Abstract
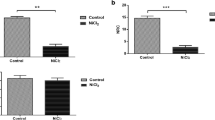
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have been widely used in medicine such as imaging, drug delivery and therapeutics due to their multifunctional properties. Alterations in neuronal function may contribute to various neurological diseases. Transferrin plays a primary role in iron transportation and delivery and has recently been utilized for drug delivery to the brain. We have investigated effects of transferrin-conjugated GNPs (Tf-GNPs) on anxiety and locomotor behavior in vivo and also hippocampal neuronal activity ex vivo. Electrophysiological effects of Tf-GNP on hippocampal neurons were determined by patch clamp method. Fifteen male young adult C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into three groups as control (200 µL PBS), GNP (bare GNP; 2.2 μg/g in PBS) and Tf-GNPs (2.2 μg/g Tf-GNP). Animals intraperitoneally received the respective treatments for seven consecutive days and were subjected to elevated plus maze (EPM) and open field tests (OFT). Ex vivo, firing frequency of the neurons significantly increased by GNP treatment (p < 0.001). In vivo, animals in Tf-GNP group showed significantly longer distance in open arms but significantly lower number of entries to the open arms in EPM (p < 0.05). Mice received bare GNPs had significantly higher locomotor activity in OFT (p < 0.05), while Tf-GNP did not alter the locomotor activity significantly (p = 0.051). Animals in Tf-GNP group spent significantly longer time in the peripheral zone in OFT (p < 0.05). The present findings have shown that Tf-GNP induces anxiety-like behavior without altering spontaneous firing rate of hippocampal neurons. We suggest that neurobiological effects of Tf-GNP should be pre-determined before using in medical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Singh P, Pandit S, Mokkapati V, Garg A, Ravikumar V, Mijakovic I (2018) Gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and therapeutics for human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071979
Wang S and Lu G (2018) Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer imaging and treatment. In: Seehra MS, Bristow AD (eds) Noble and precious metals—properties, nanoscale effects and applications. pp 291–309
Siddique S, Chow JCL (2020) Application of nanomaterials in biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanomaterials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091700
Emami T, Madani R, Golchinfar F, Shoushtary A, Amini SM (2015) Comparison of gold nanoparticle conjugated secondary antibody with non-gold secondary antibody in an ELISA kit model. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 34:366–370. https://doi.org/10.1089/mab.2015.0021
Davatgaran Taghipour Y, Kharrazi S, Amini SM (2018) Antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles for detection of small amounts of antigen based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectra. Nanomed Res J 3:102–108
Fatemi F, Amini SM, Kharrazi S, Rasaee MJ, Mazlomi MA, Asadi-Ghalehni M, Rajabibazl M, Sadroddiny E (2017) Construction of genetically engineered M13K07 helper phage for simultaneous phage display of gold binding peptide 1 and nuclear matrix protein 22 ScFv antibody. Colloids Surf B 159:770–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.08.034
Rezaeian A, Amini SM, Najafabadi MRH, Farsangi ZJ, Samadian H (2022) Plasmonic hyperthermia or radiofrequency electric field hyperthermia of cancerous cells through green-synthesized curcumin-coated gold nanoparticles. Lasers Med Sci 37:1333–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-021-03399-7
Amini SM, Kharrazi S, Rezayat SM, Gilani K (2018) Radiofrequency electric field hyperthermia with gold nanostructures: role of particle shape and surface chemistry. Artif Cell Nanomedi Biotechnol 46:1452–1462
Vines JB, Yoon J-H, Ryu N-E, Lim D-J, Park H (2019) Gold nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy. Front Chem 7:167
Chen Y, Yang J, Fu S, Wu J (2020) Gold nanoparticles as radiosensitizers in cancer radiotherapy. Int J Nanomed 15:9407–9430. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S272902
Haume K, Rosa S, Grellet S, Śmiałek MA, Butterworth KT, Solov’yov AV, Prise KM, Golding J, Mason NJ (2016) Gold nanoparticles for cancer radiotherapy: a review. Cancer Nanotechnol 7:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12645-016-0021-x
Cheng Y, A CS, Meyers JD, Panagopoulos I, Fei B and Burda C, (2008) Highly efficient drug delivery with gold nanoparticle vectors for in vivo photodynamic therapy of cancer. J Am Chem Soc 130:10643–10647. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja801631c
Tao Y, Li M, Ren J, Qu X (2015) Metal nanoclusters: novel probes for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:8636–8663. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00607d
Stafstrom CE, Carmant L (2015) Seizures and epilepsy: an overview for neuroscientists. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022426
Wada A (2006) Roles of voltage-dependent sodium channels in neuronal development, pain, and neurodegeneration. J Pharmacol Sci 102:253–268. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.crj06012x
Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D (2013) Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet 4:76. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2013.00076
Yilmaz B, Gilmore D, Wilson C (1996) Inhibition of the pre-ovulatory LH surge in the rat by central noradrenergic mediation: involvement of an anaesthetic (urethane) and opioid receptor agonists. Biog Amin 12:423–435
Kutlu S, Yilmaz B, Canpolat S, Sandal S, Ozcan M, Kumru S, Kelestimur H (2004) Mu opioid modulation of oxytocin secretion in late pregnant and parturient rats. Involv Noradrenergic Neurotransm Neuroendocrinol 79:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1159/000078101
Ozcan M, Yilmaz B, King WM, Carpenter DO (2004) Hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) is reduced by a coplanar PCB congener. Neurotoxicology 25:981–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2004.03.014
Taskin IC, Sen O, Emanet M, Culha M, Yilmaz B (2020) Hexagonal boron nitrides reduce the oxidative stress on cells. Nanotechnology 31:215101. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab6fdc
Paviolo C, Stoddart PR (2017) Gold nanoparticles for modulating neuronal behavior. Nanomaterials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040092
Upadhyay RK (2014) Drug delivery systems, CNS protection, and the blood brain barrier. Biomed Res Int 2014:869269. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/869269
Jones AR, Shusta EV (2007) Blood-brain barrier transport of therapeutics via receptor-mediation. Pharm Res 24:1759–1771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9379-0
Kutlu S, Aydin M, Alcin E, Ozcan M, Bakos J, Jezova D, Yilmaz B (2010) Leptin modulates noradrenaline release in the paraventricular nucleus and plasma oxytocin levels in female rats: a microdialysis study. Brain Res 1317:87–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.044
Kawabata H (2019) Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic Biol Med 133:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.037
Pulgar VM (2018) Transcytosis to cross the blood brain barrier. New Adv Chall Front Neurosci 12:1019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.01019
Funabashi T, Suyama K, Uemura T, Hirose M, Hirahara F, Kimura F (2001) Immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons (GT1-7 cells) exhibit synchronous bursts of action potentials. Neuroendocrinology 73:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1159/000054632
Strober W (2001) Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol Appendix. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142735.ima03bs21
Aklan I, Sayar Atasoy N, Yavuz Y, Ates T, Coban I, Koksalar F, Filiz G, Topcu IC, Oncul M, Dilsiz P, Cebecioglu U, Alp MI, Yilmaz B, Davis DR, Hajdukiewicz K, Saito K, Konopka W, Cui H, Atasoy D (2020) NTS catecholamine neurons mediate hypoglycemic hunger via medial hypothalamic feeding pathways. Cell Metab 31:313-326.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.016
Lezak KR, Missig G, Carlezon WA Jr (2017) Behavioral methods to study anxiety in rodents. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 19:181–191. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2017.19.2/wcarlezon
Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC (2015) Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/52434
Amini SM, Kharrazi S, Hadizadeh M, Fateh M, Saber R (2013) Effect of gold nanoparticles on photodynamic efficiency of 5-aminolevolenic acid photosensitiser in epidermal carcinoma cell line: an in vitro study. IET Nanobiotechnol 7:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2013.0021
Badirzadeh A, Alipour M, Najm M, Vosoogh A, Vosoogh M, Samadian H, Hashemi AS, Farsangi ZJ, Amini SM (2022) Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin coated silver nanoparticle in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major in-vitro and in a murine model. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 74:103576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103576
Repar N, Li H, Aguilar JS, Li QQ, Drobne D, Hong Y (2018) Silver nanoparticles induce neurotoxicity in a human embryonic stem cell-derived neuron and astrocyte network. Nanotoxicology 12:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2018.1425497
Engin AB, Engin A (2019) Nanoparticles and neurotoxicity: dual response of glutamatergic receptors. Prog Brain Res 245:281–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2019.03.005
Yousef MI, Abuzreda AA, Kamel MA (2019) Neurotoxicity and inflammation induced by individual and combined exposure to iron oxide nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. J Taibah Univ Sci 13:570–578. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2019.1602351
Shukla R, Bansal V, Chaudhary M, Basu A, Bhonde RR, Sastry M (2005) Biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles and their endocytotic fate inside the cellular compartment: a microscopic overview. Langmuir 21:10644–10654. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0513712
Adewale OB, Davids H, Cairncross L, Roux S (2019) Toxicological behavior of gold nanoparticles on various models: influence of physicochemical properties and other factors. Int J Toxicol 38:357–384. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581819863130
Flora SJS (2017) Chapter 8—the applications, neurotoxicity, and related mechanism of gold nanoparticles. In: Jiang X, Gao H (eds) Neurotoxicity of nanomaterials and nanomedicine. Academic Press, pp 179–203
Velasco-Aguirre C, Morales F, Gallardo-Toledo E, Guerrero S, Giralt E, Araya E, Kogan MJ (2015) Peptides and proteins used to enhance gold nanoparticle delivery to the brain: preclinical approaches. Int J Nanomed 10:4919–4936. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s82310
Dante S, Petrelli A, Petrini EM, Marotta R, Maccione A, Alabastri A, Quarta A, De Donato F, Ravasenga T, Sathya A, Cingolani R, Proietti Zaccaria R, Berdondini L, Barberis A, Pellegrino T (2017) Selective targeting of neurons with inorganic nanoparticles: revealing the crucial role of nanoparticle surface charge. ACS Nano 11:6630–6640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b00397
Salinas K, Kereselidze Z, DeLuna F, Peralta XG, Santamaria F (2014) Transient extracellular application of gold nanostars increases hippocampal neuronal activity. J Nanobiotechnology 12:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-014-0031-y
Tuna BG, Yavuz Y, Kuku G, Maharramov A, Yilmaz B, Saricam M, Ercan M, Culha M, Dogan S (2019) The effect of modified gold nanoparticles on the function of neurons of mice hippocampal brain slices. Mersin Univ Saglık Bilim Derg 12:328–340
Tuna BG, Yesilay G, Yavuz Y, Yilmaz B, Culha M, Maharramov A, Dogan S (2020) Electrophysiological effects of polyethylene glycol modified gold nanoparticles on mouse hippocampal neurons. Heliyon 6:e05824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05824
Soe ZC, Kwon JB, Thapa RK, Ou W, Nguyen HT, Gautam M, Oh KT, Choi HG, Ku SK, Yong CS, Kim JO (2019) Transferrin-conjugated polymeric nanoparticle for receptor-mediated delivery of doxorubicin in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020063
Lopes Rodrigues R, Xie F, Porter AE, Ryan MP (2020) Geometry-induced protein reorientation on the spikes of plasmonic gold nanostars. Nanoscale Adv 2:1144–1151. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9na00584f
Li JL, Wang L, Liu XY, Zhang ZP, Guo HC, Liu WM, Tang SH (2009) In vitro cancer cell imaging and therapy using transferrin-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Cancer Lett 274:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.024
De Jong WH, Hagens WI, Krystek P, Burger MC, Sips AJ, Geertsma RE (2008) Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 29:1912–1919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.12.037
Semmler-Behnke M, Kreyling WG, Lipka J, Fertsch S, Wenk A, Takenaka S, Schmid G, Brandau W (2008) Biodistribution of 1.4- and 18-nm gold particles in rats. Small 4:2108–2111. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200800922
Sonavane G, Tomoda K, Makino K (2008) Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration: effect of particle size. Colloids Surf B 66:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.07.004
Lasagna-Reeves C, Gonzalez-Romero D, Barria MA, Olmedo I, Clos A, Sadagopa Ramanujam VM, Urayama A, Vergara L, Kogan MJ, Soto C (2010) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of gold nanoparticles after repeated administration in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:649–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.046
Hirn S, Semmler-Behnke M, Schleh C, Wenk A, Lipka J, Schäffler M, Takenaka S, Möller W, Schmid G, Simon U, Kreyling WG (2011) Particle size-dependent and surface charge-dependent biodistribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 77:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.12.029
Takeuchi I, Onaka H, Makino K (2018) Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous injection: effects of PEGylation at the same particle size. Biomed Mater Eng 29:205–215. https://doi.org/10.3233/bme-171723
Terentyuk GS, Maslyakova GN, Suleymanova LV, Khlebtsov BN, Kogan BY, Akchurin GG, Shantrocha AV, Maksimova IL, Khlebtsov NG, Tuchin VV (2009) Circulation and distribution of gold nanoparticles and induced alterations of tissue morphology at intravenous particle delivery. J Biophotonics 2:292–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.200910005
Pan Y, Leifert A, Ruau D, Neuss S, Bornemann J, Schmid G, Brandau W, Simon U, Jahnen-Dechent W (2009) Gold nanoparticles of diameter 1.4 nm trigger necrosis by oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Small 5:2067–2076. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200900466
Simpson CA, Salleng KJ, Cliffel DE, Feldheim DL (2013) In vivo toxicity, biodistribution, and clearance of glutathione-coated gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 9:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2012.06.002
Papastefanaki F, Jakovcevski I, Poulia N, Djogo N, Schulz F, Martinovic T, Ciric D, Loers G, Vossmeyer T, Weller H, Schachner M, Matsas R (2015) Intraspinal delivery of polyethylene glycol-coated gold nanoparticles promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Mol Ther 23:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2015.50
Lin YL, Jen JC, Hsu SH, Chiu IM (2008) Sciatic nerve repair by microgrooved nerve conduits made of chitosan-gold nanocomposites. Surg Neurol 70(S1):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2008.01.057
Jung S, Bang M, Kim BS, Lee S, Kotov NA, Kim B, Jeon D (2014) Intracellular gold nanoparticles increase neuronal excitability and aggravate seizure activity in the mouse brain. PLoS ONE 9:e91360. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091360
Xie Y, Wang Y, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2012) Effects of nanoparticle zinc oxide on spatial cognition and synaptic plasticity in mice with depressive-like behaviors. J Biomed Sci 19:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-19-14
Torabi M, Kesmati M, Harooni HE, Varzi HN (2013) Effects of nano and conventional zinc oxide on anxiety-like behavior in male rats. Indian J Pharmacol 45:508–512. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.117784
Kesmati M, Torabi M, Teymuri Zamaneh H, Malekshahi Nia H (2014) Interaction between anxiolytic effects of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and exercise in adult male rat. Nanomed J 1:324–330. https://doi.org/10.7508/nmj.2015.05.006
Li X, Liu X, Li T, Li X, Feng D, Kuang X, Xu J, Zhao X, Sun M, Chen D, Zhang Z, Feng X (2017) SiO2 nanoparticles cause depression and anxiety-like behavior in adult zebrafish. RSC Adv 7:2953–2963. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA24215D
Martin EI, Ressler KJ, Binder E, Nemeroff CB (2009) The neurobiology of anxiety disorders: brain imaging, genetics, and psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychiatr Clin North Am 32:549–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2009.05.004
Duval ER, Javanbakht A, Liberzon I (2015) Neural circuits in anxiety and stress disorders: a focused review. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:115–126. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s48528
McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Rawlins JN, Bannerman DM (2004) Amygdala and ventral hippocampus contribute differentially to mechanisms of fear and anxiety. Behav Neurosci 118:63–78. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.118.1.63
Revest JM, Dupret D, Koehl M, Funk-Reiter C, Grosjean N, Piazza PV, Abrous DN (2009) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is involved in anxiety-related behaviors. Mol Psychiatry 14:959–967. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.15
Jimenez JC, Su K, Goldberg AR, Luna VM, Biane JS, Ordek G, Zhou P, Ong SK, Wright MA, Zweifel L, Paninski L, Hen R, Kheirbek MA (2018) Anxiety cells in a hippocampal-hypothalamic circuit. Neuron 97:670-683.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.016
Adhikari A, Topiwala MA, Gordon JA (2011) Single units in the medial prefrontal cortex with anxiety-related firing patterns are preferentially influenced by ventral hippocampal activity. Neuron 71:898–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.027
Kim SY, Adhikari A, Lee SY, Marshel JH, Kim CK, Mallory CS, Lo M, Pak S, Mattis J, Lim BK, Malenka RC, Warden MR, Neve R, Tye KM, Deisseroth K (2013) Diverging neural pathways assemble a behavioural state from separable features in anxiety. Nature 496:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12018
Adhikari A (2014) Distributed circuits underlying anxiety. Front Behav Neurosci 8:112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00112
Ahrens S, Wu MV, Furlan A, Hwang GR, Paik R, Li H, Penzo MA, Tollkuhn J, Li B (2018) A central extended amygdala circuit that modulates anxiety. J Neurosci 38:5567–5583. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0705-18.2018
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This study did not receive any grants from any third parties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY performed behavioral experiments and electrophysiological recordings; GY performed synthesis of gold nanoparticles and characterization; BGT performed characterization of gold nanoparticles, analyzed, and interpret the data; BGT, GAG, AM, and MC provided technical support, reagents, and instrumentation; BY conceived experiments, analyzed data, prepared figures, and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Yeditepe University on Experimental Animal Research (Date. 17/03/2017 /No: 599).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz, Y., Yesilay, G., Guvenc Tuna, B. et al. Investigation of effects of transferrin-conjugated gold nanoparticles on hippocampal neuronal activity and anxiety behavior in mice. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 1813–1824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04632-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04632-9