Abstract
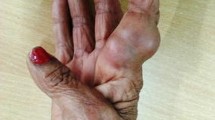
We report a case of subcutaneous infection caused by Exophiala oligosperma. Erythematous ulcerated plaque with exudate was major clinical features. Histopathological examination showed yeast-like cells and fungal hyphae. Mycological and molecular identification revealed E. oligosperma as etiologic agent. Local debridement and oral itraconazole were effective. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of phaeohyphomycosis caused by E. oligosperma in mainland China. This report highlights the potential role of E. oligosperma as an emerging cause of infection in immunocompetent patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fader RC, McGinnis MR. Infections caused by dematiaceous fungi: chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1988;2:925–38.
De Hoog GS, Guarro J, Gene J, Figueras MJ. Atlas of Clinical Fungi, 2nd ed. Utrecht: Centraal bureau voor Schimmelcultures and Reus: Universitat Rovira i Virgili, 2000.
De Hoog GS, Vicente V, Caligiorne RB, et al. Species diversity and polymorphism in the Exophiala spinifera clade containing opportunistic black yeast-like fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:4767–78.
Gonzalez-Lopez MA, Salesa R, Fernandez-Llaca MCH, Val-Bernal JF, Cano J. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala oligosperma in a renal transplant recipient. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:762–4.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi-second edition: approved Standard M38-A2. CLSI, Wayne, PA, USA, 2008.
Zeng JS, Sutton DA, Fothergill AW, Rinaldi MG, Harrak MJ, De Hoog GS. Spectrum of clinically relevant Exophiala species in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3713–20.
Kikuchi Y, Kondo M, Yaguchi H, et al. A case of chromomycosis caused by Fonsecaea pedrosoi presenting as a small plaque on the left upper arm: a review of reported cases of dematiaceous fungal infection in Japan. Jpn J Med Mycol. 2007;48:85–9.
Sato T, Yaguchi T. A case of phaeohyphomycosis of the face caused by Exophiala oligosperma in an immunocompromised host. JDDG. 2013;11:1087–9.
Li DM, Li RY, De Hoog GS, Wang YX, Wang DL. Exophiala asiatica, a new species from a fatal case in China. Med Mycol. 2009;47:101–9.
Al-Obaid I, Ahmad S, Khan ZU, Dinesh B, Hejab HM. Catheter-associated fungemia due to Exophiala oligosperma in a leukemic child and review of fungemia cases caused by Exophiala species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006;25:729–32.
Bossler AD, Richter SS, Chavez HA, et al. Exophiala oligosperma causing olecranon bursitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:4779–82.
Tokuhisa Y, Hagiya Y, Hiruma M, Nishimura K. Phaeohyphomycosis of the face caused by Exophiala oligosperma. Mycoses. 2011;54:240–3.
Kan T, Takahagi S, Kamegashira A, Ooiwa H, Yaguchi T, Hide M. Disseminated subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala oligosperma in a patient with Wegener’s Granulomatosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:356–7.
Rimawi BH, Rimawi RH, Mirdamadi M, et al. A case of Exophiala oligosperma successfully treated with voriconazole. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2013;2:144–7.
Fukai T, Hiruma M, Ogawa Y, et al. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala oligosperma successfully treated with local hyperthermia. Med Mycol J. 2013;54:297–301.
Venkateshwar S, Ambroise MM, Asir GJ, Mudhigeti N, Ramdas A, Authy K, et al. A rare case report of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycotic cyst caused by Exophiala oligosperma in an immunocompetent host with literature review. Mycpathologia. 2014;178:117–21.
Wen YM, Rajendran RK, Lin YF, Kirschner R, Hu S. Onychomycosis associated with Exophiala oligosperma in Taiwan. Mycopathologia. 2016;181:83–8.
Badali H, Hedayati MT, Bahoosh M, Kasiri A, Ghasemi M, Motahari J, et al. Exophiala oligosperma involved in a refractory chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011;15:319–23.
Revankar SG, Sutton DA. Melanized fungi in human disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:884–928.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Guixia Lv and Dr Yongnian Shen for technical support in molecular identification of the strain. They thank Dr Fei Wu and Dr Jia Chen for the help with histopathology. They also thank Dr Yichen Tang for the referral of this case.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Yuping Ran.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Cai, Q., Gao, Z. et al. Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala oligosperma in an Immunocompetent Host: Case Report and Literature Review. Mycopathologia 183, 815–820 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-018-0279-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-018-0279-0