Abstract
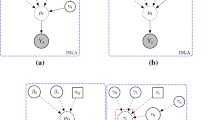
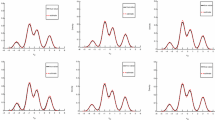
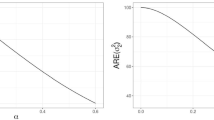
Hierarchical generalized linear models (HGLMs) have become popular in data analysis. However, their maximum likelihood (ML) and restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimators are often difficult to compute, especially when the random effects are correlated; this is because obtaining the likelihood function involves high-dimensional integration. Recently, an h-likelihood method that does not involve numerical integration has been proposed. In this study, we show how an h-likelihood method can be implemented by modifying the existing ML and REML procedures. A small simulation study is carried out to investigate the performances of the proposed methods for HGLMs with correlated random effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E.: On a formulae for the distribution of the maximum likelihood estimator. Biometrika 70, 343–365 (1983)
Breslow, N.E., Clayton, D.G.: Approximate inference in generalized linear mixed models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 88, 9–25 (1993)
Clayton, D., Kaldor, J.: Empirical Bayes estimates of age-standardized relative risks for use in disease mapping. Biometrics 43, 671–681 (1987)
Cox, D.R., Reid, N.: Parameter orthogonality and approximate conditional inference. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 49, 1–39 (1987)
Crowder, M.J.: Beta-binomial ANOVA for proportions. Appl. Stat. 27, 34–37 (1978)
Fisher, R.A.: Frequency distribution of the values of the correlation coefficient in samples of an indefinitely large population. Biometrika 10, 507–521 (1915)
Goldstein, H., Rasbash, J.: Improved approximations for multilevel models with binary responses. J. R. Stat. Soc. A 159, 505–513 (1996)
Ha, I., Noh, M., Lee, Y.: Bias reduction of likelihood estimators in semiparametric frailty models. Scand. J. Stat. 37, 307–320 (2010)
Harville, D.: Maximum likelihood approached to variance component estimation and related problems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 72, 320–340 (1977)
Joe, H.: Accuracy of Laplace approximation for discrete response mixed models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52, 5066–5074 (2008)
Lee, Y., Ha, I.: Orthodox BLUP versus h-likelihood methods for inferences about random effects in Tweedie mixed models. Stat. Comput. 20, 295–303 (2010)
Lee, Y., Nelder, J.A.: Hierarchical generalized linear models (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. B 58, 619–678 (1996)
Lee, Y., Nelder, J.A.: Hierarchical generalized linear models: A synthesis of generalized linear models, random effect model and structured dispersion. Biometrika 88, 987–1006 (2001)
Lee, Y., Nelder, J.A.: Double hierarchical generalized linear models (with discussion). Appl. Stat. 55, 139–185 (2006)
Lee, Y., Nelder, J.A., Noh, M.: H-likelihood: problems and solutions. Stat. Comput. 17, 49–55 (2007)
Lee, Y., Nelder, J.A., Pawitan, Y.: Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects: Unified Approach via h-Likelihood. Chapman and Hall, New York (2006)
Lee, W., Lim, J., Lee, Y., Castillo, J.: The hierarchical likelihood approach to autoregressive stochastic volatility models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 55, 248–260 (2011a)
Lee, Y., Jang, M., Lee, W.: Prediction interval for disease mapping using the hierarchical likelihood. Comput. Stat. 26, 159–179 (2011b)
Lin, X., Breslow, N.E.: Bias correction in generalized linear mixed models with multiple components of dispersion. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 91, 1007–1016 (1996)
Molenberghs, G., Verbeke, G., Demetrio, C.G.B., Vieira, A.: A family of generalized linear models for repeated measures with normal and conjugate random effects. Stat. Sci. 25, 325–347 (2010)
Noh, M., Lee, Y.: REML estimation for binary data in GLMMs. J. Multivar. Anal. 98, 896–915 (2007)
Pan, J., MacKenzie, G.: On modelling mean-covariance structures in longitudinal studies. Biometrika 90, 239–244 (2003)
Patterson, H.D., Thompson, R.: Recovery of interblock information when block sizes are unequal. Biometrika 58, 545–554 (1971)
Payne, R.W., Murray, D.A., Harding, S.A., Baird, D.B., Soutar, D.M.: GenStat for Windows (10th Edition) Introduction. VSN International, Hemel Hempstead (2007)
SAS Institute Inc.: SAS 9.1.3 Help and Documentation. SAS Institute Inc., Cary (2000–2004)
Schall, R.: Estimation in general linear models with random effects. Biometrika 78, 719–727 (1991)
Yun, S., Lee, Y.: Comparison of hierarchical and marginal likelihood estimators for binary outcomes. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 45, 639–650 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, W., Lee, Y. Modifications of REML algorithm for HGLMs. Stat Comput 22, 959–966 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9265-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9265-9