N. Veeraiah, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc 98, 413 (2015)
M. Durandurdu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 436, 18 (2016)
R. Ciceo Lucacel, I. Ardelean, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 8, 1124 (2006)
J. Wang, Q. Huang, T. Li, B. Xin, S. Chen, X. Guo, C. Liu, Y. Li, J. Environ. Manag. 159, 11 (2015)
J. Tang, Y. Liu, H. Li, Z. Tan, D. Li, Chem. Commun. 49, 5498 (2013)
M. Nagarjuna, T. Satyanarayana, Y. Gandhi, N. Veeraiah, J. Alloys Compd. 479, 549 (2009)
F.A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C.A. Murillo, M. Bochmann, (Wiley, New York, 1999)
G. Nagarjuna, T. Satyanarayana, V. Ravi Kumar, P.V.V. Satyanarayana, N. Veeraiah, Philos. Mag 89, 2255 (2009)
A. Gholami, T.N. Amirabad, M. Maddahfar, J. Mater. Sci. 3, 1 (2017)
S. Kabi, A. Ghosh, Solid State Ion. 187, 39 (2011)
A. Ewald, D. Hösel, S. Patel, L.M. Grover, U. Gbureck, Acta Biomater. 7, 4064 (2011)
K. Sklepić, M. Vorokhta, P. Mošner, L. Koudelka, A. Moguš-Milanković, J. Phys. Chem. B 118, 12050 (2014)
S.S. Das, N.B. Singh, Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 3008 (2008)
K. Naresh Kumar, B. Suresh, A. Ingram, M. Kostrzewa, P. Bragiel, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, Ceram. Int. 43, 4335 (2017)
M.M. Ahmaed, C.A. Hogarth, M.N. Khan, J. Mater. Sci. 19, 4040 (1984)
S. Bahfenne, L. Rintoul, J. Langhof, R.L. Frost, Am. Mineral. 97, 143 (2012)
P.J. Dunn, D.R. Peacor, B.D. Struman, Paulmooreite, Sweden. Amer. Mineral. 64, 352 (1979)
F. Pertik, Z. Kristallogr. 184, 191 (1988)
S. Md. Rakibuddin, R. Mandal, Anantha krishnan, New J. Chem. 41, 1380 (2017)
C. Noguez, Opt. Mater. 27, 1204 (2005)
T. Okamoto, I. Yamaguchi, J. Phys. Chem. B 38, 10321 (2003)
V.M. Renteria, J. Garcia-Macedo, Colloids Surf. A 273, 1 (2006)
E. Saion, E. Gharibshahi, K. Naghavi, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 7880 (2013)
J. Tauc, Mater. Res. Bull. 3, 37 (1968)
M. Manoth, K. Manzoor, M.K. Patra, P. Pandey, S.R. Vadera, N. Kumar, Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 714 (2009)
E. Culea, P. Pascuta, M. Pustan, D.R. Tamas-Gavrea, L. Pop, I. Vida-Simiti, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 408, 18 (2015)
E. Malchukova, B. Boizot, Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 1299 (2010)
C.J.F. Böttcher, P. Bordewijk, Theory of Electrical Polarization. (Elsvier, Amsterdam, 1978)
P. Nageswara Rao, B.V. Raghavaiah, D. Krishna, N. Rao, Veeraiah, Mater. Chem. Phys. 91, 381 (2005)
D.K. Durga, N. Veeraiah, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 133 (2003)
N.G. Mc Crum, B.E. Read, G. Williams, Anelastic and Dielectric Effects in Polymeric Solids. (Wiley, London, 1967)
G.M. Tsangaris, G.C. Psarras, N. Kouloumbi, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 2027 (1998)
G.C. Psarras, E. Manolakaki, G.M. Tsangaris, Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 33, 375 (2002)
S. Mohanty, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 1180 (2014)
S.R. Elliott, Physics of Amorphous Materials. (Longman, Essex, 1990)
H. Kahnt, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 203, 225 (1996)
S.R. Elliott, Adv. Phys. 36, 135 (1987)
C. Filipič, A.M. Milanković, L. Pavić, K. Srilatha, N. Veeraiah, A. Leversustik, J. Appl.Phys. 112, 073705 (2012)
G. Austin, N.F. Mott, Adv. Phys. 50, 757 (2001)
A.M. Milanković, L. Pavić, K. Srilatha, Ch..Sr.i.n.i.v.a.s.a. Rao, T. Srikumar, Y. Gandhi, N. Veeraiah, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 013714 (2012)
J. Ashok, N. Purnachand, J. Suresh Kumar, M. Srinivasa Reddy, B. Suresh, M.P.F. Graça, N. Veeraiah, J. Alloys Compd. 696, 1260 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.N., Kostrzewa, M., Ingram, A. et al. Dielectric features, relaxation dynamics and a.c. conductivity studies on Ag+ mixed lead arsenate glass ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 1153–1172 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8018-8