Abstract
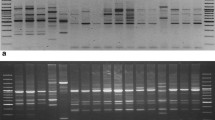
The taxonomy of the causal pathogen of basal stem rot of oil palms, Ganoderma is somewhat problematic at present. In order to determine the genetic distance relationship between G. boninense isolates and non-boninense isolates, a random amplified microsatellites DNA (RAMS) technique was carried out. The result was then compared with interfertility data of G. boninense that had been determined in previous mating studies to confirm the species of G. boninense. Dendrogram from cluster analysis based on UPGMA of RAMS data showed that two major clusters, I and II which separated at a genetic distance of 0.7935 were generated. Cluster I consisted of all the biological species G. boninense isolates namely CNLB, GSDK 3, PER 71, WD 814, GBL 3, GBL 6, OC, GH 02, 170 SL and 348781 while all non-boninense isolates namely G. ASAM, WRR, TFRI 129, G. RES, GJ, and CNLM were grouped together in cluster II. Although the RAMS markers showed polymorphisms in all the isolates tested, the results obtained were in agreement with the interfertility data. Therefore, the RAMS data could support the interfertility data for the identification of Ganoderma isolates.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flood J, Hasan Y (2004) Basal stem rot—taxonomy, biology, epidemiology, economic status and control in South East Asia and Pacific Island. In:International conference on pests and diseases of importance to the oil palm industry. Organized by Malaysian Palm Oil Board, 18–19 May 2004, Kuala Lumpur
Darmono TW (2000) Ganoderma in oil palm in Indonesia: current status and prospective use of antibodies for the detection of infection. In: Flood J, Bridge PD, Holderness M (eds) Ganoderma diseases of perennial crops. CABI Publishing, New York
Turner PD (1981) Oil palm diseases and disorders. Oxford Univ. Press, Kuala Lumpur
Utomo C, Niepold F (2000) Development of diagnostic methods for detecting Ganoderma-infected oil palms. Phytopathology 148:507–514
Ho YW, Nawawi A (1985) Ganoderma boninense Pat. from basal stem rot of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) in Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika 8:425–428
Khairudin H (1990) Basal stem rot of oil palm: incidence, etiology and control. MSc Thesis. Faculty of Agriculture, Universiti Pertanian Malaysia, Serdang
Idris AS, Ariffin D (2004) Basal stem rot—biology, detection and control. international conference on pests and diseases of importance to the oil palm industry. Organized by Malaysian Palm Oil Board. 18–19 May 2004. Kuala Lumpur
Idris AS (1999) Basal stem rot (BSR) of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) in Malaysia: factors associated with variation and disease severity. PhD Thesis. University of London, London
Gottlieb AM, Wright JE (1999) Taxonomy of Ganoderma from Southern South America: subgenus Ganoderma. Mycol Res 103(6):661–673
Latiffah Z (2002) Comparative studies on Ganoderma (Karst.) from infected oil palm and coconut stumps with special reference to their morphological, molecular and isozyme characteristics. PhD Thesis. Institute of Bioscience, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang
Latiffah Z, Harikrishna K, Tan SG, Faridah A, Ho YW (2005) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and random amplified microsatellite (RAMS) of Ganoderma from infected oil palm and coconut stumps in Malaysia. Asia Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol 13(1):23–43
Nelson M (2002) Determination of biological species of Ganoderma boninense (Pat.) and their pathogenic potential on oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) seedlings. MSc Thesis. Faculty of Science and Environmental Studies, University of Putra Malaysia, Serdang
Husrita H, Faridah A, Tan SG, Faridah QZ (2005) Random Amplified Microsatellites of Ganoderma boninense compared to their interfertility data. 6th National Congress on Genetics, 12–14 May 2005. Kuala Lumpur, pp 240–243
Rohlf FJ (1994) NTSYS-pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 1.8. Exeter Publishing Ltd., Setauket
Faridah A (2000) Conspecificity of G. boninense (Pat.) from three palm hosts. 23rd Microbiology Symposium. Organized by Microbiology Society of Malaysia. 19–21 Nov 2000. Langkawi
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funds for undergraduate studies from the Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia. The authors acknowledge the valuable contributions of the late Prof. Dr. Faridah Abdullah throughout this study. This paper is therefore dedicated to her memory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nudin, N.F.H., S., S. Comparing interfertility data with random amplified microsatellites DNA (RAMS) studies in Ganoderma Karst. Taxonomy. Mol Biol Rep 39, 2861–2866 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1045-2