Abstract
Owing to the low cost and convenience of identifying an object without physical contact, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems provide innovative, promising and efficient applications in many domains. An RFID grouping protocol is a protocol that allows an off-line verifier to collect and verify the evidence of two or more tags simultaneously present. Recently, Huang and Ku (J. Med. Syst, 2009) proposed an efficient grouping protocol to enhance medication safety for inpatients based on low-cost tags. However, the Huang–Ku scheme is not secure; an attacker can easily make up fake grouping records to cheat the verifier. This weakness would seriously endanger the safety of inpatient medication safety. This paper will show the weaknesses, and then propose two RFID-based solutions to enhance medication safety for two different scenarios. The proposed schemes are practical, secure and efficient for medication applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolotnyy, L., and Robins, G., Generalized yoking-proofs for a group of RFID tags. Proceedings of the 3rd Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems. pp. 1–4, 2006.
Van deCastle, B., Kim, J., Pedreira, M. L. G., Paiva, A., Goossen, W., and Bates, D. W., Information technology and patient safety in nursing practice: an international perspective. Int. J. Med. Inform. 73:607–614, 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2004.04.007.
Chao, C., Jen, W., Chi, Y., and Lin, B., Improving patient safety with RFID and mobile technology. Int. J. Electron. Healthc. 3:2175–2192, 2007. doi:10.1504/IJEH.2007.013099.
Chassin, M. R., and Becher, E. C., The wrong patient. Ann. Intern. Med. 136:11826–11833, 2002.
Chien, H. Y., SASI: A new ultra-lightweight RFID authentication protocol providing strong authentication and strong integrity. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secure. Comput. 4 (4)337–340, 2007.
Chien, H.-Y., and Chen, C.-H., Mutual authentication protocol for RFID conforming to EPC Class 1 Generation 2 standards. Comput. Stand. Interfaces. 29:2254–2259, 2007.
Cooper, M. C., Can a zero defects philosophy be applied to drug errors? J. Adv. Nurs. 21:3487–3491, 1995.
Duc, D. N., Park, J., Lee, H., and Kim, K., Enhancing security of EPCglobal Gen-2 RFID tag against traceability and cloning. Proceedings of the 2006 Symposium on Cryptography and Information Security, pp. 97, 2006.
EPCglobal, http://www.epcglobalinc.org/
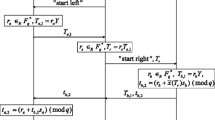
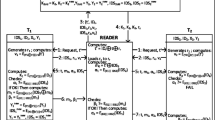
Huang, H.-H., and Ku, C.-Y., A RFID grouping proof protocol for medication safety of inpatient. J. Med. Syst2009. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9207z.
Janz, B. D., Pitts, M. G., and Otondo, R. F., Information systems and health care II: back to the future with RFID: Lessons learned—some old, some new. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 15:132–148, 2005.
Juels, A., Yoking-proofs for RFID tags. Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Pervasive Computing and Communication Security, pp. 138–143, 2004.
Juels, A., Minimalist cryptography for low-cost RFID tags. Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Security in Communication Networks, pp. 149–164, 2004.
Kaelber, D. C., and Bates, D. W., Health information exchange and patient safety. J. Biomed. Inform. 40:(Suppl 6):S40–S45, 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2007.08.011.
Koshy, R., Navigating the information technology highway: Computer solutions to reduce errors and enhance patient safety. Transfusion. 45:4189S–4205S, 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1537-2995.2005.00619.x.
Liao, P.-C., Liu, L., Kuo, F., and Jin, M.-H., Developing a patient safety based RFID information system—an empirical study in Taiwan. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Management of Innovation and Technology, pp. 585–589, 2006.
Perrin, R. A., and Simpson, N., RFID and bar codes—critical importance in enhancing safe patient care. J. Healthc. Inf. Manag. 18:433–439, 2004.
Piramuthu, S., On existence proofs for multiple RFID tags. Proceedings of the 2006 ACS/IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Services, pp. 317–320, 2006.
Saito, J., and Sakurai, K., Grouping proof for RFID tags. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, pp. 621–624, 2005.
Sandlin, D., SurgiChip—new technology for prevention of wrong site, wrong procedure, wrong person surgery. J. Perianesth. Nurs. 20:2144–2146, 2005. doi:10.1016/j.jopan.2005.02.001.
Sun, P. R., Wang, B. H., and Wu, F., A new method to guard inpatient medication safety by the implementation of RFID. J. Med. Syst. 32:4327–4332, 2008. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9137-9.
Wu, F., Kuo, F., and Liu, L.-W., The application of RFID on drug safety of inpatient nursing healthcare. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 85–92, 2005.
Westhues, J., Hacking the prox card. RFID: Applications, Security and Privacy, Addison-Wesley, 2005, pp. 291-300, 2005.
Hancke, G. P. A practical relay attack on ISO 1443 proximity cards. http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~gh275/re;ay.pdf.
Chien, H.-Y., and Laih, C.-S., ECC-Based Lightweight Authentication Protocol with Un-traceability for Low-Cost RFIDs. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 2009, http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jpdc.2009.07.007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, HY., Yang, CC., Wu, TC. et al. Two RFID-based Solutions to Enhance Inpatient Medication Safety. J Med Syst 35, 369–375 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9373-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9373-7