Abstract
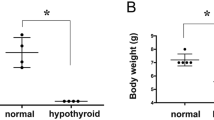
Neonatal hypothyroidism is associated with multiple and severe brain alterations. We recently demonstrated a significant increase in hydrolysis of AMP to adenosine in brain of hypothyroid rats at different ages. However, the origin of this effect was unclear. Considering the effects of adenine nucleotides to brain functions and the harmful effects of neonatal hypothyroidism to normal development of the central nervous system, in this study we investigated the metabolism of adenine nucleotides in hippocampal, cortical and cerebellar astrocyte cultures from rats submitted to neonatal hypothyroidism. ATP and AMP hydrolysis were enhanced by 52 and 210%, respectively, in cerebellar astrocytes from hypothyroid rats. In hippocampus of hypothyroid rats, the 47% increase in AMP hydrolysis was significantly reverted when the astrocytes were treated with T3. Therefore, the imbalance in the ATP and adenosine levels in astrocytes, during brain development, may contribute to some of the effects described in neonatal hypothyroidism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lazarus JH (2005) Congenital hypothyroidism. Arch Dis Child 90(2):112–113
Anderson GW (2001) Thyroid hormones and the brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 22:1–7
Dussault JH, Ruel J, (1987) Thyroid hormones and brain development. Annu Rev Physiol 49:321–334
Geel SE, Valcana T, Timiras PS (1967) Effect of neonatal hypothyroidism and of thyroxine on L-[14C] leucine incorporation in protein in vivo and the relationship to ionic levels in the developing brain of rat. Brain Res 4:143–147
Oppenheimer JH, Schwartz HL (1997) Molecular basis of thyroid hormone-dependent brain development. Endocr Rev 18:462–475
Paul S, Das S, Poddar R, Sarkar PK (1996) Role of thyroid hormone in the morphological differentiation and maturation of astrocytes: temporal correlation with synthesis and organization of actin. Eur J Neurosci 8(11):2361–2370
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50:413–492
Edwards FA, Gibb AJ, Colquhoun D (1992) ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature 359:144–147
Enjyoji K, Sévigny J, Lin Y, Frenette P, Christie PD, Schulte am Esch J, Imai M, Edelberger J M, Rayburn H, Lech M, Beeler DM, Csizmadia E, Wagner DD, Robson SC, Rosemberg RD (1999) Targeted disruption of CD39/ATP diphosphohydrolase results in disordered hemostasis and tromboregulation. Nat Med 5:1010–1017
Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Dal Susino M, Collo G, Buell G, Di Virgilio F (1997) ATP-mediated cytotoxicity in microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 36:1295–1301
Neary JT, Kang Y, Bu Y, Yu E, Akong K, Peters CM (1999) Mitogenic signaling by ATP/P2Y purinergic receptors in astrocytes: involvement of a calcium-independent protein kinase C, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase pathway distinct from the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C/calcium pathway. J Neurosci 19:4211–4220
Zimmermann H (2001) Ectonucleotidases: some developments and a note on nomenclature. Drug Dev Res 52:44–56
Zimmermann H (1992) 5′-Nucleotidase: molecular structure and functional aspects. Biochem J 285:345–365 Review
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA (2001) The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:31–55
Heilbronn V, Maienschein C, Carstensen WG, Zimmermann H (1995) Crucial role of 5′nucleotidase in differentiation and survival of developing neural cells. Neuroreport 7:257–261
Ciccarelli R, Ballerini P, Sabatino G, Rathbone MP, D`Onofrio M, Caciagli F, Di Iorio P (2001) Involvement of astrocytes in purine-mediated reparative processes in the brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 19:395–414
Wink MR, Braganhol E, Tamajusuku ASK, Casali EA, Karl J, Barreto-Chaves ML, Battastini AMO (2003) Extracellular adenine nucleotides metabolism in astrocyte cultures from different brain regions. Neurochem Int 43(7):621–628
Bruno AN, Ricachenevsky FK, Pochmann D, Bonan CD, Battastini AMO, Barreto-Chaves ML, Sarkis JJF 2005a. Hypothyroidism changes adenine nucleotide hydrolysis in synaptosomes from hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats in different phases of development. Int J Dev Neurosci 23(1):37–44
Fideu MD, Arce A, Esquifino AI, Miras-Portugal MT (1994) Thyroid hormones modulate both transport and A1 receptors in rat brain. Am J Physiol 256:1651–1656
Pipaón C, Santos A, Pérez-Castilho A (1992) Thyroid hormone up-regulates NGFI-A gene expression in rat brain during development. J Biol Chem 267:21–23
Pinto SS, Gottfried C, Mendez A, Gonçalves D, Karl J, Gonçalves CA, Wofchuk S, Rodnight R (2000) Immunocontent and secretion of S100B in astrocyte cultures from different brain regions in relation to morphology. FEBS Lett 486(3):203–207
Chan KM, Delfert D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colometric assay for Ca+2-ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 157:375–380
Bradford MMA (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:218–251
Hamberger A (1971) Amino acid uptake in neuronal and glial cell fractions from rabbit cerebral cortex. Brain Res 31:169–178
Schousboe A (1981) Transport and metabolism of glutamate and GABA in neurons and glial cells. Int Rev Neurobiol 22:1–45
Scemes E, Suadicani SO, Spray DC (2000) Intercellular communication in spinal cord astrocytes: fine tuning between gap junctions and P2 nucleotide receptors in calcium wave propagation. J Neurosci 20: 1435–1445
Kalaria RN, Harik SI (1986) Adenosine receptors of cerebral microvessels and choroid plexus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:463–470
Schoen SW, Graeber MB, Tóth L, Kreutzberg GW (1988) 5′-Nucleotidase in postnatal ontogeny of rat cerebellum: a marker for migrating nerve cells? Dev Brain Res 39:125–136
Maienschein V, Zimmermann H (1996) Immunocytochemical localization of Ecto- 5′-Nucleotidase in cultures of cerebellar granule cells. Neuroscience 70:429– 438
Marangos PJ, Patel J, Stivers J (1982) Ontogeny of adenosine binding sites in rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Neurochem 39:25– 30
Weaver DR (1996) A1-adenosine receptor gene expression in fetal rat brain. Dev Brain Res 9:205–233
Rivkees SA, Zhao Z, Porter G, Turner C (2001) Influences of Adenosine on the Fetus and Newborn. Mol Gen Metabol 74:160–171
Turner CP, Yan H, Schwartz M, Othman T, Rivkees SA (2002) A1 adenosine receptor activation induces ventriculomegaly and white matter loss. Dev Neurosci 13:1199–1204
Chantoux F, Francon J (2002) Thyroid hormone regulates the expression of NeuroD/BHF1 during the development of rat cerebellum. Mol Cell Endocrinol 194(1–2):157–163
Bruno AN, Da Silva RS, Bonan CD, Battastini AMO, Barreto-Chaves ML, Sarkis JJF (2003) Hyperthyroidism modifies ecto-nucleotidase activities in synaptosomes from hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats in different phases of development. Int J Dev Neurosci 21:401–408
Bruno AN, Diniz GP, Ricachenevsky FK, Pochmann D, Bonan CD, Barreto-Chaves ML, Sarkis JJF 2005b. Hypo-and hyperthyroidism affect the ATP, ADP and AMP hydrolysis in rat hippocampal and cortical slices. Neurosci Res 52(1):61–68
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil), Programas de Núcleos de Excelência (PRONEX-Brazil) and Fundação Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Elizandra Braganhol and Alessandra Nejar Bruno are first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braganhol, E., Bruno, A.N., Bavaresco, L. et al. Neonatal Hypothyroidism Affects the Adenine Nucleotides Metabolism in Astrocyte Cultures from Rat Brain. Neurochem Res 31, 449–454 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9041-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9041-y