Abstract
Purpose
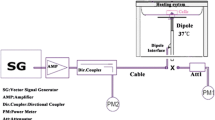
Glioblastoma is a malignant brain tumor which has one of the poorest prognosis. It is not clear if toxic environmental factors can influence its aggressiveness. Recently, it was suggested that brain cancer patients with heavy cell phone use showed reduced survival. Here we aimed to assess the effect of controlled brain averaged specific absorption rate (BASAR) from heavy use of cell phone radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF–EMF) on in vivo C6 brain tumors in Wistar rats.
Methods
C6 cells grafted male rats were exposed to GSM 900 MHz signal at environmental BASAR, 0 (sham), 0.25 or 0.5 W/kg (5 days a week, 45 min a day in restraint), or were cage controls (no restraint). At death, tumor volume and immunohistochemistry for CD31, cleaved caspase (CC) 3 and Ki67 were assessed to examine vascularization, apoptosis and cellular divisions, respectively. Moreover, immune cell invasion, necrosis and mitotic index were determined.
Results
Results showed no BASAR effect on survival (31 days post-graft median), tumor volume, mitotic index, vascularization, infiltration, necrosis or cell division. However, results suggested a BASAR-dependent reduction of immune cell invasion and apoptosis.
Conclusions
Our data suggested an action of RF–EMF by reducing immune cell invasion and glioblastoma cell apoptosis, at probably too low amplitude to impact survival. Further replication studies are needed to confirm these observations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott JN, Rewcastle NB, Brasher PM, Fulton D, MacKinnon JA, Hamilton M et al (1999) Which glioblastoma multiforme patient will become a long-term survivor? A population-based study. Ann Neurol 46(2):183–188
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2013) Non-ionizing radiation. (Part 2: radiofrequency electromagnetic fields), vol 102. IARC, Lyon
SCENIHR (2015) Scientific Committee on emerging and newly identified health risks: potential health effects of eExposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF). http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/emerging/docs/scenihr_o_041.pdf. Accessed 15 Aug 2015
Interphone Study Group (2010) Brain tumour risk in relation to mobile telephone use: results of the INTERPHONE international case-control study. Int J Epidemiol 39(3):675–694
Feychting M, Schüz J (2017) Chap. 15: electromagnetic fields. In: Thun M, Linet MS, Cerhan JR, Haiman CA, Schottenfeld D (eds) Cancer epidemiology and prevention, 4th edn. Oxford Scholarship, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780190238667.001.0001
Hardell L, Carlberg M (2013) Use of mobile and cordless phones and survival of patients with glioma. Neuroepidemiology 40(2):101–108
Salford LG, Brun A, Persson BRR, Eberhardt J (1993) Experimental studies of brain tumour development during exposure to continuous and pulsed 915 MHz radiofrequency radiation. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 30:313–318
Higashikubo R, Culbreth VO, Spitz DR, LaRegina MC, Pickard WF, Straube WL et al (1999) Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields have no effect on the in vivo proliferation of the 9L brain tumor. Radiat Res 152(6):665–671
Simko M, Remondini D, Zeni O, Scarfi MR (2016) Quality matters: systematic analysis of endpoints related to “cellular life” in vitro data of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(7):701–717
Kobayashi T, Masumoto J, Tada T, Nomiyama T, Hongo K, Nakayama J (2007) Prognostic significance of the immunohistochemical staining of cleaved caspase-3, an activated form of caspase-3, in gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 13(13):3868–3874
Liu YX, Tai JL, Li GQ, Zhang ZW, Xue JH, Liu HS et al (2012) Exposure to 1950-MHz TD-SCDMA electromagnetic fields affects the apoptosis of astrocytes via caspase-3-dependent pathway. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42332
Stagg RB, Thomas WJ, Jones RA, Adey WR (1997) DNA synthesis and cell proliferation in C6 glioma and primary glial cells exposed to a 836.55 MHz modulated radiofrequency field. Bioelectromagnetics 18(3):230–236
Dasdag S, Akdag MZ, Ulukaya E, Uzunlar AK, Ocak AR (2009) Effect of mobile phone exposure on apoptotic glial cells and status of oxidative stress in rat brain. Electromagn Biol Med 28(4):342–354
Ahmed S, Rashed H, Hegazy A, Mohamed AM, Elmesallamy W (2016) Prognostic value of ALDH1, EZH2 and Ki-67 in astrocytic gliomas. Turk Patol Derg 32(2):70–81
Capri M, Scarcella E, Fumelli C, Bianchi E, Salvioli S, Mesirca P et al (2004) In vitro exposure of human lymphocytes to 900 MHz CW and GSM modulated radiofrequency: studies of proliferation, apoptosis and mitochondrial membrane potential. Radiat Res 162(2):211–218
Zeni O, Romano M, Perrotta A, Lioi MB, Barbieri R, d’Ambrosio G et al (2005) Evaluation of genotoxic effects in human peripheral blood leukocytes following an acute in vitro exposure to 900 MHz radiofrequency fields. Bioelectromagnetics 26(4):258–265
Eghlidospour M, Ghanbari A, Mortazavi SMJ, Azari H (2017) Effects of radiofrequency exposure emitted from a GSM mobile phone on proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of neural stem cells. Anat Cell Biol 50(2):115–123
Sanchez S, Masuda H, Billaudel B, Haro E, Anane R, Leveque P et al (2006) Effect of GSM-900 and – 1800 signals on the skin of hairless rats. II: 12-week chronic exposures. Int J Radiat Biol 82(9):675–680
Sanchez S, Milochau A, Ruffie G, Poulletier de Gannes F, Lagroye I, Haro E et al (2006) Human skin cell stress response to GSM-900 mobile phone signals. In vitro study on isolated primary cells and reconstructed epidermis. FEBS J 273(24):5491–5507
Das S, Marsden PA (2013) Angiogenesis in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 369(16):1561–1563
Rao A, Manyam G, Rao G, Jain R (2016) Integrative analysis of mRNA, microRNA, and protein correlates of relative cerebral blood volume values in GBM reveals the role for modulators of angiogenesis and tumor proliferation. Cancer Inform 15:29–33
Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ (2006) ‘Pseudopalisading’ necrosis in glioblastoma: a familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65(6):529–539
Tastekin E, Caloglu VY, Puyan FO, Tokuc B, Caloglu M, Yalta TD et al (2016) Prognostic value of angiogenesis and survivin expression in patients with glioblastoma. Turk Neurosurg 26(4):484–490
Tepper OM, Callaghan MJ, Chang EI, Galiano RD, Bhatt KA, Baharestani S et al (2004) Electromagnetic fields increase in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through endothelial release of FGF-2. FASEB J 18(11):1231–1233
Barthelemy A, Mouchard A, Bouji M, Blazy K, Puigsegur R, Villegier AS (2016) Glial markers and emotional memory in rats following acute cerebral radiofrequency exposures. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(24):25343–25355
Lu Y, He M, Zhang Y, Xu S, Zhang L, He Y et al (2014) Differential pro-inflammatory responses of astrocytes and microglia involve STAT3 activation in response to 1800 MHz radiofrequency fields. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108318
Sowers JL, Johnson KM, Conrad C, Patterson JT, Sowers LC (2014) The role of inflammation in brain cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 816:75–105
Maskey D, Pradhan J, Aryal B, Lee CM, Choi IY, Park KS et al (2010) Chronic 835-MHz radiofrequency exposure to mice hippocampus alters the distribution of calbindin and GFAP immunoreactivity. Brain Res 1346:237–246
Jacobs VL, Valdes PA, Hickey WF, De Leo JA (2011) Current review of in vivo GBM rodent models: emphasis on the CNS-1 tumour model. ASN Neuro 3(3):e00063
Leveque PDC, Veyret B, Wiart J (2004) Dosimetric analysis of a 900-MHz rat head exposure system. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 52(8):2076–2083
Grobben B, De Deyn PP, Slegers H (2002) Rat C6 glioma as experimental model system for the study of glioblastoma growth and invasion. Cell Tissue Res 310(3):257–270
Paxinos G, Watsen C (2006) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Hard cover edition. Academic Press, San Diego
Olsson A, Bouaoun L, Auvinen A, Feychting M, Johansen C, Mathiesen T, Melin B, Lahkola A, Larjavaara S, Villégier AS, Deltour I, Schüz J (2018) Survival of glioma patients in relation to mobile phone use in in Denmark, Finland and Sweden. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03019-5
Burger PC (1987) The anatomy of astrocytomas. Mayo Clin Proc 62(6):527–529
Bouji M, Lecomte A, Gamez C, Blazy K, Villegier AS (2016) Neurobiological effects of repeated radiofrequency exposures in male senescent rats. Biogerontology 17(5–6):841–857
Petitdant N, Lecomte A, Robidel F, Gamez C, Blazy K, Villegier AS (2016) Cerebral radiofrequency exposures during adolescence: impact on astrocytes and brain functions in healthy and pathologic rat models. Bioelectromagnetics 37(5):338–350
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the French National Research Program for Environmental and Occupational Health of ANSES [2014/2 RF/002] and French Ministry of Ecology [Program 190].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouadah, N.S., Lecomte, A., Robidel, F. et al. Possible effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields on in vivo C6 brain tumors in Wistar rats. J Neurooncol 140, 539–546 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03012-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03012-y