Abstract
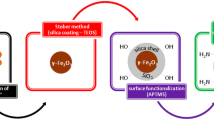
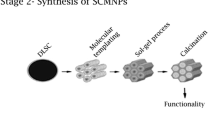
In this study, the use of horizontal low gradient magnetic field (HLGMF) (<100 T/m) for filtration, control and separation of synthesized magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) is investigated. The characteristics of the suspension, size and type of the NPs are considered and discussed. For these purposes, Fe2O3 silica-coated nanoclusters of about 150 nm are synthesized by co-precipitation, monodispersion and silica coating. Superconducting quantum interference device, TEM, XRD and ζ potential techniques were used to characterize the synthesized nanoclusters. An extensive magnetophoresis study was performed at different magnetophoretical conditions. Different reversible aggregation times were observed at different HLGMF, at each step of the synthesis route. In particular, differences of several orders of magnitude were observed when comparing citric acid-modified NPs with silica-coated nanoclusters. Reversible aggregation times are correlated to the properties of the NPs at different steps of synthesis route.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin CHU (1999) Controlled size polymeric microspheres with superparamagnetic Core International patent WO 99/12000, PCT/US98/21266
Campelj S, Makovec D, Drofenik M (2008) Preparation and properties of water-based magnetic fluids. J Phys 20:204101
Campelj S, Makovec D, Drofenik M (2009) Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with 3-aminopropyl silane. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1346–1350
Chen H, Kaminski MD, Ebner AD, Ritter JA, Rosengard AJ (2007) Theoretical análysis of a simple yet efficient portable magnetic separator design for separation of magnetic nano/micro carriers from human blood flow. J Magn Magn Mater 313:127–134
De Las Cuevas G, Faraudo J, Camacho J (2008) Low-gradient magnetophoresis throught field induced reversible aggregation. J Phys Chem C 112:945–950
Delgado AV, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Hunter RJ, Koopal LK, Lyklema J (2005) Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena IUPAC technical report. Pure Appl Chem 77:1753–1805
Earhart CM, Wilson RJ, White RL, Pormand N, Wang SX (2009) Microfabrication magnetic sifter for high-throughput and high-gradient magnetic separation. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1436–1439
Faraudo J, Camacho J (2010) Cooperative magnetophoresis of superparamagnetic colloids: theoretical aspects. Colloid Polym Sci 288:207–215
Friedman G, Yellen BB (2005) Magnetic separation, manipulation and assembly of solid phase in fluids. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 10:158–166
Goodarzi A, Sahoo Y, Swihart MT, Prasad PN (2004) Aqueous ferrofluid of citric acid coated magnetite particles. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 789:6.6.1–6.6.6
Hadju A, Illes E, Tombacz E, Borbath I (2009) Surface charging, polyanionic coating and colloid stability of magnetite nanoparticles. Colloid Surf A 347:104–108
Kallay N, Matijevic E (1985) Adsorption at solid/solution interfaces. 1. Interpretation of surface complexation of oxalic and citric acids with hematite. Langmuir 1:195–201
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterization, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Sayed ZM, Telang SD, Ramchand CN (2003) Application of magnetic techniques in the field of drug delivery and biomedicine. BioMagn Res Technol 1:2
Siraprapa M, Gamolwan T, Uthai W, Metha R (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles stabilized with polymeric bilayer of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ethter-poly(ε-caprolactone) copolymers. Polymer 49:3950–3956
Smistrup K, Lund-Olesen T, Hansen MF, Tang PT (2006) Microfluidic magnetic separator using an array of soft magnetic elements. J Appl Phys 99:08P102
Taboada E, Rodriguez E, Roig A, Oro J, Roch A, Muller RN (2007) Relaxometric and magnetic characterization of ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles with high magnetization. Lagmuir 23:4583–4588
Tartaj P, Del Puerto MM, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Gonzalez-Carreno T, Serna CJ (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D 36:R182–R197
Wilson KS, Harris LA, Goff JD, Riffle JS, Dailey JP (2002) A generalized method for magnetite nanoparticle steric stabilization utilizing block copolymers containing carboxylic acids. Eur Cell Mater 3(Suppl 2):206–209
Wilson KS, Goff JD, Riffle JS, Harris LA, St Pierre TG (2005) Polydimethylsiloxane–magnetite nanoparticle complexes and dispersions in polysiloxane carrier fluids. Polym Adv Technol 16:200–211
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Portuguese Foundation of science and technology (FCT) for financial support under grants: NANO/NMed-SD/0156/2007 and PTCD/CTM/69316/2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benelmekki, M., Caparros, C., Montras, A. et al. Horizontal low gradient magnetophoresis behaviour of iron oxide nanoclusters at the different steps of the synthesis route. J Nanopart Res 13, 3199–3206 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0218-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0218-6