Abstract
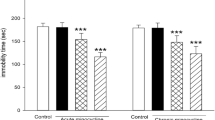
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a natural compound, is involved in the mitochondrial electron transfer chain (ETC) and plays an important pattern in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. Amelioration of ATP is related to abnormalities in cognitive function and psychiatric diseases. Previous studies have shown that depression is accompanied by the induction of inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways and amelioration of antioxidant status. In a recent study, we investigated the beneficial effects of CoQ10 on behavioral dysfunction and CoQ10 level in the rat brain. Therefore, intracerebroventricular (ICV) infusion of a single dose of streptozotocin (STZ, 0.2 mg/mouse) was used in adult male mice to induce depression. The behavioral data revealed a significant difference between the depression and control groups regarding the forced swim test (FST) and splash test results at 24 h following STZ treatment. Also, the validated and accurate high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) technique showed decreased CoQ10 level in the brain samples of the STZ group, compared to the controls. Our findings revealed that behavioral abnormalities due to STZ target mitochondria and affect energy metabolism and hemostasis, resulting in the initiation of oxidative damage in the brain. Besides, 4-week administration of CoQ10 could reverse the depressive like behavior and bioenergetic effects of STZ in the treated groups.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri S, Haj-Mirzaian A, Rahimi-Balaei M, Razmi A, Kordjazy N, Shirzadian A, Mehr SE, Sianati H, Dehpour AR (2015) Co-occurrence of anxiety and depressive-like behaviors following adolescent social isolation in male mice; possible role of nitrergic system. Physiol Behav 145:38–44
Sonei N, Amiri S, Jafarian I, Anoush M, Rahimi-Balaei M, Bergen H, Haj-Mirzaian A, Hosseini M-J (2017) Mitochondrial dysfunction bridges negative affective disorders and cardiomyopathy in socially isolated rats: pros and cons of fluoxetine. World J Biol Psychiatry 18:39–53
de Morais H, de Souza CP, da Silva LM, Ferreira DM, Werner MF, Andreatini R, da Cunha JM, Zanoveli JM (2014) Increased oxidative stress in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus is related to depressive-like behavior in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Behav Brain Res 258:52–64
Souza LC, Carlos Filho B, Fabbro LD, de Gomes MG, Goes AT, Jesse CR (2013) Depressive-like behaviour induced by an intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in mice: the protective effect of fluoxetine, antitumour necrosis factor-α and thalidomide therapies. Behav Pharmacol 24:79–86
Rai S, Kamat PK, Nath C, Shukla R (2014) Glial activation and post-synaptic neurotoxicity: the key events in Streptozotocin (ICV) induced memory impairment in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 117:104–117
Haley T, McCormick W (1957) Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 12:12–15
Kraska A, Santin MD, Dorieux O, Joseph-Mathurin N, Bourrin E, Petit F, Jan C, Chaigneau M, Hantraye P, Lestage P (2012) In vivo cross-sectional characterization of cerebral alterations induced by intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin. PLoS ONE 7:e46196
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2011) Insulin receptor signaling in rat hippocampus: a study in STZ (ICV) induced memory deficit model. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:261–273
Javed H, Khan M, Ahmad A, Vaibhav K, Ahmad M, Khan A, Ashafaq M, Islam F, Siddiqui M, Safhi M (2012) Rutin prevents cognitive impairments by ameliorating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuroscience 210:340–352
Felker GM (2010) Coenzyme Q10 and statins in heart failure: the dog that didn’t bark. J Am Coll Cardiol 56(15):1205–1206
Franke AA, Morrison CM, Bakke JL, Custer LJ, Li X, Cooney RV (2010) Coenzyme Q10 in human blood: native levels and determinants of oxidation during processing and storage. Free Radic Biol Med 48:1610–1617
Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Hosseini M-J (2015) Therapeutic implication of coenzyme Q10 during statin therapy: pros and cons. Trends Pharm Sci 1:119–128
Lee B-J, Huang Y-C, Chen S-J, Lin P-T (2012) Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces oxidative stress and increases antioxidant enzyme activity in patients with coronary artery disease. Nutrition 28:250–255
Kumar A, Kaur H, Devi P, Mohan V (2009) Role of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in cardiac disease, hypertension and Meniere-like syndrome. Pharmacol Ther 124:259–268
Turunen M, Olsson J, Dallner G (2004) Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA 1660:171–199
Hidaka T, Fujii K, Funahashi I, Fukutomi N, Hosoe K (2008) Safety assessment of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Biofactors 32:199–208
Delanty N, Dichter M (1998) Oxidative injury in the nervous system. Acta Neurol Scand 98:145–153
Ishrat T, Khan MB, Hoda MN, Yousuf S, Ahmad M, Ansari MA, Ahmad AS, Islam F (2006) Coenzyme Q10 modulates cognitive impairment against intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Behav Brain Res 171:9–16
McMurray JJ, Dunselman P, Wedel H, Cleland JG, Lindberg M, Hjalmarson Å, Kjekshus J, Waagstein F, Apetrei E, Barrios V (2010) Coenzyme Q10, rosuvastatin, and clinical outcomes in heart failure: a pre-specified substudy of CORONA (controlled rosuvastatin multinational study in heart failure). J Am Coll Cardiol 56:1196–1204
Kerr DS (2013) Review of clinical trials for mitochondrial disorders: 1997–2012. Neurotherapeutics 10:307–319
Maes M, Mihaylova I, Kubera M, Uytterhoeven M, Vrydags N, Bosmans E (2009) Lower plasma Coenzyme Q 10 in depression: a marker for treatment resistance and chronic fatigue in depression and a risk factor to cardiovascular disorder in that illness. Neuroendocrinol Lett 30:462–469
Ochoa JJ, Quiles JL, Huertas JR, Mataix J (2005) Coenzyme Q10 protects from aging-related oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial function in heart of rats fed a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)-rich diet. J Gerontol Ser A 60:970–975
Gleize B, Steib M, André M, Reboul E (2012) Simple and fast HPLC method for simultaneous determination of retinol, tocopherols, coenzyme Q10 and carotenoids in complex samples. Food Chem 134:2560–2564
Jiang P, Wu M, Zheng Y, Wang C, Li Y, Xin J, Xu G (2004) Analysis of coenzyme Q10 in human plasma by column-switching liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 805:297–301
Karpińska J, Mikołuć B, Piotrowska-Jastrzębska J (1998) Application of derivative spectrophotometry for determination of coenzyme Q10 in pharmaceuticals and plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 17:1345–1350
Karpińska J, Mularczyk B (2004) The analysis of the zero-order and the second derivative spectra of retinol acetate, tocopherol acetate and coenzyme Q10 and estimation of their analytical usefulness for their simultaneous determination in synthetic mixtures and pharmaceuticals. Spectrochim Acta Part A 60:2189–2194
Haj-Mirzaian A, Kordjazy N, Amiri S, Haj-Mirzaian A, Amini-khoei H, Ostadhadi S, Dehpour A (2016) Involvement of nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of tropisetron and ondansetron in mice forced swimming test and tail suspension test. Eur J Pharmacol 780:71–81
Haj-Mirzaian A, Kordjazy N, Ostadhadi S, Amiri S, Haj-Mirzaian A, Dehpour A (2016) Fluoxetine reverses the behavioral despair induced by neurogenic stress in mice: role of N-methyl-d-aspartate and opioid receptors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94:599–612
Garjani A, Andalib S, Biabani S, Soraya H, Doustar Y, Garjani A, Maleki-Dizaji N (2011) Combined atorvastatin and coenzyme Q10 improve the left ventricular function in isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 666:135–141
Khorrami A, Garjani A, Ghanbarzadeh S, Andalib S (2014) Reduction of coenzyme Q10 content: a possible effect of isoproterenol on heart failure and myocardial infarction in rat. Drug Res 64:177–181
Behr GA, Moreira JC, Frey BN (2012) Preclinical and clinical evidence of antioxidant effects of antidepressant agents: implications for the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/609421
Gardner A, Boles RG (2011) Beyond the serotonin hypothesis: mitochondria, inflammation and neurodegeneration in major depression and affective spectrum disorders. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:730–743
Cornelius N, Byron C, Hargreaves I, Fernandez Guerra P, Furdek AK, Land J, Radford WW, Frerman F, Corydon TJ, Gregersen N (2013) Secondary coenzyme Q10 deficiency and oxidative stress in cultured fibroblasts from patients with riboflavin responsive multiple Acyl-CoA dehydrogenation deficiency. Hum Mol Genet 22:3819–3827
Lee B-J, Tseng Y-F, Yen C-H, Lin P-T (2013) Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation (300 mg/day) on antioxidation and anti-inflammation in coronary artery disease patients during statins therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J 12:142
Sanoobar M, Eghtesadi S, Azimi A, Khalili M, Khodadadi B, Jazayeri S, Gohari MR, Aryaeian N (2015) Coenzyme Q10 supplementation ameliorates inflammatory markers in patients with multiple sclerosis: a double blind, placebo, controlled randomized clinical trial. Nutr Neurosci 18:169–176
Morris G, Anderson G, Berk M, Maes M (2013) Coenzyme Q10 depletion in medical and neuropsychiatric disorders: potential repercussions and therapeutic implications. Mol Neurobiol 48:883–903
Slattery D, Cryan J (2017) Modelling depression in animals: at the interface of reward and stress pathways. Psychopharmacology 234:1451–1465
Schmelzer C, Lindner I, Rimbach G, Niklowitz P, Menke T, Döring F (2008) Functions of coenzyme Q10 in inflammation and gene expression. Biofactors 32:179–183
Maes M, Fišar Z, Medina M, Scapagnini G, Nowak G, Berk M (2012) New drug targets in depression: inflammatory, cell-mediated immune, oxidative and nitrosative stress, mitochondrial, antioxidant, and neuroprogressive pathways. And new drug candidates—Nrf2 activators and GSK-3 inhibitors. Inflammopharmacology 20:127–150
Maes M, Kubera M, Mihaylova I, Geffard M, Galecki P, Leunis J-C, Berk M (2013) Increased autoimmune responses against auto-epitopes modified by oxidative and nitrosative damage in depression: implications for the pathways to chronic depression and neuroprogression. J Affective Disord 149:23–29
Maes M, Galecki P, Chang YS, Berk M (2011) A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro) degenerative processes in that illness. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:676–692
Maes M, Ruckoanich P, Chang YS, Mahanonda N, Berk M (2011) Multiple aberrations in shared inflammatory and oxidative & nitrosative stress (IO&NS) pathways explain the co-association of depression and cardiovascular disorder (CVD), and the increased risk for CVD and due mortality in depressed patients. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:769–783
Butterfield DA, Boyd-Kimball D (2004) Amyloid β-peptide (1-42) contributes to the oxidative stress and neurodegeneration found in Alzheimer disease brain. Brain Pathol 14:426–432
Gasparini L, Netzer WJ, Greengard P, Xu H (2002) Does insulin dysfunction play a role in Alzheimer’s disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:288–293
Vajda FJE (2004) Neuroprotection and neurodegenerative disease. In: Richter RW, Richter BZ (eds) Alzheimer’s disease. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 235–243
Balercia G, Arnaldi G, Fazioli F, Serresi M, Alleva R, Mancini A, Mosca F, Lamonica G, Mantero F, Littarru G (2002) Coenzyme Q10 levels in idiopathic and varicocele-associated asthenozoospermia. Andrologia 34:107–111
De Pinieux G, Chariot P, Ammi-Said M, Louarn F, Lejonc J, Astier A, Jacotot B, Gherardi R (1996) Lipid-lowering drugs and mitochondrial function: effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on serum ubiquinone and blood lactate/pyruvate ratio. Br J Clin Pharmacol 42:333–337
Tiano L, Belardinelli R, Carnevali P, Principi F, Seddaiu G, Littarru GP (2007) Effect of coenzyme Q10 administration on endothelial function and extracellular superoxide dismutase in patients with ischaemic heart disease: a double-blind, randomized controlled study. Eur Heart J 28:2249–2255
Kuettner A, Pieper A, Koch J, Enzmann F, Schroeder S (2005) Influence of coenzyme Q10 and cerivastatin on the flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: results of the ENDOTACT study. Int J Cardiol 98:413–419
Ozcan ME, Gulec M, Ozerol E, Polat R, Akyol O (2004) Antioxidant enzyme activities and oxidative stress in affective disorders. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 19:89–95
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant from the deputy of research of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences (Grant No.: A-12-769-26).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andalib, S., Mashhadi-Mousapour, M., Bijani, S. et al. Coenzyme Q10 Alleviated Behavioral Dysfunction and Bioenergetic Function in an Animal Model of Depression. Neurochem Res 44, 1182–1191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02761-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02761-0