Abstract
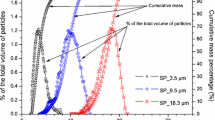
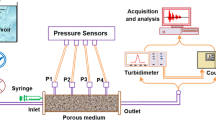
An experimental study on the transport and deposition of suspended particles (SP) in a saturated porous medium (calibrated sand) was undertaken. The influence of the size distribution of the SP under different flow rates is explored. To achieve this objective, three populations with different particles size distributions were selected. The median diameter \(d_{50}\) of these populations was 3.5, 9.5, and \(18.3~\upmu \hbox {m}\). To study the effect of polydispersivity, a fourth population noted “Mixture” (\(d_{50} = 17.4\; \upmu \hbox {m}\)) obtained by mixing in equal proportion (volume) the populations 3.5 and \(18.3\;\upmu \hbox {m}\) was also used. The SP transfer was compared to the dissolved tracer (DT) one. Short pulse was the technique used to perform the SP and the DT injection in a column filled with the porous medium. The breakthrough curves were competently described with the analytical solution of a convection–dispersion equation with first-order deposition kinetics. The results showed that the transport of the SP was less rapid than the transport of the DT whatever the flow velocity and the size distribution of the injected SP. The mean diameter of the recovered particles increases with flow rate. The longitudinal dispersion increases, respectively, with the increasing of the flow rates and the SP size distribution. The SP were more dispersive in the porous medium than the DT. The results further showed that the deposition kinetics depends strongly on the size of the particle transported and their distribution.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BTCs:
-
Breakthrough curves
- \(C\) :
-
DT/SP concentration in solution
- \(C_0 \) :
-
Initial concentration
- \(C_\mathrm{R} \) :
-
Relative concentration
- \(d_{50}\) :
-
Median diameter
- \(D_0 \) :
-
Molecular diffusion coefficient
- \(D_\mathrm{L} \) :
-
Longitudinal dispersion coefficient
- DT:
-
Dissolved tracer
- \(K\) :
-
Hydraulic conductivity
- \(K_\mathrm{{dep}}\) :
-
Deposition kinetics coefficient
- \(L\) :
-
Column length
- \(M\) :
-
Mass of DT/SP injected, equals \(V_\mathrm{{inj}} C_0 \)
- \(m\) :
-
A power coefficient (in \(D_\mathrm{L} =D_0 \tau ^{2}+\alpha _\mathrm{L} u^{m})\)
- NTU:
-
Nephelometric turbidity units
- \(n\) :
-
A power coefficient (in \(K_\mathrm{{dep}} =\alpha U^{n})\)
- \(P_\mathrm{{ed}}\) :
-
Diffusion Péclet number
- \(P_\mathrm{e} \) :
-
Dynamic Péclet number
- \(Q\) :
-
Flow rate
- \(R\) :
-
Recovery rate
- SP:
-
Suspended particles
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(t_\mathrm{c}\) :
-
Convection time
- \(t_\mathrm{{DT}}\) :
-
Residence time of DT
- \(t_\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Retardation factor, equals t\(_\mathrm{{SP}}/t_\mathrm{{DT}}\)
- \(t_\mathrm{{SP}}\) :
-
Residence time of SP
- \(U\) :
-
Darcy’s velocity
- \(u\) :
-
Average pore velocity
- \(V_\mathrm{{inj}}\) :
-
Injected volume
- \(V_\mathrm{P}\) :
-
Pore volume of the porous medium
- \(x\) :
-
Travel distance (column length)
- \(\alpha \) :
-
A constant (in \(K_\mathrm{{dep}} =\alpha U^{n})\)
- \(\alpha _\mathrm{L}\) :
-
Longitudinal dispersivity
- \(\delta (t)\) :
-
Dirac function
- \(\beta \) :
-
A power coefficient (in \(\alpha _\mathrm{L} =\kappa d_{50}^\beta )\)
- \(\kappa \) :
-
A constant (in \(\alpha _\mathrm{L} =\kappa d_{50}^\beta )\)
- \(\tau \) :
-
Tortuosity
References
Ahfir, N.-D., Wang, H.Q., Benamar, A., Alem, A., Massei, N., Dupont, J.-P.: Transport and deposition of suspended particles in saturated porous media: hydrodynamic effect. Hydrogeol. J. 15, 659–668 (2007)
Ahfir, N.-D., Benamar, A., Alem, A., Wang, H.Q.: Influence of internal structure and medium length on transport and deposition of suspended particles: a laboratory study. Transp. Porous Med. 76, 289–307 (2009)
Alem, A., Elkawafi, A., Ahfir, N.-D., Wang, H.Q.: Filtration of kaolinite particles in a saturated porous medium: hydrodynamic effects. Hydrogeol. J. 21, 573–586 (2013)
Bear, J.: Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover Publications Inc, New York (1972)
Benamar, A., Wang, H.Q., Ahfir, N.-D., Alem, A., Massei, N., Dupont, J.P.: Flow velocity effects on the transport and the deposition rate of suspended particles in a saturated porous medium. C. R. Geosci. 337, 497–504 (2005)
Bonelli, S., Brivois, O., Borghi, R., Benahmed, N.: On the modelling of piping erosion. C. R. Mecanique 334, 555–559 (2006)
Bouwer, H.: Artificial recharge of groundwater: hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 10, 121–142 (2002)
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., Bettahar, M., Van Genuchten, M.T., Yates, S.R.: Modeling colloid attachment, straining, and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 2242–2250 (2003)
de Marsily, G.: Quantitative Hydrogeology. Groundwater Hydrology for Engineers. Academic Press Inc, New York (1986)
Elimelech, M., Gregory, J., Jia, X., Williams, R.A.: Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modeling, and Simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1995)
Frey, J.M., Schmitz, P., Dufreche, I., Gohr Pinheiro, I.: Particle deposition in porous media: analysis of hydrodynamic and weak inertial effects. Transp. Porous Media 37, 25–54 (1999)
Gohr Pinheiro, I., Schmitz, P., Houi, D.: Particle capture in porous media when physico-chemical effects dominate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 54, 3801–3813 (1999)
Grolimund, D., Elimelich, M., Borcovec, M., Barmettler, K., Kretzschmar, R., Sticher, H.: Transport of in situ mobilized colloidal particles in packed soil columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 3562–3569 (1998)
Hater, T., Wagner, S., Atwill, E.R.: Colloid transport and filtration of cryptosporidium parvum in sandy soils and aquifer sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 62–70 (2000)
Herzig, J.P., Leclerc, D.M., Le Goff, P.: Flow of suspension through porous media: application to deep bed filtration. Indian Eng. Chem. 62, 8–35 (1970)
Hu, Q., Brusseau, M.L.: The effect of solute size on diffusive-dispersion transport in porous media. J. Hydrol. 158, 305–317 (1994)
Kanti Sen, T., Khilar, K.C.: Review on subsurface colloids and colloid-associated contaminant transport in saturated porous media. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 119, 71–96 (2006)
Keller, A.A., Auset, M.: A review of visualization techniques of biocolloid transport processes at the pore scale under saturated and unsaturated conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 30, 1392–1407 (2007)
Koltz, D., Seiler, K.P., Moser, H., Neumaier, F.: Dispersivity and velocity relationship from laboratory and field experiments. J. Hydrol. 45, 169–184 (1980)
Kretzschmar, R., Barmettler, K., Grolimund, D., Yan, Y.D., Borkovec, M., Sticher, H.: Experimental determination of colloid deposition rates and collision efficiencies in natural porous media. Water Resour. Res. 33, 1129–1137 (1997)
Kretzschmar, R., Borkovec, M., Grolimund, D., Elimelech, M.: Mobile subsurface colloids and their role in contaminant transport. Adv. Agron. 66, 121–194 (1999)
Massei, N., Lacroix, M., Wang, H.Q., Dupont, J.P.: Transport of particulate material and dissolved tracer in a highly permeable porous medium: comparison of the transfer parameters. J. Contam. Hydrol. 57, 21–39 (2002)
McCarthy, J.F., Zachara, J.M.: Subsurface transport of contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 496–502 (1989)
McDowell-Boyer, L.M., Hunt, J.R., Sitar, N.: Particle transport through porous media. Water Resour. Res. 22(13), 1901–1921 (1986)
McGechan, M.B., Lewis, D.R.: Transport of particulate and colloid-sorbed contaminants through soil. Part 1: general principales. Biosyst. Eng. 83, 255–273 (2002)
Moghadasi, J., Müller-Steinhagen, H., Jamialahmadi, M., Sharif, A.: Theoretical and experimental study of particle movement and deposition in porous media during water injection. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 43, 163–181 (2004)
Niehren, S., Kinzelbach, W.: Artificial colloid tracer tests: development of a compact on-line microsphere counter and application to soil column experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 35, 249–259 (1998)
Pfannkuch, H.O.: Contribution à l’étude des déplacements de fluides miscibles dans un milieu poreux [Contribution to the study of miscible fluids displacements in a porous medium]. Rev. Inst. Fr. Pétrol. 18, 215–270 (1963)
Ryan, J.N., Elimelech, M.: Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloids Surf. A 107, 1–56 (1996)
Saiers, J.E.: Laboratory observations and mathematical modeling of colloid-facilitated contaminant transport in chemically heterogeneous systems. Water Resour. Res. 38(4), 1032 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001WR000320
Vigneswaran, S., Suazo Ronillo, B.: A detailed investigation of physical and biological clogging during artificial recharge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 35, 119–140 (1987)
Vigneswaran, S., Jeyaseelan, S., Das Gupta, A.: A pilot-scale investigation of particle retention during artificial recharge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 25, 1–13 (1985)
Wang, H.Q.: Transferts de matières en milieu saturé: outils mathématiques et modélisation numérique [Mass transfer in saturated porous media: mathematical tools and numerical modelling]. Mémoire HDR, Université de Rouen, France (2001)
Wang, H.Q., Crampon, N., Huberson, S., Garnier, J.M.: Linear graphical method for determining hydrodispersive characteristics in tracer experiments with instantaneous injection. J. Hydrol. 95, 143–154 (1987)
Wang, H.Q., Lacroix, M., Massei, N., Dupont, J.P.: Particle transport in porous medium: determination of hydrodispersive characteristics and deposition rates. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sci. Terre Planèt. 331, 97–104 (2000)
Weronski, P., Walz, J.Y., Elimelech, M.: Effect of depletion interactions on transport of colloidal particles in porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 262, 372–383 (2003)
Xu, S.P., Saiers, J.E.: Colloid straining within water-saturated porous media: effect of colloid size nonuniformity. Water Resour. Res. 45, W05501 (2009). doi:10.1029/02008WR007258
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Région Haute Normandie (CPER) and the Franco-Algerian program for higher education (PROFAS). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and constructive criticism to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennacer, L., Ahfir, ND., Bouanani, A. et al. Suspended Particles Transport and Deposition in Saturated Granular Porous Medium: Particle Size Effects. Transp Porous Med 100, 377–392 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0220-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0220-4