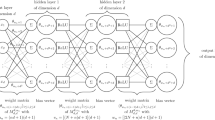
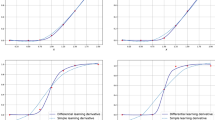
Abstract
Machine learning methods for solving nonlinear partial differential equations (PDEs) are hot topical issues, and different algorithms proposed in the literature show efficient numerical approximation in high dimension. In this paper, we introduce a class of PDEs that are invariant to permutations, and called symmetric PDEs. Such problems are widespread, ranging from cosmology to quantum mechanics, and option pricing/hedging in multi-asset market with exchangeable payoff. Our main application comes actually from the particles approximation of mean-field control problems. We design deep learning algorithms based on certain types of neural networks, named PointNet and DeepSet (and their associated derivative networks), for computing simultaneously an approximation of the solution and its gradient to symmetric PDEs. We illustrate the performance and accuracy of the PointNet/DeepSet networks compared to classical feedforward ones, and provide several numerical results of our algorithm for the examples of a mean-field systemic risk, mean-variance problem and a min/max linear quadratic McKean-Vlasov control problem.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data used during this study are generated by Monte Carlo samples using the parameters provided in the text. More details are available upon reasonable request.
References
Achdou, Y., Capuzzo-Dolcetta, I.: Mean field games: numerical methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48(3), 1136–1162 (2010)
Achdou, Y., Laurière, M.: On the system of partial differential equations arising in mean field type control. Discr. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 35(9), 3879–3900 (2015)
Basei, M., Pham, H.: A weak martingale approach to linear-quadratic McKean-Vlasov stochastic control problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 181(2), 347–382 (2019)
Beck, C., Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A., Kuckuck, B.: An overview on deep learning-based approximation methods for partial differential equations. http://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12348v1(2020)
Carmona, R., Delarue, F.: Probabilistic theory of mean field games: vol. i, mean field FBSDEs, control, and games. Springer, New York (2018)
Carmona, R., Delarue, F.: probabilistic theory of mean field games: vol. II, mean field FBSDEs, control, and games. Springer, New York (2018)
Carmona, R., Fouque, J.P., Sun, L.: Mean field games and systemic risk. Commun. Math. Sci. 13(4), 911–933 (2015)
Carmona, R., Laurière, M.: Convergence analysis of machine learning algorithms for the numerical solution of mean field control and games: II- the finite horizon case. http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.01613to appear in The Annals of Applied Probability (2019)
Chan-Wai-Nam, Q., Mikael, J., Warin, X.: Machine learning for semi linear PDEs. J. Scientif. Comput. 79, 1667–1712 (2019)
Clevert, D., Unterthiner, T., Hochreiter, S.: Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (elus). In: Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y. (eds.) 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, May 2-4, 2016, Conference Track Proceedings (2016). URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07289
Djete, F.: Extended mean-field control problem: a propagation of chaos result. http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.12996(2020)
Han, E.W., Jentzen, A.: Deep learning-based numerical methods for high-dimensional parabolic partial differential equations and backward stochastic differential equations. Commun. Math. Stat. 5(4), 349–380 (2017)
Fouque, J.P., Zhang, Z.: Deep learning methods for mean field control problems with delay. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 6, 74 (2020)
Gangbo, W., Mayorga, S., Swiech, A.: Finite dimensional approximations of Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations in spaces of probability measures. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 53(2), 1320–1356 (2021)
Germain, M., Mikael, J., Warin, X.: Numerical resolution of McKean-Vlasov FBSDEs using neural networks. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-022-09946-1
Germain, M., Pham, H., Warin, X.: Convergence analysis of particles approximation of PDEs in Wasserstein space. http://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00837, to appear in Journal of Applied Probability 59.4 (2022)
Germain, M., Pham, H., Warin, X.: Neural networks based algorithms for stochastic control and PDEs in finance. In: Capponi, A., Lehalle, C. (eds.) http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.08068 to appear in Machine Learning And Data Sciences For Financial Markets: A Guide To Contemporary Practices. Cambridge University Press (2022)
Han, J., Jentzen, A., Weinan, E.: Solving high-dimensional partial differential equations using deep learning. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 115(34), 8505–8510 (2018)
Hornik, K.: Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks. Neural Netw. 4, 251–257 (1991)
Huang, M., Caines, P., Malhamé, R.: Large population stochastic dynamic games: closed-loop McKean-Vlasov systems and the Nash certainty equivalence principle. Commun. Inf. Syst. 3, 221–252 (2006)
Huré, C., Pham, H., Warin, X.: Deep backward schemes for high-dimensional nonlinear pdes. Math. Comput. 89(324), 1547–1579 (2020)
Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A., Kruse, T., Nguyen, T.: A proof that rectified deep neural networks overcome the curse of dimensionality in the numerical approximation of semilinear heat equation. SN Partial Diff. Eq. Appl. 1(10), 1–34 (2020)
Ismail, A., Pham, H.: Robust markowitz mean-variance portfolio selection under ambiguous covariance matrix. Math. Finance 29, 174–207 (2019)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980(2014)
Labordère, P.: Counterparty risk valuation: a marked branching diffusion approach. Hal-00677348 (2012)
Lacker, D.: Limit theory for controlled McKean-Vlasov dynamics. SIAM J. Control Optim. 55(3), 1641–1672 (2017)
Lasry, J., Lions, P.: Mean field games. Japanese J. Math. 2, 229–260 (2007)
Pardoux, E., Peng, S.: Adapted solution of a backward stochastic differential equation. Syst. Control Lett. 14(1), 55–61 (1990)
Pham, H., Warin, X., Germain, M.: Neural networks-based backward scheme for fully nonlinear PDEs. SN Partial Diff. Eq. Appl. 2, 16 (2021)
Pham, H., Wei, X.: Dynamic programming for optimal control of stochastic McKean-Vlasov dynamics. SIAM J. Control Optim. 55(2), 1069–1101 (2017)
R. Qi, C., Su, H., Mo, K., J. Guibas, L.: Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 77–85 (2017)
Ruthotto, L., Osher, S.J., Li, W., Nurbekyan, L., Fung, S.W.: A machine learning framework for solving high-dimensional mean field game and mean field control problems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117(17), 9183–9193 (2020)
Salhab, R., Malhamé, R.P., Le Ny, J.: A dynamic game model of collective choice in multi-agent systems. In: 2015 IEEE 54th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 4444–4449 (2015)
Smulevici, J.: On the area of the symmetry orbits of cosmological spacetimes with toroidal or hyperbolic symmetry. Anal. PDE 4(2), 191–245 (2011)
Wagstaff, E., Fuchs, F., Engelcke, M., Posner, I., Osborne, M.A.: On the limitations of representing functions on sets. pp. 6487–6494 (2019)
Wyk, S.V.: Partial differential equations and quantum mechanics. Computer solution in Physics, pp. 99–139 (2008)
Zaheer, M., Kottur, S., Ravanbakhsh, S., Poczos, B., Salakhutdinov, R.R., Smola, A.J.: Deep sets. In: Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, pp. 3391–3401. Curran Associates, Inc. (2017)
Funding
This work was supported by FiME (Finance for Energy Market Research Centre) and the “Finance et Développement Durable - Approches Quantitatives” EDF - CACIB Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code Availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by FiME (Finance for Energy Market Research Centre) and the “Finance et Développement Durable - Approches Quantitatives” EDF - CACIB Chair. The work of M. Laurière was supported by NSF grant DMS-1716673 and ARO grant W911NF-17-1-0578.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Germain, M., Laurière, M., Pham, H. et al. DeepSets and Their Derivative Networks for Solving Symmetric PDEs. J Sci Comput 91, 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01796-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01796-w