Abstract
Background
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a devastating disorder of the lung by various causes and its cardinal features are tissue inflammation, pulmonary edema, low lung compliance, and widespread capillary leakage. Among phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), PI3K-γ isoform has been shown to play an important role in a number of immune/inflammatory responses.
Methods
We investigated the role of PI3K-γ and its molecular basis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI using a selective inhibitor for PI3K-γ, AS 605240, and LPS-treated C57BL/6 mice.
Results
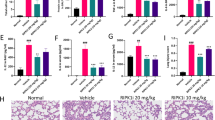
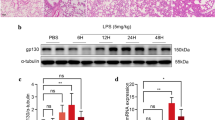
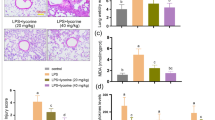
Treatment of mice with LPS showed an increase of lung inflammation and vascular leakage. Production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and IL-4, adhesion molecule, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was also increased. Administration of AS 605240 to LPS-treated mice markedly reduced the pathophysiological features of ALI and the increased production of ROS, cytokines, adhesion molecule, and VEGF in the lung. Our results also showed that treatment of mice with LPS activates nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and degradation of inhibitory κBα (IκBα) through PI3K-γ. Additionally, infiltration of dendritic cells (DCs) and expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) were significantly increased in the lung of LPS-treated mice, and inhibition of PI3K-γ reduced the infiltration of DCs and TLR4 expression in the lung.
Conclusions
These results indicate that PI3K-γ is critically involved in LPS-induced ALI by regulating IκBα/NF-κB pathway and innate immune responses. Based on our data, we suggest that PI3K-γ isoform is a promising target for the treatment of ALI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Z, Zhu Y, Jiang H. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced collagen secretion by phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway in fibroblasts during acute lung injury. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2009;29:119–25.
Thimmulappa RK, Scollick C, Traore K, Yates M, Trush MA, Liby KT, et al. Nrf2-dependent protection from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality by CDDO-Imidazolide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351:883–9.
Park HS, Kim SR, Lee YC. Impact of oxidative stress on lung diseases. Respirology. 2009;14:27–38.
Fink MP. Reactive oxygen species as mediators of organ dysfunction caused by sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or hemorrhagic shock: potential benefits of resuscitation with Ringer’s ethyl pyruvate solution. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002;5:167–74.
Imai Y, Kuba K, Neely GG, Yaghubian-Malhami R, Perkmann T, van Loo G, et al. Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury. Cell. 2008;133:235–49.
Fan J, Frey RS, Malik AB. TLR4 signaling induces TLR2 expression in endothelial cells via neutrophil NADPH oxidase. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1234–43.
Park HS, Jung HY, Park EY, Kim J, Lee WJ, Bae YS. Cutting edge: direct interaction of TLR4 with NAD(P)H oxidase 4 isozyme is essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced production of reactive oxygen species and activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 2004;173:3589–93.
Henderson Jr WR, Chi EY, Teo JL, Nguyen C, Kahn M. A small molecule inhibitor of redox-regulated NF-kappa B and activator protein-1 transcription blocks allergic airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model. J Immunol. 2002;169:5294–9.
Yum HK, Arcaroli J, Kupfner J, Shenkar R, Penninger JM, Sasaki T, et al. Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinases in neutrophil activation and the development of acute lung injury. J Immunol. 2001;167:6601–8.
Hua F, Ha T, Ma J, Li Y, Kelley J, Gao X, et al. Protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in TLR4-deficient mice is mediated through a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 2007;178:7317–24.
Medina-Tato DA, Ward SG, Watson ML. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in lung disease: leucocytes and beyond. Immunology. 2007;121:448–61.
Ward SG, Finan P. Isoform-specific phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003;3:426–34.
Barberis L, Hirsch E. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma to fight inflammation and more. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:279–85.
Park SJ, Min KH, Lee YC. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta inhibitor as a novel therapeutic agent in asthma. Respirology. 2008;13:764–71.
Reutershan J, Saprito MS, Wu D, Rückle T, Ley K. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma required for lipopolysaccharide-induced transepithelial neutrophil trafficking in the lung. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:1137–47.
Shang GH, Lin DJ, Xiao W, Jia CQ, Li Y, Wang AH, et al. Ethyl pyruvate reduces mortality in an endotoxin-induced severe acute lung injury mouse model. Respir Res. 2009;10:91.
Zerfaoui M, Naura AS, Errami Y, Hans CP, Rezk BM, Park J, et al. Effects of PARP-1 deficiency on airway inflammatory cell recruitment in response to LPS or TNF: differential effects on CXCR2 ligands and Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:1385–92.
Kim SR, Lee KS, Park HS, Park SJ, Min KH, Moon H, et al. HIF-1α inhibition ameliorates an allergic airway disease via VEGF suppression in bronchial epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:2858–69.
Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Irani K, Finkel T. Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science. 1995;270:296–9.
Sung MJ, Kim DH, Jung YJ, Kang KP, Lee AS, Lee S, et al. Genistein protects the kidney from cisplatin-induced injury. Kidney Int. 2008;74:1538–47.
Sun L, Chen T, Wang X, Chen Y, Wei X. Bufalin induces reactive oxygen species dependent Bax translocation and apoptosis in ASTC-a-1 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. doi:10.1093/ecam/nep082.
Kim TB, Kim SY, Moon KA, Park CS, Jang MK, Yun ES, et al. Five-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside attenuates poly (I:C)-induced airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:1709–19.
Hammad H, Chieppa M, Perros F, Willart MA, Germain RN, Lambrecht BN. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat Med. 2009;15:410–6.
Wheeler AP, Bernard GR. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a clinical review. Lancet. 2007;369:1553–64.
McCabe AJ, Dowhy M, Holm BA, Glick PL. Myeloperoxidase activity as a lung injury marker in the lamb model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 2001;36:334–7.
Rückle T, Schwarz MK, Rommel C. PI3Kγ inhibition: towards an ‘aspirin of the 21st century’? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:903–18.
Venable JD, Ameriks MK, Blevitt JM, Thurmond RL, Fung-Leung WP. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kgamma) inhibitors for the treatment of inflammation and autoimmune disease. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2010;4:1–15.
Lionetti V, Lisi A, Patrucco E, De Giuli P, Milazzo MG, Ceci S, et al. Lack of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-γ attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:134–41.
Uhlig U, Fehrenbach H, Lachmann RA, Goldmann T, Lachmann B, Vollmer E, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase inhibition prevents ventilation-induced lung cell activation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169:201–8.
Park HS, Kim SY, Kim SR, Lee YC. Targeting abnormal airway vascularity as a therapeutical strategy in asthma. Respirology. 2010;15:459–71.
Kuroki M, Voest EE, Amano S, Beerepoot LV, Takashima S, Tolentino M, et al. Reactive oxygen intermediates increase vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:1667–75.
Rahman I, MacNee W. Role of transcription factors in inflammatory lung diseases. Thorax. 1998;53:601–12.
Tong Q, Zheng L, Lin L, Wang D, Huang C, Li D. VEGF is upregulated by hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor via the PI-3 K/Akt-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Respir Res. 2006;7:37.
Montefort S, Holgate ST. Adhesion molecules and their role in inflammation. Respir Med. 1991;85:91–9.
Moser R, Fehr J, Bruijnzeel PL. IL-4 controls the selective endothelium-driven transmigration of eosinophils from allergic individuals. J Immunol. 1992;149:1432–8.
D’Andrea A, Ma X, Aste-Amezaga M, Paganin C, Trinchieri G. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 on the production of cytokines by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: priming for IL-12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J Exp Med. 1995;181:537–46.
Kambayashi T, Jacob CO, Strassmann G. IL-4 and IL-13 modulate IL-10 release in endotoxin-stimulated murine peritoneal mononuclear phagocytes. Cell Immunol. 1996;171:153–8.
Roy S, Charboneau R, Melnyk D, Barke RA. Interleukin-4 regulates macrophage interleukin-12 protein synthesis through a c-fos mediated mechanism. Surgery. 2000;128:219–24.
Major J, Fletcher JE, Hamilton TA. IL-4 pretreatment selectively enhances cytokine and chemokine production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 2002;168:2456–63.
Reddy SA, Huang JH, Liao WS. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase as a mediator of TNF-induced NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol. 2000;164:1355–63.
Toker A. Protein kinases as mediators of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;57:652–8.
Frey RS, Gao X, Javaid K, Siddiqui SS, Rahman A, Malik AB. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma signaling through protein kinase Czeta induces NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidant generation and NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:16128–38.
Gukovsky I, Cheng JH, Nam KJ, Lee OT, Lugea A, Fischer L, et al. Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase gamma regulates key pathologic responses to cholecystokinin in pancreatic acinar cells. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:554–66.
Cella M, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Origin, maturation and antigen presenting function of dendritic cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:10–6.
Steinman RM, Inaba K. Myeloid dendritic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;66:205–8.
Togbe D, Schnyder-Candrian S, Schnyder B, Couillin I, Maillet I, Bihl F, et al. TLR4 gene dosage contributes to endotoxin-induced acute respiratory inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80:451–7.
Bhattacharyya S, Dudeja PK, Tobacman JK. Lipopolysaccharide activates NF-kappaB by TLR4-Bcl10-dependent and independent pathways in colonic epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295:G784–90.
Xu H, Su Z, Wu J, Yang M, Penninger JM, Martin CM, et al. The alarmin cytokine, high mobility group box 1, is produced by viable cardiomyocytes and mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial dysfunction via a TLR4/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma pathway. J Immunol. 2010;184:1492–8.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A084144).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dong Im Kim and So Ri Kim contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 216 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.I., Kim, S.R., Kim, H.J. et al. PI3K-γ Inhibition Ameliorates Acute Lung Injury Through Regulation of IκBα/NF-κB Pathway and Innate Immune Responses. J Clin Immunol 32, 340–351 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9628-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9628-1