Abstract
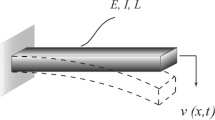
In this paper we analyze the vibrations of nonlinear structures by means of the novel approach of isogeometric finite elements. The fundamental idea of isogeometric finite elements is to apply the same functions, namely B-Splines and NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines), for describing the geometry and for representing the numerical solution. In case of linear vibrational analysis, this approach has already been shown to possess substantial advantages over classical finite elements, and we extend it here to a nonlinear framework based on the harmonic balance principle. As application, the straight nonlinear Euler–Bernoulli beam is used, and overall, it is demonstrated that isogeometric finite elements with B-Splines in combination with the harmonic balance method are a powerful means for the analysis of nonlinear structural vibrations. In particular, the smoother k-method provides higher accuracy than the p-method for isogeometric nonlinear vibration analysis.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ginsberg, J.H.: Mechanical and Structural Vibrations: Theory and Applications. Wiley, New York (2001)
Hughes, T.J.R.: The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element Analysis. Dover, Mineola, New York (2000)
Farin, G.E.: Curves and Surfaces for CAGD: A Practical Guide. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (2002)
Piegl, L., Tiller, W.: The NURBS Book. Springer, London (1995)
Rogers, D.F.: An Introduction to NURBS with Historical Perspective. Academic Press, San Diego (2001)
Hughes, T.J.R., Cottrell, J.A., Bazilevs, Y.: Isogeometric analysis: cad, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194(39-41), 4135–4195 (2005)
Szabó, B., Babuška, I.: Finite Element Analysis. Wiley, New York (1991)
Bazilevs, Y., Calo, V.M., Hughes, T.J.R., Zhang, Y.: Isogeometric fluid-structure interaction: theory, algorithms, and computations. Comput. Mech. 43(1), 3–37 (2008)
Cottrell, J.A., Reali, A., Bazilevs, Y., Hughes, T.J.R.: Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195(41–43), 5257–5296 (2006)
Vuong, A.-V., Heinrich, C., Simeon, B.: Isogat: a 2d tutorial Matlab code for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 27, 644–655 (2010)
Ziani, M., Duvigneau, R., Dörfel, M.: On the role played by NURBS weights in isogeometric structural shape optimization. In: International Conference on Inverse Problems, Control and Shape Optimization, Cartagena, Spain, April 2010
Aigner, M., Heinrich, C., Jüttler, B., Pilgerstorfer, E., Simeon, B., Vuong, A.-V.: Swept volume parameterization for isogeometric analysis. In: Mathematics of Surfaces XIII. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 5654, pp. 19–44. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg (2009)
Bazilevs, Y., Beirão de Veiga, L., Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Sangalli, G.: Isogeometric analysis: approximation stability and error estimates for h-refined meshes. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 16(7), 1031–1090 (2006)
Dörfel, M., Jüttler, B., Simeon, B.: Adaptive isogeometric analysis by local h-refinement with t-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(5–8), 264–275 (2010)
Hughes, T.J.R., Reali, A., Sangalli, G.: Efficient quadrature for NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(5–8), 301–313 (2010)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Buffa, A., Rivas, J., Sangalli, G.: Some estimates for h-p-k-refinement in isogeometric analysis. Numer. Math. 118, 271–305 (2011)
Vuong, A.-V., Gianelli, C., Jüttler, B., Simeon, B.: A hierarchical approach to adaptive local refinement in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200(49–52), 3554–3567 (2011)
Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Bazilevs, Y.: Isogeometric Analysis: Toward Integration of CAD and FEA. Wiley, New York (2009)
Ferri, A.A.: On the equivalence of the incremental harmonic balance method and the harmonic balance-Newton–Raphson method. J. Appl. Mech. 53(2), 455–457 (1986)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical Computational, and Experimental Methods. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (1995)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley Classics Library. Wiley, New York (1995)
Szemplinska-Stupnicka, W.: The Behaviour of Nonlinear Vibrating Systems. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, Boston, London (1990)
Wagg, D., Neild, S.: Nonlinear Vibration with Control: For Flexible and Adaptive Structures. Solid Mechanics and Its Applications. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Worden, K., Tomlinson, G.R.: Nonlinearity in Structural Dynamics: Detection, Identification and Modelling. Institute of Physics, Bristol (2001)
Lewandowski, R.: Non-linear, steady-state vibration of structures by harmonic balance/finite element method. Comput. Struct. 44(1–2), 287–296 (1992)
Lewandowski, R.: Computational formulation for periodic vibration of geometrically nonlinear structures, part 1: theoretical background; part 2: numerical strategy and examples. Int. J. Solids Struct. 34(15), 1925–1964 (1997)
Ribeiro, P., Petyt, M.: Non-linear vibration of beams with internal resonance by the hierarchical finite element method. J. Sound Vib. 224(15), 591–624 (1999)
Ribeiro, P.: Hierarchical finite element analyses of geometrically non-linear vibration of beams and plane frames. J. Sound Vib. 246(2), 225–244 (2001)
Ribeiro, P.: Non-linear forced vibrations of thin/thick beams and plates by the finite element and shooting methods. Comput. Struct. 82(17–19), 1413–1423 (2004)
Cheung, Y.K., Chen, S.H., Lau, S.L.: Application of the incremental harmonic balance method to cubic non-linearity systems. J. Sound Vib. 140(2), 273–286 (1990)
Chen, S.H., Cheung, Y.K., Xing, H.X.: Nonlinear vibration of plane structures by finite element and incremental harmonic balance method. Nonlinear Dyn. 26, 87–104 (2001)
Reddy, J.N.: An Introduction to Nonlinear Finite Elements. Oxford University Press, New York (2004)
Gross, D., Hauger, W., Wriggers, P.: Technische Mechanik 4—Hydromechanik, Elemente der Höheren Mechanik, Numerische Methoden, 7. auflage edition. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2009)
Bobylev, N.A., Burman, Y.M., Korovin, S.K.: Approximation Procedures in Nonlinear Oscillation Theory. De Gruyter Series in Nonlinear Analysis and Applications. W. de Gruyer, Berlin (1994)
Schneider, M., Wever, U., Zheng, Q.: Parallel harmonic balance. In: VLSI 93, Proceedings of the IFIP TC10/WG 10.5 International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration, Grenoble, France, 7–10 September, 1993, pp. 251–260 (1993)
Allgower, E.L., Georg, K.: Introduction to Numerical Continuation Methods. Colorado State University, Fort Collins (1990)
Haisler, W.E., Stricklin, J.A., Key, J.E.: Displacement incrementation in non-linear structural analysis by the self-correcting method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 11(1), 3–10 (1977)
Belytschko, T., Liu, W.K., Moran, B.: Nonlinear Finite Elements for Continua and Structures. Wiley, New York (2000)
Oden, J.T.: Finite Elements of Nonlinear Continua. Dover Civil and Mechanical Engineering Series. Dover, New York (2006)
TERRIFIC: Towards enhanced integration of design and production in the factory of the future through isogeometric technologies. EU Project FP7, FoF-ICT-2011.7.4
Acknowledgements
The authors were supported by the 7th Framework Programme of the European Union, project TERRIFIC (FP7-2011-NMP-ICT-FoF 284981) [40].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weeger, O., Wever, U. & Simeon, B. Isogeometric analysis of nonlinear Euler–Bernoulli beam vibrations. Nonlinear Dyn 72, 813–835 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-0755-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-0755-5