Abstract
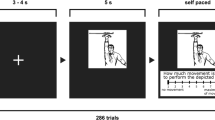
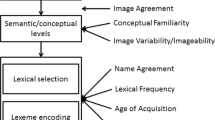
The present study investigates the effects of word category (nouns versus verbs) and their subcategories on naming latencies in German, with a focus on the influence of lexical parameters on naming performance. The experimental material met linguistic construction criteria and was carefully matched for age of spontaneous production, frequency, and name agreement. Additional lexical parameters (objective age-of-acquisition, word length, visual complexity, imageability) were obtained. The results demonstrated a clear effect of word category on naming latencies. This effect was supported by two different observations. First, there was evidence for category and subcategory effects in naming: nouns were named faster than verbs, and intransitive verbs were named faster than transitive verbs. Second, while objective age-of-acquisition (naming age) turned out to be an important predictor of reaction times for both word categories, naming latencies for nouns and verbs were affected differentially by other lexical parameters. The results are discussed with respect to current controversies on the noun–verb-asymmetry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggujaro S., Crepaldi D., Pistarini C., Taricco M., Luzzatti C. (2006). Neuro-anatomical correlates of impaired retrieval of verbs and nouns: Interaction of grammatical class, imageability and actionality. Journal of Neurolinguistics 19, 175–194
Baayen R.H., Piepenbrock R., Gulikers L. (1995). The CELEX Lexical Database (Release 2) [CD-ROM]. Philadelphia, PA: Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania
Barry C., Morrison C.M., Ellis A.W. (1997). Naming the Snodgrass and Vanderwart pictures: Effects of age-of-acquisition, frequency, and name agreement. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 50A, 560–585
Bird H., Howard D., Franklin S. (2000a). Why is a verb like an inanimate object? Grammatical category and semantic category deficits. Brain and Language 72, 246–309
Bird H., Lambon Ralph M.A., Patterson K., Hodges J.R. (2000b). The rise and fall of frequency and imageability: Noun and verb production in semantic dementia. Brain and Language 73, 17–49
Black M., Chiat S. (2000). Putting thoughts into verbs: Developmental and acquired impairments. In: Best W., Bryan K., Maxim J. (eds) Semantic Processing Theory and Practice. London, Whurr Publishers, pp. 52–79
Black M., Chiat S. (2003). Noun–verb dissociations: A multifaceted phenomenon. Journal of Neurolinguistics 16, 231–250
Bogka N., Masterson J., Druks J., Fragkioudaki M., Chatziprokopiou E.-S., Economou K. (2003). Object and action picture naming in English and Greek. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology 15(3): 371–403
Bornstein M.H., Cote L.R., Maital S., Painter K., Park S.-Y., Pascual L., Pecheux M.-G., Ruel J., Venuti P., Vyt A. (2004). Cross-linguistic analysis of vocabulary in young children: Spanish, Dutch, French, Hebrew, Italian, Korean, and American English. Child Development 75(4): 1115–1139
Brace N., Kemp R., Snelgar R. (2006). SPSS for psychologists. A guide to data analysis using SPSS for windows. London, Palgrave
Chen S., Bates E. (1998). The dissociation between nouns and verbs in Broca’s and Wernicke’s aphasia: Findings from chinese. Aphasiology 12, 5–36
Chiarello C., Liu S., Shears C., Kacinik N. (2002). Differential asymmetries for recognizing nouns and verbs: Where are they? Neuropsychology 16(1): 35–48
Colombo L., Burani C. (2001). The influence of age of acquisition, root frequency, and context availability in processing nouns and verbs. Brain and Language 81, 398–411
Cuetos F., Alija M. (2003). Normative data and naming times for action pictures. Behavior Research Measures, Instruments, & Computers 3571, 168–177
Damasio A., Tranel D. (1993). Nouns and verbs are retrieved with differently distributed neural systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA 90, 4957–4960
Daniele A., Giustolisi L., Silveri M., Colosimo C., Gainotti G. (1994). Evidence for a possible neuroanatomical basis for lexical processing of nouns and verbs. Neuropsychologia 32, 1325–1341
Davidoff J., Masterson J. (1995). The development of picture naming: Differences between verbs and nouns. Journal of Neurolinguistics 9, 69–83
De Bleser R., Kauschke C. (2003). Acquisition and loss of nouns and verbs: Parallel or divergent patterns?. Journal of Neurolinguistics 16(2/3): 213–229
Druks J. (2002). Verbs and nouns—a review of the literature. Journal of Neurolinguistics 15, 289–315
Duden in 12 Bänden: das Aussprachewörterbuch (1998). Bibliographisches Institut & F.A. Brockhaus AG.
Gentner D. (1981) Some interesting differences between verbs and nouns. Cognition and Brain Theory 4, 161–178
Gentner D. (1982). Why nouns are learned before verbs: Linguistic relativity versus natural partitioning. In: Kuczaj S. (eds) Language development, Vol. 2: Language, thought and culture. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, pp. 301–334
Gentner D., Boroditsky L. (2000). Individuation, relativity, and early word learning. In: Bowerman M., Levinson S.C. (eds) Language acquisition and conceptual development. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, pp. 215–256
Ghyselinck M., Lewis M.B., Brysbaert M. (2004). Age of acquisition and the cumulative-frequency hypothesis: A review of the literature and a new multi-task investigation. Acta Psychologica 115, 43–67
Hirsh-Pasek K., Michnick Golinkoff R. (2006) Action meets word: How children learn verbs. Oxford, University Press
Humphreys G.W., Price C., Riddoch M.J. (1999). From objects to names: A cognitive neuroscience approach. Psychological Research 62, 118–130
Jonkers R. (2000). Verb-finding problems in Broca's aphasics: The influence of transitivity. In: Bastiaanse R., Grodzinsky R.J. (eds) Grammatical disorders in aphasia: A neurolinguistic perspective. London, Whurr Publishers, pp. 105–122
Jonkers R., Bastiaanse R. (1998). How selective are selective word class deficits? Two case studies of action and object naming. Aphasiology 12, 245–256
Kauschke C. (2007). Erwerb und Verarbeitung von Nomen und Verben. Tübingen, Niemeyer
Kauschke C., Lee H.-W., Pae S. (2007). Similarities in noun and verb acquisition—a crosslinguistic study of children learning German, Korean, and Turkish. Language and Cognitive Processes 22(7): 1–28
Kim M., Thompson C.K. (2000). Patterns of comprehension and production of nouns and verbs in agrammatism: Implications for lexical organisation. Brain and Language 74, 1–25
Laiacona M., Caramazza A. (2004). The noun/verb dissociation in language production: Varieties of causes. Cognitive Neuropsychology 21, 103–123
Lloyd-Jones T., Humphreys G.W. (1997a). Perceptual differentiation as so source of category effects in object processing: Evidence from naming and object decision. Memory & Cognition 25(1): 18–35
Lloyd-Jones T., Humphreys G.W. (1997b). Categorizing chairs and naming pears: Category differences in object processing as a function of task and priming. Memory & Cognition 25(5): 606–624
Luzzatti C., Raggi R., Zonca G., Pistarini C., Contardi A., Pinna G.D. (2002). Verb–noun double dissociation in aphasic lexical impairments: The role of word frequency and imageability. Brain and Language 81, 432–444
Marshall J. (2003). Noun–verb dissociations—evidence from acquisition and developmental and acquired impairments. Journal of Neurolinguistics 16, 67–84
Miceli G., Silveri M., Nocentini O., Caramazza A. (1988). Patterns of dissociation in comprehension and production of nouns and verbs. Aphasiology 2, 351–358
Monaghan, P., Chater, N., & Christiansen, M. H. (2003). Inequality between the classes: Phonological and distributional typicality as predictors of lexical processing. Proceedings of the 25th annual conference of the cognitive science society (pp. 810–815).
Morrison C.M., Champell T.D., Ellis A.W. (1997). Age of acquisition norms for a large set of object names and their relation to adult estimates and other variables. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 50A, 528–559
Morrison C.M., Ellis A.W. (2000). Real age of acquisition effects in word naming and lexical decision. British Journal of Psychology 91, 167–180
Perani D., Cappa S., Schnur T., Tettamanti M., Collina S., Rosa M.M., Fazio F. (1999). The neural correlates of verb and noun processing. A PET study. Brain 122, 2337–2344
Postler, J. (2006). Die neuronale Verarbeitung von Nomen und Verben. Dissertation. University of Potsdam.
Sereno J.A. (1999). Hemispheric differences in grammatical class. Brain and Language 70, 13–28
Shapiro K.A., Mottaghy F.M., Schiller N.O., Poeppel T.D., Flüß M.O., Müller H.-W., Caramazza A., Krause B. (2005). Dissociating neural correlates for nouns and verbs. NeuroImage 24, 1058–1067
Snodgrass J.G., Vanderwart M. (1980). A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. Journal of Experimental Psychology 6, 174–215
Sörös P., Cornelissen K., Laine M., Salmelin R. (2003). Naming actions and objects: Cortical dynamics in healthy adults and in a anomic patient with a dissociation in action/object naming. Neuroimage 19, 1787–1801
Szekely A., D’Amico S., Devescovi A., Federmeier K., Herron D., Iyer G., Jacobsen T., Bates E. (2005). Timed action and object naming. Cortex 41(1): 7–26
Thompson C.K., Lange K.L., Schneider S.L., Shapiro L.P. (1997). Agrammatic and non-brain-damaged subjects’ verb and verb argument structure production. Aphasiology 11(4/5): 473–490
Tranel D., Martin C., Damasio H., Grabowski T., Hichwa R. (2005). Effects of noun–verb homonymy on the neural correlates of naming concrete entities and actions. Brain and Language 92, 288–299
Tyler L.K., Russel R., Fadili J., Moss H.E. (2001). The neural representations of nouns and verbs: PET studies. Brain 124, 1619–1634
Tyler L.K., Stamatakis E.A., Dick E., Bright P., Fletcher P., Moss H. (2003). Objects and their actions: Evidence for a neurally distributed semantic system. NeuroImage 18, 542–557
Tyler L.K., Bright P., Fletcher P., Stamatakis E.A. (2004). Neural processing of nouns and verbs: The role of inflectional morphology. Neuropsychologia 42, 512–523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kauschke, C., von Frankenberg, J. The Differential Influence of Lexical Parameters on Naming Latencies in German. A Study on Noun and Verb Picture Naming. J Psycholinguist Res 37, 243–257 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-007-9068-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-007-9068-5