Abstract
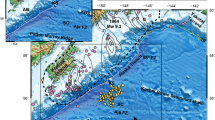
The earthquake of 21 May 2014 (Mw 6.0) in the northern Bay of Bengal (BOB) highlights the importance of studies on intraplate earthquakes in the oceanic regime for understanding the stress state of the oceanic lithosphere. The epicenter of the earthquake is located at a water depth of 2.5 km where the sediment thickness is nearly 12 km, and it occurs at a depth of ~50 km within the upper mantle. Its location on the seismotectonic map of the region shows that the epicenter is far from the seismically active zone of the Burmese Arc in the east and low-to-moderately active seismic region of the east coast of India in the west. The fault plane solution of this earthquake indicates that it was a strike-slip event with a right-lateral sense of motion on a NW-oriented nodal plane, and it occurred on one of the NW-SE-trending fracture zones previously mapped in the BOB. Based on a compilation of long-term (1900–2011) intraplate earthquakes along with available focal mechanisms in the BOB and the adjoining east coast of India, we conclude the following: (1) the Precambrian structural trends, basin-scale faults and minor lineaments on the east coast of India are favorably reactivated in their offshore extensions up to the shelf-slope areas of the margin; (2) earthquake occurrences in the BOB region can be correlated with the fracture zone trends in the central BOB and along the Ninetyeast ridge or at the intersections of fracture zones with the subsurface trace of the 85°E ridge. The 21 May 2014 earthquake is the result of reactivation of such a NW-SE-trending fracture zone lying in the lithosphere of >100 Ma in age. Further evaluation of this event in light of the global occurrence of oceanic intraplate earthquakes in the older lithosphere (>80 Ma) suggests that such reactivation is possible in the high ambient stress state.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen O, Knudsen P (2008) The DNSC08 Global gravity and bathymetry, European Geophysical Union meeting, April 14–18th, Vienna
Bastia R, Radhakrishna M, Srinivas T, Nayak S, Nathaniel DM, Biswal TK (2010) Structural and tectonic interpretation of geophysical data along the Eastern continental margin of India with special reference to the deep water petroliferous basins. J Asian Earth Sci 39:608–619
Bergman EA (1986) Intraplate earthquakes and the state of stress in oceanic lithosphere. Tectonophysics 132:1–35
Bergman EA, Solomon SC (1984) Source mechanisms of earthquakes near mid-ocean ridges from body waveform inversion: implications for the early evolution of oceanic lithosphere. J Geophys Res 89:11415–11441
Bergman EA, Solomon SC (1985) Earthquake source mechanisms from body wave inversion and intra-plate tectonics in the Northern Indian Ocean. Phys Earth Planet Inter 40:1–23
Biswas S, Majumdar RK (1997) Seismicity of the Bay of Bengal: evidence for intraplate deformation of the northern Indian plate. Tectonophysics 269:323–336
Blakely RJ (1995) Potential theory in gravity and magnetic applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 464
Brune JN, Curray J, Dorman L, Raitt R (1992) A proposed super-thick sedimentary basin, Bay of Bengal. Geophys Res Lett 19:565–568
Bull JM (1990) Structural style of intra-plate deformation Central Indian Ocean Basin: evidence for the role of fracture zones. Tectonophysics 184:213–228
Chandra U (1977) Earthquake of peninsular India—a seismotectonic study. Bull Seismol Soc Am 67:1387–1413
Cloetingh S, Wortel R (1985) Regional stress field of the Indian plate. Geophys Res Lett 12:77–80
Cordell L, Grauch VJS (1985) Mapping basement magnetization zones from aeromagnetic data in the San Juan basin, New Mexico. The utility of regional gravity and magnetic anomaly maps. Soc Explor Geophys 181–197. doi:10.1190/1.0931830346.ch16
Curray JR (1994) Sediment volume and mass beneath the Bay of Bengal. Earth Planet Sci Lett 125:371–383
Curray JR, Emmel FJ, Moore DG, Raitt RW (1982) Structure, tectonics and geological history of the northeastern Indian Ocean. In: Nairn AEM, Stehli FG (eds) The ocean basins and margins. The Indian ocean, 6. Plenum Press, New York, pp 399–450
Curray JR, Emmel FJ, Moore DG (2003) The Bengal fan: morphology, geometry, stratigraphy, history and processes. Mar Pet Geol 19:1191–1223
Dasgupta S, Mukhopadhyay M (1993) Seismicity and plate deformation below the Andaman arc, northeastern Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics 225:529–542
DeMets C, Gordon RG, Argus DF, Stein S (1990) Current plate motions. Geophys J Int 101:425–478
Dziewonski AM, Chou T-A, Woodhouse JH (1981) Determination of earthquake source parameters from waveform data for studies of global and regional seismicity. J Geophys Res 86:2825–2852
Ekström G, Nettles M, Dziewonski AM (2012) The global CMT project 2004–2010: centroid-moment tensors for 13,017 earthquakes. Phys Earth Planet Inter 200–201:1–9
Fuloria RC, Pandey RN, Bharali BR, Mishra JK (1992) Stratigraphy, structure and tectonics of the Mahanadi offshore Basin. Geol Surv India Spec Publ 29:255–265
Gaina C, Mueller RD, Brown B, Ishihara T (2003) Microcontinent formation around Australia. Geol Soc Aust Spec Publ 22:399–410
Gaina C, Mueller RD, Brown B, Ishihara T, Ivanov S (2007) Breakup and early seafloor spreading between India and Antarctica. Geophys J Int 170:151–169
Geller GA, Weissel JK, Anderson RN (1983) Heat transfer and intraplate deformation in the central Indian Ocean. J Geophys Res 88:1018–1032
GopalaRao D, Krishna KS, Sar D (1997) Crustal evolution and sedimentation history of the Bay of Bengal since the Cretaceous. J Geophys Res 102:17747–17768
Gowd TN, SriramaRao SV, Chary KB (1996) Stress field and seismicity in the Indian shield: effects of the collison between India and Eurasia. PAGEOPH 146:503–531
GSI (1993) Geological map of India, 1:2,000,000. Geological Survey of India and Indian Space Research Organization, Bangalore
GSI (ed) (2000) Seismotectonic Atlas of India and its environs. Geological Survey of India, Bangalore
GSI (2014) A brief note on 21st May 2014 Bay of Bengal earthquake (Mb 5.9). http://www.portal.gsi.gov.in/portal/page?_pageid=108,1620115&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL. Accessed 2 June 2014
Harvard (2014) Global CMT catalog search. http://www.globalcmt.org/CMTsearch.html. Accessed Aug 2014
Jarvis A, Reuter HI, Nelson A, Guevara, E, (2008) Hole-filled SRTM for the globe version 4, available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. (http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org)
Krishna KS, Michael Laju, Bhattacharyya R, Majumdar TJ (2009) Geoid and gravity anomaly data of conjugate regions of Bay of Bengal and Enderby Basin—new constraints on breakup and early spreading history between India and Antarctica. J Geophys Res 114:B03102. doi:10.1029/2008JB005808
Lal NK, Siawal A, Anil Kaul K (2009) Evolution of east coast of India e a plate tectonic reconstruction. J Geol Soc India 73:249–260
Lisker F, Fachmann S (2001) Phanerozoic history of the Mahanadi region, India. J Geophys Res B Solid Earth 106(B10):22027–22050
Mahalik NK (1996) Lithology and tectonothermal history of the precambrian rocks of Orissa along the eastern coast of India. J Southeast Asian Earth Sci 14:209–219
Martin SS, Hough SE (2015) The 21 May 2014 Mw 5.9 Bay of Bengal earthquake: macroseismic data suggest a high-stress-drop event. Seismol Res Lett 86:369–377
Maurin T, Rangin C (2009) Impact of the 90 degrees E ridge at the Indo-Burmese subduction zone imaged from deep seismic reflection data. Mar Geol 266:143–155
Maus S, Barckhausen U, Berkenbosch H, Bournas N, Brozena J, Childers V, Dostaler F, Fairhead JD, Finn C, von Frese RRB, Gaina C, Golynsky S, Kucks R, Lühr H, Milligan P, Mogren S, Müller RD, Olesen O, Pilkington M, Saltus R, Schreckenberger B, Thébault E, Caratori Tontini F (2009) EMAG2: a 2-arc-minute resolution earth magnetic anomaly grid compiled from satellite, airborne and marine magnetic measurements. Geochem Geophy Geosyst 10:Q08005. doi:10.1029/2009GC002471
Murthy KSR, Subrahmanyam V, Subrahmanyam AS, Murty GPS, Sarma KVLNS (2010) Land-ocean tectonics (LOTs) and the associated seismic hazard over the Eastern continental margin of india (ECMI). Nat Hazards 55:167–175
Nemcok M, Sinha ST, Stuart CJ, Welker C, Choudhuri M, Sharma SP, Misra AA, Sinha N, Venkatraman S (2013) East Indian margin evolution and crustal architecture: integration of deep reflection seismic interpretation and gravity modeling. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 369:477–496. doi:10.1144/SP369.6
Pavlis NK, Holmes SA, Kenyon SC, Factor JK (2012) The development and evaluation of the earth gravitational model 2008 (EGM2008). J Geophys Res 117:B04406. doi:10.1029/2011JB008916
Powell CM, Roots SR, Veevers JJ (1988) Pre-breakup continental extension in East Gondwanaland and the early opening of the eastern Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics 155:261–283
Radhakrishna M, Verma RK, Arora SK (1998) Near-ridge intraplate seismicity in the Indian Ocean. Mar Geol 147:109–122
Radhakrishna M, Chand Shyam, Subrahmanyam C (2000) Gravity anomalies, sediment loading and lithospheric flexure associated with the Krishna–Godavari basin, eastern continental margin of India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 175:223–232
Radhakrishna M, Lasitha S, Mukhopadhyay M (2008) Seismicity, gravity anomalies and lithospheric structure of the Andaman arc, NE Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics 460:248–262
Radhakrishna M, Subrahmanyam C, Twinkle D (2010) Thin oceanic crust below Bay of Bengal inferred from 3-D gravity interpretation. Tectonophysics 493:93–105
Radhakrishna M, Rao GS, Nayak S, Bastia R, Twinkle D (2012) Early cretaceous fracture zones in the Bay of Bengal and their tectonic implications: constraints from multi-channel seismic reflection and potential field data. Tectonophysics 522:187–197
Rajaram M, Anand SP, Balakrishna TS (2006) Composite magnetic anomaly map of India and its contiguous regions. J Geol Soc India 68:569–576
Ramana MV, Nair RR, Sarma KVLNS, Ramprasad T, Krishna KS, Subrahmanyam V, D’Cruz M, Subrahmanyam C, Paul J, Subrahmanyam AS, Chandra Sekhar DV (1994) Mesozoic anomalies in the Bay of Bengal, earth planet. Sci Lett 121:469–475
Rao NCh, Rao NP, Kumar MR, Prasanna S, Srinagesh D (2015) Structure and tectonics of the Bay of Bengal through waveform modeling of the 21 May 2014 earthquake of magnitude 6.0. Seismol Res Lett 86:378–384
Rastogi BK (1992) Seismotectonics inferred from earthquakes and earthquake sequences in India during the 1980s. Curr Sci 62:1–25
Rastogi BK (2001) EQ News DST Biannu Newsl 2:3
Ray DK (1963) Tectonic Map of India, 1:2,000,000. Geological Society of India, Calcutta
Reddy PR, Chandrakala KJ (2004) Seismicity in and around Ongole, Andhra Pradesh—an appraisal. J Indian Geophys Union 8:143–146
Roest W, Verhoef J, Pilkington M (1992) Magnetic interpretation using the 3-D analytic signal. Geophysics 57:116–125
Royer J-Y, Sandwell DT (1989) Evolution of the Eastern Indian ocean since the late cretaceous: constraints from GEOSAT altimetry. J Geophys Res 94:13755–13782
Sandwell DT (1984) Thermo-mechanical evolution of oceanic fracture zones. J Geophys Res 89:11401–11413
Sandwell DT, Schubert G (1982) Lithospheric flexure at fracture zones. J Geophys Res 87:4657–4667
Sarma KVLNS, Subrahmanyam V, Subrahmanyam AS, Murty GPS, Murthy KSR (2009) Significance of Gundlakamma river (Krishna Basin) fault over Eastern continental margin of Indian—a qualitative appraisal. Curr Sci 98:1438–1439
Satyanarayan GV, Chakracarthy DC, Rao PR, Pathan MS, Meetei LI (2014) Geophysical evidences of recent earthquake in Bay of Bengal. GSI: 1–3. http://www.portal.gsi.gov.in/portal/page?_pageid=108,1620115&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL. Accessed 12 June 2014
Steckler MS, Akhter SH, Seeber L (2008) Collision of the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta with the Burma Arc: implications for earthquake hazard. Earth Planet Sci Lett 273:367–378
Stein CA, Weissel JK (1990) Constraints on central Indian ocean basin thermal structure from heat flow, seismicity and bathymetry. Tectonophysics 176:315–332
Subrahmanyam C, Singh RN (1992) Geotectonics of the Bay of Bengal. Indian J Pet Geol 1:161–180
Subrahmanyam AS, Lakshminarayana S, Chandrasekhar DV, Murthy KSR, Rao TCS (1995) Offshore structural trends from magnetic data over Cauvery Basin, east coast of India. J Geol Soc India 46:269–273
Subrahmanyam C, Thakur NK, Rao TG, Ramana MV, Subrahmanyam V (1999) Tectonics of the Bay of Bengal, northeastern Indian ocean: new insights from satellite-derived gravity and ship-borne geophysical data. Earth Planet Sci Lett 171:237–251
Subrahmanyam AS, Murty GPS, Sarma KVLNS, Mohana Rao K, Reddy NPC, Malleswara Rao MM, Subrahmanyam V, Suneetha Rani P, Anuradha A, Murthy KSR (2007) Qualitative assessment of tectonic lineaments over the coastal and inner-shelf of Kakinada and Kalingapatnam, central east coast of India. J Geol Soc India 69:1328–1334
Subrahmanyam V, Subrahmanyam AS, Murty GPS, Murthy KSR (2008) Morphology and tectonics of Mahanadi Basin, northeastern continental margin of India from geophysical studies. Mar Geol 253:63–72
Talukdar SN (1982) Geology and hydrocarbon prospects of east coast basins of India and their relationship to evolution of the Bay of Bengal. In: Offshore south-east Asia conference. (Singapore), Exploration I, Gen. Sess., pp 1–8
Talwani M, Heirtzler JR (1964) Computations of magnetic anomalies caused by two-dimensional bodies of arbitrary shape. In: Parks GA (ed) Computers in the mineral industry, part I, vol 9. Stanford University Publication Geological Science, Stanford, pp 464–480
Talwani M, Worzel JL, Landisman M (1959) Rapid gravity computations for two-dimensional bodies with application to the Mendocino submarine fracture zone. J Geophys Res 64:49–59
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) (2014) M6.0-Bay of Bengal. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/dyfi/events/us/b000qy82/us/index.html. Accessed August 2014
Venkatarengan R, Ray D (1993) Geology and petroleum systems, Krishna-Godavari basin. In: Biswas SK (ed) Proceedings of the second seminar on petroliferous basins of India, vol 1. Indian Petrol Publication, Dehra Dun, pp 331–354
Weins DA (1985) Historical seismicity near Chagos: a complex deformation zone in the equatorial Indian ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 76:350–360
Weissel JK, Andreson RN, Geller CA (1980) Deformation of the Indo–Australian plate. Nature 287:284–291
Yoshida M, Rajesh HM, Santosh M (1999) Juxtaposition of India and Madagascar: a perspective. Gondwana Res 2:449–462
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out as part of the IITB-NIO collaborative project sponsored by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES/P.O.(Seismo)/1(141) 2011). The financial support by the MoES is gratefully acknowledged. The Generic Mapping Tool (GMT) software is used for drawing the figures in this study. Critical comments from two anonymous reviewers and the editor while revising the manuscript were of great benefit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, G.S., Radhakrishna, M. & Murthy, K.S.R. A seismotectonic study of the 21 May 2014 Bay of Bengal intraplate earthquake: evidence of onshore-offshore tectonic linkage and fracture zone reactivation in the northern Bay of Bengal. Nat Hazards 78, 895–913 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1750-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1750-6