Abstract
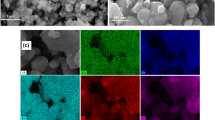
A series of BaDyxFe12−xO19 ferrite microfibres have been synthesized from metal nitrates and citric acid by the sol–gel method. TG-DSC, XRD, FTIR, FESEM, TEM and VSM were employed to characterize the thermal decomposition process, crystallite sizes, structure and magnetic properties of ferrite microfibres. The effect of calcined temperature, holding time, ion substitution on structure, magnetic properties of barium ferrite microfibres was investigated. The nanoparticle growth mechanism of ferrite microfibres was discussed. The results indicated that the hexaferrite phase was formed at 750 °C and Dy3+ ions entered the magnetoplumbite lattice. However, the reflections shift to a lower angle and the characteristic peaks of ferrite microfibres in FTIR shift to the lower wavenumber with the Dy content increasing. The VSM results shown that saturation magnetization (M s ) gradually increased with calcined temperature increasing and holding time prolonging, while coercive force (H c ) revealed an increase at first and then decreases. With the Dy content increasing, the M s achieved values of M s = 50 emu g−1 (297 K) and 70 emu g−1 (77 K) and the H c value shown a continuous reduction from 515 kA m−1 (297 K) and 435 kA m−1 (77 K) (x = 0.0) to 242 and 215 kA m−1 (x = 0.4).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allwood DA, Xiong G, Cooke MD et al (2002) Submicrometer ferromagnetic not gate and shift register. Science 296:2003–2006
Redl FX, Cho KS, Murray CB et al (2003) Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots. Nature 423:968–971
Liu XG, Fu L, Hong SH et al (2002) Arrays of magnetic nanoparticles patterned via “Dip-Pen” nanolithography. Adv Mater 14:231–234
Doyle PS, Bibette J, Bancaud A et al (2002) Self-assembled magnetic matrices for DNA separation chips. Science 295:2237
Morales AM, Lieber CM (1998) A laser ablation method for the synthesis of crystalline semiconductor nanowires. Science 279:208–211
Han W, Fan S, Li Q (1997) Synthesis of gallium nitride nanorods through a carbon nanotube-confined reaction. Science 277:1287–1289
Pan ZW, Dai ZR, Wang EL (2001) Nanobelts of semiconducting oxides. Science 291:1947–1949
Shen XQ, Liu MQ, Song FZ et al (2010) Structural evolution and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 nanofibers by electrospinning. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 53:448–453
Song FZ, Shen XQ, Liu MQ et al (2012) Microstructure, magnetic properties and exchange–coupling interactions for one-dimensional hard/soft ferrite nanofibers. J Solid State Chem 185:31–36
Li D, McCann JT, Xia YN et al (2006) Electrospinning: a simple and versatile technique for producing ceramic nanofibers and nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 89(6):1861–1869
Song FZ, Shen XQ, Xiang J (2010) Formation and magnetic properties of M-Sr ferrite hollow fibers via organic gel-precursor transformation process. Mater Chem Phys 120:213–216
Shen XQ, Liu MQ, Song FZ et al (2011) Characterization and magnetic properties of electrospun Co1−x Zn x Fe2O4 nanofibers. Applied Physics A Mater Sci Proc 104:109–116
Song J, Wang LX, Xu NC et al (2010) Microwave electromagnetic and absorbing properties of Dy3+ doped MnZn ferrites. J Rare Earth 28:451–456
Verma V, Kotnala RK, Pandey V et al (2008) The effect on dielectric losses in lithium ferrite by cerium substitution. J Alloy Compd 466:404–407
El-Sayed MM (2007) Rare-earth substitution effect on the quality of Mg-Ti ferrite. Ceram Int 33:413–418
Ravinder D, Ravi Kumar B (2003) Electrical conductivity of cerium substituted Mn–Zn ferrites. Mater Lett 57:1738–1742
Wang J, Zhang H, Bai SX et al (2007) Microwave absorbing properties of rare-earth elements substituted W-type barium ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 312:310–313
Xu HT, Yang H, Xu W et al (2008) Magnetic properties of Ce, Gd-substituted yttrium iron garnet ferrite powders fabricated using a sol–gel method. J Mater Prof Tech 197:296–300
Zhao WY, Wei P, Cheng HB et al (2007) FTIR spectra, lattice shrinkage, and magnetic properties of CoTi-substituted M-Type barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J Am Ceram Soc 90:2013–2095
Stoner EC, Wohlfarth EP (1991) A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. IEEE Trans Magn 27:599–642
Sürig C, Hempel KA, Bonnenberg D (1993) Formation and microwave absorption of barium and strontium ferrite prepared by sol-gel technique. Appl Phys Lett 63:2836–2838
Song FZ, Shen XQ, Xiang J et al (2010) Characterization and magnetic properties of BaxSr1-xFe12O19 (x = 0–1) ferrite hollow fibers via gel-precursor transformation process. J Alloy Compd 50:297–301
Fang HC, Ong CK, Zhang XY et al (1999) Low temperature characterization of nano-sized BaFe12-2xZnxSnxO19 particle. J Magn Magn Mater 191:277–281
Hochepied JF, Pilent MP (2000) Magnetic properties of mixed cobalt–zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 87:2472–2479
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51202091) and Research Fund of Key Laboratory for Advanced Technology in Environmental Protection of Jiangsu Province (AE201103) and A project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Ji, Y. Effect of chemical composition and heat treatment condition on microstructure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline BaDyxFe12−xO19 (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) microfibres. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 67, 18–28 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3046-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3046-1