Abstract
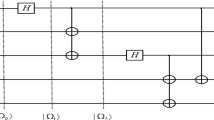
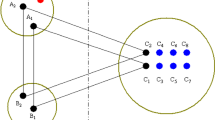
A novel scheme for quantum communication having substantial applications in practical life is designed and analyzed. Specifically, we have proposed a hierarchical counterpart of the joint remote state preparation (JRSP) protocol, where two senders can jointly and remotely prepare a quantum state. One sender has the information regarding amplitude, while the other one has the phase information of a quantum state to be jointly prepared at the receiver’s port. However, there exists a hierarchy among the receivers, as far as powers to reconstruct the quantum state are concerned. A 5-qubit cluster state has been used here to perform the task. Further, it is established that the proposed scheme for hierarchical JRSP (HJRSP) is of enormous practical importance in critical situations involving defense and other sectors, where it is essential to ensure that an important decision/order that can severely affect a society or an organization is not taken by a single person, and once the order is issued, all the receivers do not possess an equal right to implement it. Further, the effect of different noise models (e.g., amplitude damping (AD), phase damping (PD), collective noise and Pauli noise models) on the HJRSP protocol proposed here is investigated. It is found that in AD and PD noise models a higher-power agent can reconstruct the quantum state to be remotely prepared with higher fidelity than that done by the lower-power agent(s). In contrast, the opposite may happen in the presence of collective noise models. We have also proposed a scheme for probabilistic HJRSP using a non-maximally entangled 5-qubit cluster state.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grover, L.K.: Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 325–328 (1997)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe. IEEE Computer Society Press (1994)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, New Delhi (2008)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Pathak, A.: Elements of Quantum Computation and Quantum Communication. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2013)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4394 (1998)
Pathak, A., Banerjee, A.: Efficient quantum circuits for perfect and controlled teleportation of n-qubit non-maximally entangled states of generalized Bell-type. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 9, 389–403 (2011)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Bertaiume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Wang, X.-W., Xia, L.-X., Wang, Z.-Y., Zhang, D.-Y.: Hierarchical quantum-information splitting. Opt. Commun. 283, 1196–1199 (2010)
Shukla, C., Pathak, A.: Hierarchical quantum communication. Phys. Lett. A 377, 1337–1344 (2013)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63, 014302 (2000)
Wang, X.-W., Zhang, D.-Y., Tang, S.-Q., Zhan, X.-G., You, K.-M.: Hierarchical quantum information splitting with six-photon cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 2691–2697 (2010)
Wang, X.-W., Zhang, D.-Y., Tang, S.-Q., Xie, L.-J.: Multiparty hierarchical quantum-information splitting. J. Phys. B 44, 035505 (2011)
Mishra, S., Shukla, C., Pathak, A., Srikanth, R., Venugopalan, A.: An integrated hierarchical dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54, 3143–3154 (2015)
An, N.B., Kim, J.: Joint remote state preparation. J. Phys. B 41, 095501 (2008)
Peng, J.-Y., Luo, M.-X., Mo, Z.-W.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-particle states via GHZ-type states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 2325–2342 (2013)
Chen, Q.Q., Xia, Y., Song, J., An, N.B.: Joint remote state preparation of a W-type state via W-type states. Phys. Lett. A 374, 4483–4487 (2010)
An, N.B.: Joint remote state preparation via W and W-type states. Opt. Commun. 283, 4113–4117 (2010)
An, N.B., Cao, T.B., Nung, V.D., Kim, J.: Remote state preparation with unit success probability. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2, 035009 (2011)
Sharma, V., Shukla, C., Banerjee, S., Pathak, A.: Controlled bidirectional remote state preparation in noisy environment: a generalized view. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3441–3464 (2015)
Luo, M.-X., Deng, Y., Chen, X.-B., Yang, Y.-X.: The faithful remote preparation of general quantum states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 279–294 (2013)
Dai, H.Y., Chen, P.X., Liang, L.M., Li, C.Z.: Classical communication cost and remote preparation of the four-particle GHZ class state. Phys. Lett. A 355, 285–288 (2006)
Ma, P.-C., Zhan, Y.-B.: Scheme for probabilistic remotely preparing a multi-particle entangled GHZ state. Chin. Phys. B 17, 445 (2008)
Ma, P.-C., Zhan, Y.-B.: Scheme for remotely preparing a four-particle entangled cluster-type state. Opt. Commun. 283, 2640–2643 (2010)
Zhan, Y.-B., Fu, H., Li, X.-W., Ma, P.-C.: Deterministic remote preparation of a four-qubit cluster-type entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 2615–2622 (2013)
Peters, N.A., Barreiro, J.T., Goggin, M.E., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Remote state preparation: arbitrary remote control of photon polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 150502 (2005)
Liu, W.T., Wu, W., Ou, B.Q., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z., Yuan, J.M.: Experimental remote preparation of arbitrary photon polarization states. Phy. Rev. A 76, 022308 (2007)
Knoll, L.T., Schmiegelow, C.T., Larotonda, M.A.: Remote state preparation of a photonic quantum state via quantum teleportation. Appl. Phys. B 115, 541–546 (2014)
Xiang, G.Y., Li, J., Yu, B., Guo, G.C.: Remote preparation of mixed states via noisy entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012315 (2005)
Rådmark, M., Wieśniak, M., Żukowski, M., Bourennane, M.: Experimental multilocation remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. A 88, 032304 (2013)
Peng, X., Zhu, X., Fang, X., Feng, M., Liu, M., Gao, K.: Experimental implementation of remote state preparation by nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Lett. A 306, 271–276 (2003)
Wang, M.M., Wang, W., Chen, J.G., et al.: Secret sharing of a known arbitrary quantum state with noisy environment. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4211–4224 (2015)
Guan, X.-W., Chen, X.-B., Wang, L.-C., Yang, Y.-X.: Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state in noisy environments. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53, 2236–2245 (2014)
Lu, C.-Y., Gao, W.-B., Zhang, J., Zhou, X.-Q., Yang, T., Pan, J.-W.: Experimental quantum coding against qubit loss error. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 11050–11054 (2008)
Pan, J.W., Chen, Z.B., Lu, C.Y., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A., Ż ukowski, M.: Multiphoton entanglement and interferometry. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 777 (2012)
Sharma, R.D., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A., Pan, A.K., De, A.: Which verification qubits perform best for secure communication in noisy channel? Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 1703–1718 (2016)
Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Applications of quantum cryptographic switch: various tasks related to controlled quantum communication can be performed using Bell states and permutation of particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 2599–2616 (2015)
Li, Y.H., Jin, X.M.: Bidirectional controlled teleportation by using nine-qubit entangled state in noisy environments. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 929–945 (2016)
Zanardi, P., Rasetti, M.: Noiseless quantum codes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 3306 (1997)
Bourennane, M., Eibl, M., Gaertner, S., Kurtsiefer, C., Cabello, A., Weinfurter, H.: Decoherence-free quantum information processing with four-photon entangled states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 107901 (2004)
Prakash, H., Chandra, N., Prakash, R.: Improving the teleportation of entangled coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 75, 044305 (2007)
Wang, M.M., Qu, Z.G., Wang, W., Chen, J.G.: Effect of noise on deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 140 (2017)
Fortes, R., Rigolin, G.: Fighting noise with noise in realistic quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 92, 012338 (2015)
Henderson, L., Hardy, L., Vedral, V.: Two-state teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 61, 062306 (2000)
Sisodia, M., Verma, V., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Teleportation of a qubit using entangled non-orthogonal states: a comparative study. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 76 (2017)
Preskill, J.: Lecture Notes for Physics 229: Quantum Information and Computation. California Institute of Technology (1998)
Joo, J., Park, Y.J., Oh, S., Kim, J.: Quantum teleportation via a W state. New J. Phys. 5, 136 (2003)
Srikanth, R., Banerjee, S.: Squeezed generalized amplitude damping channel. Phys. Rev. A 77, 012318 (2008)
Thapliyal, K., Banerjee, S., Pathak, A., Omkar, S., Ravishankar, V.: Quasiprobability distributions in open quantum systems: spin-qubit systems. Ann. Phys. 362, 261–286 (2015)
Sharma, V., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A., Banerjee, S.: A comparative study of protocols for secure quantum communication under noisy environment: single-qubit-based protocols versus entangled-state-based protocols. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 4681–4710 (2016)
Chiuri, A., Rosati, V., Vallone, G., Pádua, S., Imai, H., Giacomini, S., Macchiavello, C., Mataloni, P.: Experimental realization of optimal noise estimation for a general Pauli channel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 253602 (2011)
Fischer, D.G., Mack, H., Cirone, M.A., Freyberger, M.: Enhanced estimation of a noisy quantum channel using entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 64, 022309 (2001)
Fern, J., Whaley, K.B.: Lower bounds on the nonzero capacity of Pauli channels. Phys. Rev. A 78, 062335 (2008)
Acknowledgements
CS thanks Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows No. 15F15015. AP thanks Department of Science and Technology (DST), India, for the support provided through the Project No. EMR/2015/000393. Authors thank M. Ozawa for his interest in the work and for some useful suggestions and comments. Authors thank Roopal Vegad for her help in preparing a schematic diagram.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, C., Thapliyal, K. & Pathak, A. Hierarchical joint remote state preparation in noisy environment. Quantum Inf Process 16, 205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1654-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1654-3