Abstract
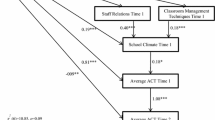
In recent discussions regarding concerns about the academic achievement of US students, educational policy makers have suggested the implementation of certain teacher policies. To address the limited empirical research on the putative educational impact of such policies, this study used multilevel structural equation models to investigate the longitudinal associations between teacher evaluation and reward policies, and student mathematics achievement and dropout with a national sample of students (n = 7,779) attending one of 431 public high schools. The student sample included an equal number of boys and girls averaging 16 years of age, and included a White (53%) majority. This study examined whether associations between teacher policies and student achievement were mediated by the teacher–student relationship climate. Results of this study were threefold. First, teacher evaluation policies that allowed students to evaluate their teachers were associated with more positive student reports of the classroom teaching climate. Second, schools with teacher reward policies that included assigning higher performing teachers with higher performing students had a negative association with student perceptions of the teaching climate. Lastly, schools with better student perceptions of the teaching climate were associated with lower student dropout rates by students’ senior year. These findings are discussed in light of their educational policy implications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliance for Excellent Education. (2007). The high cost of high school dropouts: What the nation pays for inadequate high schools. Unpublished manuscript Washington, DC.
Baldi, S., Jin, Y., Skemer, M., Green, P. J., Herget, D. (2007). Highlights from PISA 2006: Performance of US 15-year-old students in science and mathematics literacy in an international context. National Center for education Statistics Institute of Education Sciences, US Department of Education.
Ballou, D., & Podgursky, M. (1993). Teachers’ attitudes toward merit pay: Examining conventional wisdom. Industrial and Labor Relations Review, 47, 50–61.
Burns, L.J., Heuer, R., Ingels, S.J., Pollack, J.M., Pratt, D.J., Rock, D., Rogers, J., Scott, L.A., Siegel, P., Stutts, E. (2003). ELS: 2002 Base Year Field Test Report (NCES 2003-03). US Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics.
Colby, S. A., Bradshaw, L. K., Joyner, R. L. (2002). Perceptions of teacher evaluation systems and their impact on school improvement, professional development and student learning. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association.
Cook-Sather, A. (2007). What would happen if we treated students as those with opinions that matter? The benefits to principals and teachers of supporting youth engagement in school. NASSP Bulletin, 91, 343–362.
Davis-Kean, P. E. (2005). The influence of parent education and family income on child achievement: The indirect role of parental expectations and the home environment. Journal of Family Psychology, 19, 294-304.
Figlio, D. N., & Kenny, L. W. (2007). Individual teacher incentives and student performance. Journal of Public Economics, 91, 901–914.
Hart, B., & Risley, R. T. (1995). Meaningful differences in the everyday experience of young American children. Baltimore: Paul H. Brooks.
Heck, R. H., & Thomas, S. L. (2009). An introduction to multilevel modeling techniques (2nd ed.). New York: Routledge.
Hoffer, T. (1995). High school curriculum differentiation and postsecondary outcomes. Transforming schools, 98, 371–402.
Hoffer, T. (1997). High school graduate requirements: Effects on dropping out and student achievement. The Teachers College Record, 98, 584–607.
Ingels, S.J., Pratt, D.J., Rogers, J.E., Siegel, P.H., Stutts, E.S. (2005). Education Longitudinal Study of 2002: Base-Year to First Follow-up Data File Documentation (NCES 2006-344). US Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics.
Jacob, B. A., & Lefgren, L. (2008). Can principals identify effective teachers? Evidence on subjective performance evaluation in education. Journal of Labor Economics, 26, 101–136.
Lee, V. E. (2000). School size and the organization of secondary schools. In M. T. Hallinan (Ed.), Handbook of the sociology of education (pp. 327–344). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers.
Lee, V. E., & Burkam, D. T. (2003). Dropping out of high school: The role of school organization and structure. American Educational Research Journal, 2, 353–393.
Ma, X., & Klinger, D. A. (2000). Hierarchical linear modelling of student and school effects on academic achievement. Canadian Journal of Education, 25(1), 41–55.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7, 83–103.
Malen, B. (1999). On rewards, punishments, and possibilities: Teacher compensation as an instrument for education reform. Journal of Personnel Evaluation in Education, 12, 387–394.
Mallinckrodt, B., Abraham, W., Wei, M., & Russell, D. (2006). Advances in testing the statistical significance of mediation effects. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 53(3), 372–378.
Manefield, J., Collins, R., Moore, J., Mahar, S., Warne, C. (2007). Student voice: A historical perspective and new directions. Research and Innovation Division, Office of Learning and Teaching, Department of Education.
Medley, D. M., & Coker, H. (1987). The accuracy of principals’ judgments of teacher performance. Journal of Educational Research, 80, 242–247.
Muller, C., Katz, S., & Dance, L. J. (1999). Investing in teaching and learning: Dynamics of teacher–student relationship from each actor’s perspective. Urban Education, 34, 292–337.
Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (1998–2007). Mplus User’s Guide (5th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthen and Muthen.
National Center for Education Statistics, I. o. E. S., US Department of Education. (2010). Education Longitudinal Study of 2002 (ELS:2002) from http://nces.ed.gov/surveys/ELS2002/.
Noakes, L. A. (2009). Adapting the utilization-focused approach for teacher evaluation. Journal of MultiDisciplinary Evaluation, 6, 83–88.
Obama, B. (2009). Remarks by the president to the Hispanic Chamber of Commerce on a complete and competitive American Education [Website]. The White House. Retrieved 21 April 2010, from the World Wide Web: http://www.whitehouse.gov/the_press_office/Remarks-of-the-President-to-the-United-States-Hispanic-Chamber-of-Commerce/.
O’Connor, E., & McCartney, K. (2007). Examining teacher–child relationships and achievement as part of an ecological model of development. American Educational Research Journal, 44, 340–369.
Planty, M., Hussar, W., Snyder, T., Kena, G., KewalRamani, A., Kemp, J., et al. (2009). The Condition of Education 2009. National Center for Education Statistics, Institue of Education Sciences, US Department of Education.
Podgursky, M. J., & Springer, M. G. (2007). Teacher performance pay: A review. Policy Retrospectives, 26, 909–949.
Rumberger, R. W. (1987). High school dropouts: A review of issues and evidence. Review of Educational Research, 57, 101–121.
Sampson, R. J., Sharkey, P., & Raudenbush, S. W. (2008). Durable effects of concentrated disadvantage on verbal ability among African-American children. Proceedings of National Academic Science U S A, 105(3), 845–852.
Toch, T., & Rothman, R. (2008). Rush to judgement: Teacher evaluation in public education. Washington, DC: Education Sector.
Vieno, A., Perkins, D. D., Smith, T. M., & Santinello, M. (2005). Democratic school climate and sense of community in school: A multilevel analysis. American Journal of Community Psychology, 36, 327–341.
Weiss, C. C., Carolan, B. V., & Baker-Smith, E. C. (2010). Big school, small school: (Re) testing assumptions about high school size, school engagement and mathematics achievement. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 163–176.
Wigfield, A., Eccles, J. S., Schiefele, U., Roeser, R., & Davis-Kean, P. (2006). Development of achievement motivation. In W. Damon & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (pp. 933–1002). NewYork: Wiley.
Wright, S. P., Horn, S. P., & Sanders, W. L. (1997). Teacher and classroom context effects on student acheivement: Implecations for teacher evaluation. Journal of Personnel Evaluation in Education, 1, 57–67.
Acknowledgments
This article is a modified version of a paper presented at the Third Annual Sloboda-Bukoski Society for Prevention Research Cup Competition as part of Society for Prevention Research 17th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barile, J.P., Donohue, D.K., Anthony, E.R. et al. Teacher–Student Relationship Climate and School Outcomes: Implications for Educational Policy Initiatives. J Youth Adolescence 41, 256–267 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-011-9652-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-011-9652-8