Abstract
Purpose
A series of C2-substituted ATP analogues was previously shown to have potent insulin-secreting properties, yet with poor tissue-selectivity for the pancreatic β-cell. The present study was designed to evaluate the binding profile on β-cell membranes and the effects on insulin release and pancreatic vascular resistance of a second generation of P2Y1 receptor agonists, based on C2-substitution of the adenosine 5′-O-(1-boranotriphosphate) scaffold.
Materials and Methods
Functional experiments were performed in the rat isolated pancreas model; binding studies with ATP-α-[35S] were performed in membrane homogenates from the rat insulinoma INS-1 cell line. The diastereoisomers of the compounds are designated by A and B.
Results
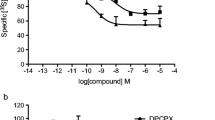
Under 8.3 mmol l−1 glucose, 2-methylthio-ATP-α-B, A isomer, induced a biphasic and concentration dependent insulin response; its maximal efficacy reaches ninefold the baseline secretion and its EC50 is 28.1 nmol l−1. No significant effect of this isomer was observed on vascular resistance, whereas the B isomer, which was a less potent insulin secretagogue, consistently induced a transient vasoconstriction. Interestingly, the insulin response induced by 2-methylthio-ATP-α-B, A isomer, was clearly glucose-dependent. This drug competes with ATP-α-[35S] binding in a complex two sites interaction model, with a K 0.5 value of 17.7 nmol l−1. 2-Chloro-ATP-α-B had a similar insulin-secreting profile as 2-methylthio-ATP-α-B, with a lower tissue-selectivity. The non-substituted ATP-α-B analog, A isomer, was less potent than the C2-substituted derivatives (A isomers) and had a vasorelaxant effect.
Conclusions
We conclude that 2-methylthio-ATP-α-B, A isomer, is a potent and tissue-selective P2Y receptor agonist with high efficacy. Its insulin-releasing action is glucose-dependent, which gives interest to this compound as a drug candidate for treating type 2 diabetes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Bertrand, J. Chapal, M. M. Loubatières-Mariani, and M. Roye. Evidence for two different P2-purinoceptors on β-cell and pancreatic vascular bed. Br. J. Pharmacol.91:783–787 (1987).
J. Fernandez-Alvarez, D. Hillaire-Buys, M. M. Loubatières-Mariani, R. Gomis, and P. Petit P. P2 receptor agonists stimulate insulin release from human pancreatic islets. Pancreas22:69–71 (2001).
P. Petit, D. Hillaire-Buys, M. M. Loubatières-Mariani, and J. Chapal. Purinergic receptors and the pharmacology of type 2 diabetes. In M. P. Abbrachio and M. Williams (eds.), Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology: Purinergic and Pyrimidinergic Signalling, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 2001, pp. 377–391.
A. Farret, M. Vignaud, S. Dietz, J. Vignon, P. Petit, and R. Gross. P2Y purinergic potentiation of glucose-induced insulin secretion and pancreatic β-cell metabolism. Diabetes 53 (Suppl 3):S63–S66 (2004).
P. Petit, D. Hillaire-Buys, M. Manteghetti, S. Debrus, J. Chapal, and M. M. Loubatières-Mariani. Evidence for two different types of P2-receptors stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cell. Br. J. Pharmacol.125:1368–1374 (1998).
H. Chevassus, A. Roig, C. Belloc, A. D. Lajoix, M. Manteghetti, and P. Petit. P2Y-receptor activation enhances insulin release from pancreatic β-cells by triggering the cyclic AMP/protein kinase A pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol.366:464–469 (2002).
R. Coutinho-Silva, M. Parsons, T. Robson, and G. Burnstock. Changes in expression of P2 receptors in rat and mouse pancreas during development and ageing. Cell Tissue Res.306:373–383 (2001).
R. Coutinho-Silva, M. Parsons, T. Robson, J. Lincoln, and G. Burnstock. P2X and P2Y purinoceptor expression in pancreas from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.204:141–154 (2003).
C. Léon, M. Freund, O. Latchoumanin, A. Farret, P. Petit, and J. P. Cazenave. The P2Y1 receptor is involved in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis and in insulin secretion in mice. Purinergic Signalling1:145–151 (2005).
P. Petit, G. Bertrand, W. Schmeer, and J. C. Henquin. Effects of extracellular nucleotides on the electrical, ionic and secretory events in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol.98:875–882 (1989).
C. R. Poulsen, K. Bokvist, H. L. Olsen, M. Hoy, K. Capito, P. Gilon, and J. Gromada. Multiple sites of purinergic control of insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes48:2171–2181 (1999).
J. Chapal, D. Hillaire-Buys, G. Bertrand, D. Pujalte, P. Petit, and M. M. Loubatières-Mariani. Comparative effects of adenosine-5′-triphosphate and related analogues on insulin secretion from the rat pancreas. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol.11:537–545 (1997).
B. Fischer, J. L. Boyer, C. H. Hoyle, A. U. Ziganshin, A. L. Brizzolara, G. E. Knight, J. Zimmet, G. Burnstock, T. K. Harden, and K. A. Jacobson. Identification of potent, selective P2Y-purinoceptor agonists: structure-activity relationships for 2-thioether derivatives of adenosine 5′-triphosphate. J. Med. Chem.36:3937–3946 (1993).
B. Fischer, A. Chulkin, J. L. Boyer, K. T. Harden, F. P. Gendron, A. R. Beaudoin, J. Chapal, D. Hillaire-Buys, and P. Petit. 2-Thioether 5′-O-(1-thiotriphosphate)adenosine derivatives as new insulin secretagogues acting through P2Y-receptors. J. Med. Chem.42:3636–3646 (1999).
D. Hillaire-Buys, L. Shahar, B. Fischer, A. Chulkin, N. Linck, J. Chapal, M. M. Loubatières-Mariani, and P. Petit. Pharmacological evaluation and chemical stability of 2-benzylthioether-5′-O-(1-thiotriphosphate)-adenosine, a new insulin secretagogue acting through P2Y receptors. Drug Dev. Res.53:33–43 (2001).
V. Nahum, G. Zundorf, S. A. Levesque, A. R. Beaudoin, G. Reiser, and B. Fischer. Adenosine 5′-O-(1-boranotriphosphate) derivatives as novel P2Y(1) receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem.45:5384–5396 (2002).
M. M. Loubatières-Mariani, H. Demalbosc, G. Ribes, and J. Chapal. Etude expérimentale d’un nouveau sulfamide hypoglycémiant particulièrement actif, le HB 419 ou glibenclamide. Diabetologia5:1–10 (1969).
D. Hillaire-Buys, J. Chapal, P. Petit, and M. M. Loubatières-Mariani. Dual regulation of pancreatic vascular tone by P2X and P2Y purinoceptor subtypes. Eur. J. Pharmacol.199:309–314 (1991).
M. Asfari, D. Janjic, P. Meda, G. Li, P. A. Halban, and C. B. Wollheim. Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology130:167–178 (1992).
G. Bertrand, J. Chapal, R. Puech, and M. M. Loubatières-Mariani. Adenosine-5′-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) is a potent agonist at P2 purinoceptors mediating insulin secretion from perfused rat pancreas. Br. J. Pharmacol. 102:627–630 (1991).
G. Burnstock and G. E. Knight. Cellular distribution and functions of P2 receptor subtypes in different systems. Int. Rev. Cyt.240:31–304 (2004).
V. Ralevic and G. Burnstock. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev.50:413–492 (1998).
M. E. Tulapurkar, W. Laubinger, V. Nahum, B. Fischer, and G. Reiser. Subtype specific internalization of P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors induced by novel adenosine 5′-O-(1-boranotriphosphate) derivatives. Br. J. Pharmacol.142:869–878 (2004).
R. Filhol, L. Lugo-Garcia, C. Jahannault, C. Didier, R. Gross, P. Petit, and J. Vignon. Complex interaction of ATP-alpha-[35S] with membrane P2 receptors of insulin-secreting β-cells. 9th Annual Meeting of the Société Française de Pharmacologie, Bordeaux, April 26–28. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol.19:226 (2005).
R. Schäfer and G. Reiser. ATP-α-S is a ligand for P2Y receptors in synaptosomal membranes: solubilization of [35S]ATP-α-S binding proteins associated with G-proteins. Neurochem. Int.34:303–317 (1999).
W. Laubinger and G. Reiser. Differential characterization of binding sites for adenine and uridine nucleotides in membranes from rat lung as possible tools for studying P2 receptors in lung. Biochem. Pharmacol.55:687–695 (1998).
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Mr. Michel Tournier for expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farret, A., Filhol, R., Linck, N. et al. P2Y Receptor Mediated Modulation of Insulin Release by a Novel Generation of 2-Substituted-5′-O-(1-Boranotriphosphate)-Adenosine Analogues. Pharm Res 23, 2665–2671 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9112-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9112-4