Abstract
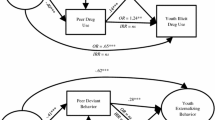
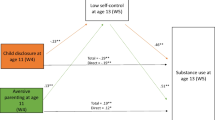
This study purports that parental rejection and warmth are critical to the development of adolescent drug use, and investigates a model that also considers children's vulnerability and deviant peer affiliations. It tests mediation through the proximal risk factor of deviant peers. Poisson growth curve modeling was used to examine participants from the Canadian National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth (NLSCY; N=2194) over 4 waves. Results indicated that parental rejection was positively related to drug use, whereas parental warmth was negatively related to it. Both effects were significant when child ADHD symptoms were taken into account. Parental rejection and warmth had differential effects over time. Deviant peer affiliations were positively associated with drug use, did not have a differential influence over time, and did not mediate the other effects. There was significant between-individual (level 2) variability in drug use. Results are discussed in light of adolescent perceptions of parent-child relationships.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlaf EM, Paglia A, Ivis FJ, Ialomiteanu A (2000) Nonmedical drug use among adolescent students: Highlights from the 1999 Ontario Drug Use Survey. Can Med Assoc J 162(12):1677–1680
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator-mediator distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182
Baumrind D (1991) The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. J Ear Adolesc 11(1):56–95
Boyle MH, Offord DR, Racine YA, Szatmari P (1992) Predicting substance use in late adolescence: Results from the Ontario Child Health Study Follow-up. Am J Psychiatry 149(6):761–767
Boyle MH, Offord DR, Racine YA, Fleming JE, Szatmari P, Sanford MN (1993) Evaluation of the revised Ontario Child Health Study Scales. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 34:189–213
Buysse WH (1997) Behaviour problems and relationships with family and peers during adolescence. J Adolesc 20:645–659
Chassin L, Hussong A, Barrera M, Molina BSG, Trim R, Ritter J (2004) Adolescent substance use. In: Lerner RM, Steinberg L (eds) Handbook of adolescent psychology, second edition. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, pp 665–696
Dekovic M, Wissink IB, Meijer AM (2004) The role of family and peer relations in adolescent antisocial behaviour: Comparison of four ethnic groups. J Adolesc. Special Issue: Families, Peers and Contexts as Multiple Determinants of Adolescent Problem Behavior 27(5):497–514
Dishion TJ, Nelson SE, Bullock BM (2004) Premature adolescent autonomy: Parent disengagement and deviant peer process in the amplification of problem behaviour. J Adolesc. Special Issue: Families, Peers and Contexts as Multiple Determinants of Adolescent Problem Behavior 27(5):515–530
Dishion TJ, Patterson GR, Griesler PC (1994) Peer adaptations in the development of antisocial behavior: A confluence model. In: Huesmann LR (ed) Aggressive behavior: Current perspectives. Plenum Press, New York, pp 61–95
Dishion TJ, Owen LD (2002) A longitudinal analysis of friendships and substance use: Bidirectional influence from adolescence to adulthood. Dev Psychol 38(4):480–491
Ellickson PL, Martino SC, Collins RL (2004) Marijuana use from adolescence to young adulthood: Multiple developmental trajectories and their associated outcomes. Health Psychol 23(3):299–307
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (1999) Prospective childhood predictors of deviant peer affiliations in adolescence. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 40(4):581–592
Fiske DW, Campbell DT (1992) Citations do not solve problems. Psychol Bull 112(3):393–395
Fletcher AC, Steinberg L, Williams-Wheeler M (2004) Parental influences on adolescent problem behavior: Revisiting Stattin and Kerr. Child Dev 75(3):781–796
Fuligni AJ, Eccles JS (1993) Perceived parent-child relationships and early adolescents' orientation toward peers. Dev Psychol 29(4):622–632
Galambos NL, Leadbeater BJ (2000) Trends in adolescent research for the new millennium. Int J Behav Dev 24(3):289–294
Ge X, Best KM, Conger RD, Simons RL (1996) Parenting behaviours and the occurrence and co-occurrence of adolescent depressive symptoms and conduct problems. Dev Psychol 32(4):717–731
Gray MR, Steinberg L (1999) Unpacking authoritative parenting: Reassessing a multidimensional construct. J Marriage Fam 61(3):574–587
Greenberg MT, Siegel JM, Leitch CJ (1983) The nature and importance of attachment relationships to parents and peers during adolescence. J Youth Adolesc 12:373–386
Grotevant HD (1998) Adolescent development in family contexts. In: Damon W (Series ed) and Eisenberg N (Vol. ed) Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. Social, emotional, and personality development. 5th ed. Wiley, New York, pp 1097–1149
Harris JR (1995) Where is the child's environment? A group socialization theory of development. Psychol Rev 102(3):458–489
Ivis FJ, Adlaf EM (1999) A comparison of trends in drug use among students in the USA and Ontario, Canada: 1975–1997. Drugs: Educ Prev Policy 6(1):17–27
Johnston L, O’Malley P, Bachman J (2002). Monitoring the future: National survey results on drug use, 1975-1999 (NIH Publication No. 00-4802). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Kandel DB, Davies M (1996) High school students who use crack and other drugs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53(1):71–80
Kim JE, Hetherington EM, Reiss D (1999) Associations among family relationships, antisocial peers, and adolescents' externalizing behaviours: Gender and family type differences. Child Dev 70(5): 1209–1230
Kim KJ, Conger RD, Lorenz FO, Elder GH (2001) Parent-adolescent reciprocity in negative affect and its relation to early adult social development. Dev Psychol 37(6):775–790
King SM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2004) Childhood externalizing and internalizing psychopathology in the prediction of early substance use. Addiction 99(12):1548–1559
Krull JL, MacKinnon DP (2001) Multilevel modeling of individual and group level mediated effects. Multivariate Behav Res. Special Issue: Multilevel Models 36(2):249–277
Lacourse E, Nagin D, Tremblay RE, Vitaro F, Claes M (2003) Developmental trajectories of boys' delinquent group membership and facilitation of violent behaviors during adolescence. Dev Psychopathol 15(1):183–197
Lamborn SD, Mounts NS, Steinberg L, Dornbusch SM (1991) Patterns of competence and adjustment among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent and neglectful families. Child Dev 62:1049–1065
Laursen B, Coy KC, Collins WA (1998) Reconsidering changes in parent-child conflict across adolescence: A meta-analysis. Child Dev 69(3):817–832
Lempers JD, Clark-Lempers D, Simons RL (1989) Economic hardship, parenting, and distress in adolescence. Child Dev 60(1):25–39
Lieberman M, Doyle A, Markiewicz D (1999) Developmental patterns in security of attachment to mother and father in late childhood and early adolescence: Associations with peer relations. Child Development 70(1):202–213
MacKinnon DP, Dwyer JH (1993). Estimating mediated effects in prevention studies. Eval Rev 17(2):144–158
Marshal MP, Molina BSG, Pelham WEJ (2003) Childhood ADHD and adolescent substance use: An examination of deviant peer group affiliation as a risk factor. Psychol Addict Behav 17(4):293–302
Mason WA, Windle M (2002) Reciprocal relations between adolescent substance use and delinquency: A longitudinal latent variable analysis. J Abnorm Psychol 111(1):63–76
Molina BSG, Pelham WEJ (2003) Childhood predictors of adolescent substance use in a longitudinal study of children with ADHD. J Abnorm Psychol 112(3):497–507
Paley B, Conger RD, Harold GT (2000) Parents' affect, adolescent cognitive representations, and adolescent social development. J Marriage Fam 62:761–776
Patterson GR, Reid JB, Dishion TJ (1992) Antisocial boys. Castalia, Eugene, OR
Rasbash J, Steele F, Browne W, Prosser B (2004) A user's guide to MLwiN version 2.0. University of London, Institute of Education, London
Rubin DB (1987) Multiple imputation for nonresponse in surveys. Wiley, New York
Rubin KH, Bukowski W, Parker JG (1998) Peer interactions, relationships and groups. In: Damon W (Series Ed.) and Eisenberg N (vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. Social, emotional, and personality development, 5th ed. Wiley, New York, pp 619–700
Schafer JL (1997) Analysis of incomplete multivariate data. Chapman and Hall, New York
Silberg J, Rutter M, D'Onofrio B, Eaves L (2003) Genetic and environmental risk factors in adolescent substance use. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 44(5):664–676
Singer JD, Willett JB (2003) Applied longitudinal data analysis: Modeling change and event occurrence. Oxford University Press, New York
Smetana JG (1996) Adolescent-parent conflict: Implications for adaptive and maladaptive development. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL (eds) Rochester symposium on developmental psychopathology: Vol. 7. Adolescence: Opportunities and challenges. University of Rochester, New York, pp 1–46.
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, Van Der Linde A (2002) Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J Royal Stat Soc Series B 64:583–640
Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada (1995) National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth: Overview of survey instruments for 1994–95 data collection—cycle 1. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada, Catalogue no. 89F0078XIE
Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada (1997) National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth: Overview of survey instruments for 1996-97 data collection—cycle 2. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada, Catalogue no. 89F0078XIE, no. 2
Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada (1999) National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth: Overview of survey instruments for 1998-99 data collection - cycle 3. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Statistics Canada and Human Resources Development Canada, Catalogue no. 89FOO78XPE, no. 3
Statistics Canada (2001) Microdata user guide: National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth, cycle 4, September 2000 to May 2001. Statistics Canada: Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Tremblay RE, Vitaro F, Bertrand L, LeBlanc M, Beauchesne H, Boileau H, David L (1992) Parent and child training to prevent early onset of delinquency: The Montreal longitudinal-experimental study. In: McCord J, Tremblay RE (eds) Preventing antisocial behavior: Interventions from birth through adolescence. Guilford, New York, pp 117–138
Vitaro F, Brendgen M, Tremblay RE (2000) Influence of deviant friends on delinquency: Searching for moderator variables. J Abnorm Child Psychol 28(4):313–325
Vitaro F, Brendgen M, Ladouceur R, Tremblay RE (2001) Gambling, delinquency, and drug use during adolescence: Mutual influences and common risk factors. J Gambling Stud 17(3):171–190
Vitaro F, Ferland F, Jacques C, Ladouceur R (1998) Gambling, substance use, and impulsivity during adolescence. Psychol Addict Behav 12(3):185–194
Walker-Barnes CJ, Mason CA (2004) Delinquency and substance use among gang-involved youth: The moderating role of parenting practices. Am J Community Psychol 34(3–4):235–250
Warr M (1993) Age, peers and delinquency. Criminology 31: 17–40
Weinberg NZ, Rahdert E, Colliver JD, Glantz MD (1998). Adolescent substance abuse: A review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37(3):252–261
Wills TA, McNamara G, Vaccaro D, Hirky AE (1996) Escalated substance use: A longitudinal grouping analysis from early to middle adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol 105(2):166–180
Wills TA, Resko JA, Ainette MG, Mendoza D (2004) Role of parent support and peer support in adolescent substance use: A test of mediated effects. Psychol Addict Behav 18(2):122–134
Wills TA, Sandy JM, Shinar O, Yaeger A (1999) Contributions of positive and negative affect to adolescent substance use: Test of a bidimensional model in a longitudinal study. Psychol Addict Behav 13(4):327–338
Wills TA, Sandy JM, Yaeger A, Cleary SD, Shinar O (2001) Coping dimensions, life stress, and adolescent substance use: A latent growth analysis. J Abnorm Psychol 110(2):309–323
Wortley NS (1996) Social networks, social support and substance abuse: Testing social ability and disability theories of deviance. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Toronto, Ontario
Wu NS, Lu Y, Sterling S, Weisner C (2004) Family environment factors and substance abuse severity in an HMO adolescent treatment population. Clin Pediatr 43(4):323–333
Zapert K, Snow DL, Tebes K (2002) Patterns of substance use in early through late adolescence. American J Community Psychol 30(6):835–852
Zoccolillo M, Vitaro F, Tremblay RE (1999) Problem drug and alcohol use in a community sample of adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38(7):900–907
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jon Rasbash for statistical guidance and Statistics Canada for access to the NLSCY data through the Research Data Centre at the University of Toronto. While the research and analyses are based on data from Statistics Canada, the opinions expressed do not represent the views of Statistics Canada. To access the microdata housed in the Research Data Centre, researchers must submit a project proposal to an adjudicating committee operating under the auspices of the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) and Statistics Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research Interests: social and emotional development; family processes; adolescent problem behaviours; main area of work is about understanding risk and protective factors in typical and atypical adolescent development Department of Human Development and Applied Psychology, University of Toronto, 252 Bloor Street West, Toronto, Ontario, M5S 1V6, Canada
Research Interests: social and emotional development; family interaction; child psychopathology; main area of work is about understanding emotion processes in children and in family life that help us to understand psychopathology in childrenDepartment of Human Development and Applied Psychology, University of Toronto, 252 Bloor Street West, Toronto, Ontario, M5S 1V6, Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pires, P., Jenkins, J.M. A Growth Curve Analysis of the Joint Influences of Parenting Affect, Child Characteristics and Deviant Peers on Adolescent Illicit Drug Use. J Youth Adolescence 36, 169–183 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9127-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9127-5