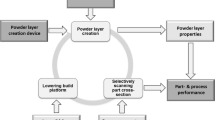
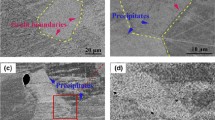
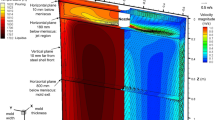
Processes of formation of structure and properties in the functional layer from chromium-nickel cast iron of two-layer centrifugally cast indefinite forming rolls under crystallization and subsequent tempering are investigated. The temperatures of the start and finish of the phase transformations, the phase composition, and the contents of martensite and retained austenite in the material of the functional layer after the tempering are determined.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Traino, “Rational roller operation and restoration,” Steel Transl., 38(10), 871 – 875 (2008) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091208100185).
Ray Amitava, M. S. Prasad, S. K. Dhua, et al., “Microstructural features of prematurely failed hot-strip mill work rolls: Some studies in spalling propensity,” J. Mater. Sci. Eng. Perform., 9(4), 449 – 456 (2000) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994900770345854).
F. Martini and K. A. Gostev, “New generation of wear-resistant bimetallic rolls for sheet mills,” Metallurgist, 43(5), 200 – 204 (1999).
Ray Amitava, M. S. Prasad, P. K. Barhai, and S. K. Mukherjee, “Metallurgical investigation of prematurely failed hot-strip mill work-rolls: Some microstructural observations,” J. Failure Anal. Prev., 4(3), 58 – 66 (2004) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-996-0016-8).
Pankhuri Sinha, Shivanandan S. Indimath, Goutam Mukhopadhyay, and Sandip Bhattacharyya, “Failure of a work roll of a thin strip rolling mill. A case study,” Proc. Eng., 86, 940 – 948 (2014) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.117).
F. Martini, “Main manufacturing and service requirements for the backup rolls and work rolls of modern hot-strip mills,” Metallurgist, 43(8), 365 – 370 (1999), (*).
K. A. Gostev, “Heat treatment in the production of rolls,” Stal’, No. 9, 79 – 84 (2008).
Piyas Palita, Hrishikesh R. Jugadea, Arvind Kumar Jhab et al., “Failure analysis of work rolls of a thin hot strip mill,” Case Stud. Eng. Failure Anal., 3, 39 – 45 (2015) (DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csefa.2015.01.001).
J. Asensio-Lozano and J. F. Álvarez-Antolín, “Saturated fractional design of experiments: toughness and graphite phase optimizing in Nihard cast irons,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 17(2), 216 – 223 (2008) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9138-8).
Minwoo Kanga, Yongchan Suhb, Yong-Jun Ohc, and Young-Kook Leea, “The effects of vanadium on the microstructure and wear resistance of centrifugally cast Ni-hard rolls,” J. Alloys Compd., 609(5), 25 – 32 (2014).
A. Ray, D. Mukherjee, B. Sarkar, and S. Mishra, “Influence of microstructure on the premature failure of a second-intermediate sendzimur mill drive roll,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 3(5), 649 – 656 (1994) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645263).
Sunghak Lee, Do Hyung Kim, Jae Hwa Ryu, and Keesam Shin, “Correlation of microstructure and thermal fatigue property of three work rolls,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 28(12), 2595 – 2608 (1997) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0017-6).
M. Nilssona and M. Olssona, “Microstructural, mechanical and tribological characterisation of roll materials for the finishing stands of the hot strip mill for steel rolling,” Wear, 307(1 – 2), 209 – 217 (2013).
Kassim S. Al-Rubaiea and Michael Pohlb, “Heat treatment and two-body abrasion of Ni-hard 4,” Wear, 312(1 – 2), 21 – 28 (2014).
Jinzhu Liu, Shuzhuo Li, and Yongfa Man, “Wear resistance of Ni-hard 4 and high-chromium cast iron re-evaluated,” Wear, 166(1), 37 – 40 (1993).
Yu. M. Kuskov, “Effect of graphite inclusions on endurance of cast and clad hot-forming rolls,” Stal’, No. 2 (2006).
J. Asesio-Lozanoa, J. F. Álvarez-Antolín, and G. F. Vander Voortc, “Identification and quantification of active manufacturing factors for graphite formation in centrifugally cast Nihard cast irons,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 206(1 – 3), 202 – 215 (2008) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.015).
K. N. Vdovin, D. A. Gorlenko, and A. N. Zavalishchin, “Influence of industrial tempering on the composition of complex cast iron,” Steel Transl., 43(5), 288 – 290 (2013).
K. N. Vdovin, D. A. Gorlenko, and A. N. Zavalishchin, “Structure changes of chromium-nickel indefinite cast irons in heating,” Vest. Magnitogorsk Gos. Tekh. Univ. Im. G. I. Nosova, No. 5(45), 9 – 11 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 7 – 11, April, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vdovin, K.N., Gorlenko, D.A., Zavalishchin, A.N. et al. Effect of Production Process on the Structure and Properties of the Functional Layer of Forming Rolls from Cast Iron LPKhND-71. Met Sci Heat Treat 62, 247–252 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00543-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00543-y