Abstract
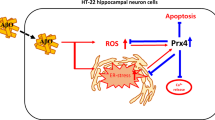
Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the loss of neurons in AD. The phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) plays an important role in regulating neuronal survival processes. However, the direct effects of the PTEN on ER stress and apoptosis in AD have not been elucidated. In this study, we demonstrate that the expression of PTEN and ER stress related proteins, GRP78 and CHOP, increased in APP/PS1 transgenic AD mice compared with WT mice. A PTEN inhibitor, dipotassium bisperoxo-(5-hydroxypyridine-2-carboxyl)-oxovanadate (bpv) could decrease apoptosis, induce AKT phosphorylation and inhibit the ER stress response proteins in hippocampus in APP/PS1 transgenic AD model mice. Furthermore, treatment with the specific PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, significantly blocked the anti-apoptotic effects of bpv in AD mice. The expression in GRP78, CHOP and apoptosis levels by bpv was reversed after PI3K inhibitor treatment. Taken together, our results indicate that the neuroprotective role of bpv involves the suppression of ER stress via the activation of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways in APP/PS1 transgenic AD model mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryu J, Hong BH, Kim YJ, Yang EJ, Choi M, Kim H, Ahn S, Baik TK, Woo RS, Kim HS (2016) Neuregulin-1 attenuates cognitive function impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis 7:e2117
Sachdeva AK, Chopra K (2015) Lycopene abrogates Abeta(1–42)-mediated neuroinflammatory cascade in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem 26(7):736–744
Scheff SW, Price DA, Ansari MA, Roberts KN, Schmitt FA, Ikonomovic MD, Mufson EJ (2015) Synaptic change in the posterior cingulate gyrus in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 43(3):1073–1090
Janyou A, Changtam C, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus C, Tocharus J (2015) Suppression effects of O-demethyldemethoxycurcumin on thapsigargin triggered on endoplasmic reticulum stress in SK-N-SH cells. Neurotoxicology 50:92–100
Placido AI, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI, Pereira CM (2015) Enhanced amyloidogenic processing of amyloid precursor protein and cell death under prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress in brain endothelial cells. Mol Neurobiol 51(2):571–590
Placido AI, Pereira CM, Duarte AI, Candeias E, Correia SC, Carvalho C, Cardoso S, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI (2015) Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress: an opportunity to prevent neurodegeneration? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 14(4):518–533
Zhang HY, Wang ZG, Lu XH, Kong XX, Wu FZ, Lin L, Tan X, Ye LB, Xiao J (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: relevance and therapeutics in central nervous system diseases. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):1343–1352
Liu B, Zhu Y, Zhou J, Wei Y, Long C, Chen M, Ling Y, Ge J, Zhuo Y (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes amyloid-beta peptides production in RGC-5 cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 19(6):827–835
Huang RR, Hu W, Yin YY, Wang YC, Li WP, Li WZ (2015) Chronic restraint stress promotes learning and memory impairment due to enhanced neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress in the frontal cortex and hippocampus in male mice. Int J Mol Med 35(2):553–559
Ghribi O (2006) The role of the endoplasmic reticulum in the accumulation of beta-amyloid peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Mol Med 6(1):119–133
Liu B, Rasool S, Yang Z, Glabe CG, Schreiber SS, Ge J, Tan Z (2009) Amyloid-peptide vaccinations reduce {beta}-amyloid plaques but exacerbate vascular deposition and inflammation in the retina of Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 175(5):2099–2110
Doh SH, Kim JH, Lee KM, Park HY, Park CK (2010) Retinal ganglion cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in a chronic glaucoma model. Brain Res 1308:158–166
Huang HC, Tang D, Lu SY, Jiang ZF (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a novel neuronal mediator in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Res 37(4):366–374
Kitagishi Y, Matsuda S (2013) Diets involved in PPAR and PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway may contribute to neuroprotection in a traumatic brain injury. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 5 (5):42
Mao D, Sun X (2015) Reactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by the bisperoxovanadium compound bpV(pic) attenuates photoreceptor apoptosis in experimental retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56 (9):5519–5532
Wong HK, Veremeyko T, Patel N, Lemere CA, Walsh DM, Esau C, Vanderburg C, Krichevsky AM (2013) De-repression of FOXO3a death axis by microRNA-132 and -212 causes neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22(15):3077–3092
Chen Y, Luo C, Zhao M, Li Q, Hu R, Zhang JH, Liu Z, Feng H (2015) Administration of a PTEN inhibitor BPV(pic) attenuates early brain injury via modulating AMPA receptor subunits after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neurosci Lett 588:131–136
Dal Ponte C, Alchera E, Follenzi A, Imarisio C, Prat M, Albano E, Carini R (2011) Pharmacological postconditioning protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Liver Transpl 17(4):474–482
Tan L, Chen X, Wang W, Zhang J, Li S, Zhao Y, Wang J, Luo A (2017) Pharmacological inhibition of PTEN attenuates cognitive deficits caused by neonatal repeated exposures to isoflurane via inhibition of NR2B-mediated tau phosphorylation in rats. Neuropharmacology 114:135–145
Liu XY, Zhang LJ, Chen Z, Liu LB (2017) The PTEN inhibitor bpV(pic) promotes neuroprotection against amyloid beta-peptide (25–35)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Neurol Res 23:1–8
Grande V, Manassero G, Vercelli A (2014) Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory roles of the phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome Ten (PTEN) Inhibition in a Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. PloS ONE 9(12):e114554
Mao L, Jia J, Zhou X, Xiao Y, Wang Y, Mao X, Zhen X, Guan Y, Alkayed NJ, Cheng J (2013) Delayed administration of a PTEN inhibitor BPV improves functional recovery after experimental stroke. Neuroscience 231:272–281
Noshita N, Lewen A, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2001) Evidence of phosphorylation of Akt and neuronal survival after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(12):1442–1450
Yin G, Li LY, Qu M, Luo HB, Wang JZ, Zhou XW (2011) Upregulation of AKT attenuates amyloid-beta-induced cell apoptosis. J Alzheimer’s Dis 25(2):337–345
Shrestha S, Yang K, Guy C, Vogel P, Neale G, Chi H (2015) Treg cells require the phosphatase PTEN to restrain TH1 and TFH cell responses. Nat Immunol 16(2):178–187
He Z, Deng Y, Li W, Chen Y, Xing S, Zhao X, Ding J, Gao Y, Wang X (2014) Overexpression of PTEN suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced lung fibroblast proliferation, differentiation and collagen secretion through inhibition of the PI3-K-Akt-GSK3beta pathway. Cell Biosci 4 (1):2
Ding J, Guo J, Yuan Q, Yuan F, Chen H, Tian H (2013) Inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 decreases rat cortical neuron injury and blood-brain barrier permeability, and improves neurological functional recovery in traumatic brain injury model. PloS ONE 8(11):e80429
Knafo S, Sanchez-Puelles C, Palomer E, Delgado I, Draffin JE, Mingo J, Wahle T, Kaleka K, Mou L, Pereda-Perez I, Klosi E, Faber EB, Chapman HM, Lozano-Montes L, Ortega-Molina A, Ordonez-Gutierrez L, Wandosell F, Vina J, Dotti CG, Hall RA, Pulido R, Gerges NZ, Chan AM, Spaller MR, Serrano M, Venero C, Esteban JA (2016) PTEN recruitment controls synaptic and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s models. Nat Neurosci 19(3):443–453
Schmid AC, Byrne RD, Vilar R, Woscholski R (2004) Bisperoxovanadium compounds are potent PTEN inhibitors. FEBS Lett 566 (1–3):35–38
Maria DA, de Souza JG, Morais KL, Berra CM, Zampolli Hde C, Demasi M, Simons SM, de Freitas Saito R, Chammas R, Chudzinski-Tavassi AM (2013) A novel proteasome inhibitor acting in mitochondrial dysfunction, ER stress and ROS production. Invest New Drugs 31(3):493–505
Clarke JR, Lyra ESNM, Figueiredo CP, Frozza RL, Ledo JH, Beckman D, Katashima CK, Razolli D, Carvalho BM, Frazao R, Silveira MA, Ribeiro FC, Bomfim TR, Neves FS, Klein WL, Medeiros R, LaFerla FM, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ, Munoz DP, Velloso LA, Ferreira ST, De Felice FG (2015) Alzheimer-associated Abeta oligomers impact the central nervous system to induce peripheral metabolic deregulation. EMBO Mol Med 7(2):190–210
Lin L, Yang SS, Chu J, Wang L, Ning LN, Zhang T, Jiang Q, Tian Q, Wang JZ (2014) Region-specific expression of tau, amyloid-beta protein precursor, and synaptic proteins at physiological condition or under endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. J Alzheimer’s Dis 41(4):1149–1163
Brown MK, Naidoo N (2012) The endoplasmic reticulum stress response in aging and age-related diseases. Front Physiol 3:263
Kam TI, Gwon Y, Jung YK (2014) Amyloid beta receptors responsible for neurotoxicity and cellular defects in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 71 (24):4803–4813
Pinkaew D, Changtam C, Tocharus C, Thummayot S, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus J (2015) Di-O-demethylcurcumin protects SK-N-SH cells against mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptotic cell death induced by Abeta25-35. Neurochem Int 80:110–119
Wang XY, Yang CT, Zheng DD, Mo LQ, Lan AP, Yang ZL, Hu F, Chen PX, Liao XX, Feng JQ (2012) Hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cells against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biochem 363(1–2):419–426
Bononi A, Bonora M, Marchi S, Missiroli S, Poletti F, Giorgi C, Pandolfi PP, Pinton P (2013) Identification of PTEN at the ER and MAMs and its regulation of Ca(2+) signaling and apoptosis in a protein phosphatase-dependent manner. Cell Death Differ 20(12):1631–1643
Chen WT, Zhu G, Pfaffenbach K, Kanel G, Stiles B, Lee AS (2014) GRP78 as a regulator of liver steatosis and cancer progression mediated by loss of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Oncogene 33(42):4997–5005
Costa RO, Lacor PN, Ferreira IL, Resende R, Auberson YP, Klein WL, Oliveira CR, Rego AC, Pereira CM (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs downstream of GluN2B subunit of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in mature hippocampal cultures treated with amyloid-beta oligomers. Aging Cell 11(5):823–833
Viana RJ, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2011) Amyloid-beta peptide-induced secretion of endoplasmic reticulum chaperone glycoprotein GRP94. J Alzheimer’s Dis 27(1):61–73
Yoshino Y, Ishisaka M, Tsujii S, Shimazawa M, Hara H (2015) Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects the murine hippocampus against stressors via Akt and ERK1/2 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(2):274–279
Suwanna N, Thangnipon W, Soi-Ampornkul R (2014) Neuroprotective effects of diarylpropionitrile against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neurotoxicity in rat cultured cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 578:44–49
Wang C, Xie N, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang Y (2014) Puerarin protects against beta-amyloid-induced microglia apoptosis via a PI3K-dependent signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 39(11):2189–2196
Martins AH, Hu J, Xu Z, Mu C, Alvarez P, Ford BD, El Sayed K, Eterovic VA, Ferchmin PA, Hao J (2015) Neuroprotective activity of (1 S,2E,4R,6R,-7E,11E)-2,7,11-cembratriene-4,6-diol (4R) in vitro and in vivo in rodent models of brain ischemia. Neuroscience 291:250–259
Hadj Ayed Tka K, Mahfoudh Boussaid A, Zaouali MA, Kammoun R, Bejaoui M, Ghoul Mazgar S, Rosello Catafau J, Ben Abdennebi H (2015) Melatonin modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and Akt/GSK3-beta signaling pathway in a rat model of renal warm ischemia reperfusion. Anal Cell Pathol 2015:635172
Quan X, Wang J, Liang C, Zheng H, Zhang L (2015) Melatonin inhibits tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 463(4):1102–1107
Wang Z, Wang Y, Ye J, Lu X, Cheng Y, Xiang L, Chen L, Feng W, Shi H, Yu X, Lin L, Zhang H, Xiao J, Li X (2015) bFGF attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial injury on myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion via activation of PI3K/Akt/ERK1/2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 19(3):595–607
Acknowledgements
This study was supported partly by the support project for the Disciplinary group of Psychology and Neuroscience, Xinxiang Medical University (2016PN-KFKT-11), the Henan Key Laboratory of Neural Regeneration and Repairment (HNSJXF-2016-007), key research areas of Xinxiang Medical University (Grant No. ZD2011-28), the Science and Technology Project of Department of Education of Henan Province (Grant No. 13A310862), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81301174, 81260211, 81560236).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., Wang, S., Wang, Z. et al. Inhibition of PTEN Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis via Activation of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 42, 3052–3060 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2338-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2338-1