Abstract
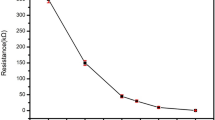
A compressible capacitive mechanical pressure sensor has been developed. Porous polydimethylsiloxane (p-PDMS) has been chosen as dielectric insulator because of its dielectric constant value. Gold nanoparticles have been embedded in p-PDMS to change the dielectric properties and to tune its elasticity. p-PDMS and its nanocomposite have been synthesized using the sugar leaching process. The p-PDMS physical characterization, with and without the gold nanoparticles, has been conducted to investigate its elastic response to compressive stresses as a function of both the polymer preparation thermal treatment and the gold nanoparticle concentration. A sensor operating in a low-pressure range between about 100 Pa and 10 kPa with a strain ranging between about 5% and 95% has been realized. Dielectric constant and electrical resistivity measurements have been performed using samples with a starting volume of the order of 1 cm3. The relationship between the dielectric constant, the electrical resistivity and the compressive stress/strain has been also deduced. The described sensor is flexible, biocompatible, water equivalent and can have applications in biomedicine (orthopedic, dentistry), engineering (stress–strain measurements, robotics), and microelectronics (microbalances, stress test on electronic devices).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Tarjányi, D. Káčik, M. Uhríčik, P. Palček, PMMA birefringence-based optical sensor of load. Proc. SPIE 11354, 113542L (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2555881
K.F. Lei, K.F. Lee, M.Y. Lee, Development of a flexible PDMS capacitive pressure sensor for plantar pressure measurement. Microelectron. Eng. 99, 1–5 (2012)
J. Chen, J. Zheng, Q. Gao, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, O.M. Omisore, L. Wang, H. Li, Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based flexible resistive strain sensors for wearable applications. Appl. Sci. 8, 345–360 (2018)
D.S. Kim, Y.J. Jeong, B.K. Lee, A. Shanmugasundaram, D.W. Lee, Piezoresistive sensor-integrated PDMS cantilever: a new class of device for measuring the drug-induced changes in the mechanical activity of cardiomyocytes. Sens. Actuators B 240, 566–572 (2017)
A.S. Cruz-Felix, A. Santiago-Alvarado, J. Marquez-Garcí, J. Gonzalez-García, PDMS samples characterization with variations of synthesis parameters for tunable optics applications. Heliyon 6, e03064 (2020)
V. Borjanovića, L. Bistričić, I. Vlasov, K. Furić, I. Zamboni, M. Jakšić, O. Shenderova, Influence of proton irradiation on the structure and stability of poly(dimethylsiloxane)and poly(dimethylsiloxane)-nanodiamond composite. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 27(6), 2396–2403 (2009)
Material Properties Database PDMS, Actual Website 2020 http://www.mit.edu/~6.777/matprops/pdms.htm
R. Seghir, S. Arscott, Extended PDMS stiffness range for flexible systems. Sens. Actuators A 230, 33–39 (2015)
A.R.M. Dalod, O.G. Grendal, A.B. Blichfeld, V. Furtula, J. Pérez, L. Henriksen, T. Grande, M.A. Einarsrud, Structure and Optical Properties of titania-PDMS hybrid nanocomposites prepared by in situ non-aqueous synthesis. Nanomaterials 7, 460 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120460
L. Torrisi, M. Cutroneo, A. Torrisi, G. Di Marco, B. Fazio, L. Silipigni, IR ns pulsed laser irradiation of Polydimethylsiloxane in vacuum. Vacuum 177, 109361 (2020)
S. Vlassov, S. Oras, M. Antsov, I. Sosnin, B. Polyakov, A. Shutka, M.Y. Krauchanka, L.M. Dorogin, Adhesion and mechanical properties of PDMS-based materials probed with AFM: a review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 56, 62–78 (2018)
D. Zhu, S. Handschuh-Wang, X. Zhou, Recent progress in fabrication and application of polydimethylsiloxane sponges. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 16467–16497 (2017)
P. Pan, Z. Bian, X. Song, X. Zhou, Properties of porous PDMS and stretchability of flexible electronics in moist environment. J. Appl. Mech. 87(10), 101009–101018 (2020)
M.N. Biutty, J.M. Koo, M. Zakia, P.L. Handayani, U.H. Choi, S.I.L. Yoo, Dielectric control of porous polydimethylsiloxane elastomers with Au nanoparticles for enhancing the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. RSC Adv. 10, 21309–21317 (2020)
Sigma-Aldrich actual website 2020: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/741957?lang=en®ion=CZ
M. Cutroneo, A. Torrisi, V. Ryukhtin, M. Dopita, L. Silipigni, A. Mackova, P. Malinsky, P. Slepicka, L. Torrisi, Polydimethylsiloxane containing gold nanoparticles for optical applications. J. Inst. 15, C03044 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/15/03/C03044
I.D. Johnston, D.K. McCluskey, C.K.L. Tan, M.C. Tracey, Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 035017 (2014)
L. Silipigni, G. Salvato, B. Fazio, G. Di Marco, E. Proverbio, M. Cutroneo, A. Torrisi, L. Torrisi, Temperature sensor based on IR-laser reduced Graphene Oxide. J. Inst 15, C04006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/15/04/C04006
L. Chen, X. Chen, Z. Zhang, T. Li, T. Zhao, X. Li, J. Zhang, PDMS-based capacitive pressure sensor for flexible transparent electronics. J. Sens. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1418374
S. El-Molla, A. Albrecht, E. Cagatay, P. Mittendorfer, G. Cheng, P. Lugli, J.F. Salmerón, A. Rivadeneyra, Integration of a thin film PDMS-based capacitive sensor for tactile sensing in an electronic skin. J. Sens. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1736169
S.H. Bae, Y. Lee, B.K. Sharma, H.J. Lee, J.H. Kim, J.H. Ahn, Graphene-based transparent strain sensor. Carbon 52, 236–242 (2013)
Y. Zheng, Y. Li, K. Dai, Y. Wang, G. Zheng, C. Liu, C. Shen, A highly stretchable and stable strain sensor based on hybrid carbon nanofillers/polydimethylsiloxane conductive composites for large human motions monitoring. Compos. Sci. Technol. 156, 276–286 (2018)
A. Mata, A.J. Fleischman, S. Roy, Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) properties for biomedical micro/nanosystems. Biomed. Microdevice 7(4), 281–293 (2005)
W.M. Lee, A. Upadhya, P.J. Reece, T.G. Phan, Fabricating low cost and high performance elastomer lenses using hanging droplets. Biomed. Opt. Express 5(5), 1627 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.5.001626
Acknowledgements
Part of this research has been realized at the CANAM (Centre of Accelerators and Nuclear Analytical Methods) infrastructure LM 2015056 and has been supported by Project GACR 19-02482S. This publication was supported by OP RDE, MEYS, Czech Republic under the project CANAM OP, CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001812.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silipigni, L., Salvato, G., Torrisi, A. et al. Pressure sensor based on porous polydimethylsiloxane with embedded gold nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 8703–8715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05541-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05541-1