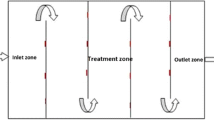
Abstract
Aiming to evaluate the efficacy of constructed floating wetlands (CFW) in removing agrochemicals (nutrients and pesticides), a series of experiments were run continuously for a 16-week period in pilot-scale CFW systems to study the effect of two aquatic plant species (duckweed and water hyacinth) and climatic parameters. The CFW systems were loaded daily with agricultural polluted water containing a fertilizer and five pesticides, whose concentrations and removal efficiencies were measured in the experiments. Average nutrient and pesticide reductions varied from 27.4% to 83.6% and from 12.4% to 42.7%, respectively. The two plants performed almost equally well. High temperatures and increased solar radiation significantly contributed to increased removal performance. The results suggest the use of CFW systems as effective and low-cost agricultural pollution control technologies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akratos CS, Tsihrintzis VA (2007) Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 29(2):173–191
Alemu T, Lemma E, Mekonnen A, Leta S (2016) Performance of pilot scale anaerobic-SBR system integrated with constructed wetlands for the treatment of tannery wastewater. Environ Process 3(4):815–827
Alencar BTB, Ribeiro VHV, Cabral CM, dos Santos NMC, Ferreira EA, Francino DMT, dos Santos JB, Silva DV, de Freitas Souza M (2020) Use of macrophytes to reduce the contamination of water resources by pesticides. Ecol Indic 109:105785
Angassa K, Leta S, Mulat W, Kloos H, Meers E (2018) Organic matter and nutrient removal performance of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Phragmite karka and Vetiveria zizanioide for treating municipal wastewater. Environ Process 5(1):115–130
Angassa K, Leta S, Mulat W, Kloos H, Meers E (2019) Evaluation of pilot-scale constructed wetlands with Phragmites karka for phytoremediation of municipal wastewater and biomass production in Ethiopia. Environ Process 6(1):65–84
Anudechakul C, Vangnai AS, Ariyakanon N (2015) Removal of chlorpyrifos by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and the role of a plant-associated bacterium. Int J Phytoremediation 17(7):678–685
Aremu AS, Ojoawo SO, Alade GA (2012) Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) culture in sewage: nutrient removal and potential applications of bye-products. Transnatl J Sci Technol 2(7):103–114
Chen X, Chen X, Wan X, Weng B, Huang Q (2010) Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) waste as an adsorbent for phosphorus removal from swine wastewater. Bioresour Technol 101(23):9025–9030
Dosnon-Olette R, Couderchet M, Biagianti S, Eullaffroy P (2008) Toxicity and removal of pesticides by selected aquatic plants. Chemosphere 70(8):1414–1421
Dosnon-Olette R, Couderchet M, Eullaffroy P (2009) Phytoremediation of fungicides by aquatic macrophytes: toxicity and removal rate. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 72(8):2096–2101
Dosnon-Olette R, Couderchet M, El Arfaoui A, Sayen S, Eullaffroy P (2010) Influence of initial pesticide concentrations and plant population density on dimethomorph toxicity and removal by two duckweed species. Sci Total Environ 408(10):2254–2259
Dosnon-Olette R, Couderchet M, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Eullaffroy P (2011) Potential use of Lemna minor for the phytoremediation of isoproturon and glyphosate. Int J Phytoremediation 13(6):601–612
Economopoulou MA, Tsihrintzis VA (2004) Design methodology of free water surface constructed wetlands. Water Resour Manag 18(6):541–565
Ekperusi AO, Sikoki FD, Nwachukwu EO (2019) Application of common duckweed (Lemna minor) in phytoremediation of chemicals in the environment: State and future perspective. Chemosphere 223:285–309
Feng W, Xiao K, Zhou W, Zhu D, Zhou Y, Yuan Y, Xiao N, Wan X, Hua Y, Zhao J (2017) Analysis of utilization technologies for Eichhornia crassipes biomass harvested after restoration of wastewater. Bioresour Technol 223:287–295
Fertig W (2021) Plant of the week: Common duckweed (Lemna minor). US Department of Agriculture, https://www.fs.fed.us/wildflowers/plant-of-the-week/lemna_minor.shtml (accessed 13 Jul 2021)
Fox LJ, Struik PC, Appleton BL, Rule JH (2008) Nitrogen phytoremediation by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms). Water Air Soil Pollut 194(1):199–207
Gatidou G, Stasinakis AS, Iatrou EI (2015) Assessing single and joint toxicity of three phenylurea herbicides using Lemna minor and Vibrio fischeri bioassays. Chemosphere 119:S69–S74
Gikas GD, Pérez-Villanueva M, Tsioras M, Alexoudis C, Pérez-Rojas G, Masís-Mora M, Lizano-Fallas V, Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, Vryzas Z, Tsihrintzis VA (2017) Low-cost approaches for the removal of terbuthylazine from agricultural wastewater: constructed wetlands and biopurification system. Chem Eng J 335:647–656
Gikas GD, Vryzas Z, Tsihrintzis VA (2018) S-metolachlor herbicide removal in pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Chem Eng J 339:108–116
Gupta C, Prakash D (2013) Duckweed: an effective tool for phyto-remediation. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(8):1256–1266
Ioannidou VG, Pearson JM (2018) Hydraulic and design parameters in full-scale constructed wetlands and treatment units: six case studies. Environ Process 5(1):5–22
Jayaweera MW, Kasturiarachchi JC (2004) Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from industrial wastewaters by phytoremediation using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms). Water Sci Technol 50(6):217–225
Kadir AA, Abdullah SRS, Othman BA, Hasan HA, Othman AR, Imron MF, Ismail NI, Kurniawan SB (2020) Dual function of Lemna minor and Azolla pinnata as phytoremediator for palm oil mill effluent and as feedstock. Chemosphere 259:127468
Kamyab H, Chelliapan S, Din MFM, Shahbazian-Yassar R, Rezania S, Khademi T, Kumar A, Azimi M (2017) Evaluation of Lemna minor and Chlamydomonas to treat palm oil mill effluent and fertilizer production. J Water Process Eng 17:229–236
Kostopoulou S, Ntatsi G, Arapis G, Aliferis KA (2020) Assessment of the effects of metribuzin, glyphosate, and their mixtures on the metabolism of the model plant Lemna minor L. applying metabolomics. Chemosphere 239:124582
Kotti IP, Sylaios GK, Tsihrintzis VA (2016) Fuzzy modeling for nitrogen and phosphorus removal estimation in free-water surface constructed wetlands. Environ Process 3(1):65–79
Ladislas SA, El-Mufleh AC, Gerente CF, Chazarenc FY, Andres YB, Bechet B (2012) Potential of aquatic macrophytes as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in urban stormwater runoff. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:877–888
Li X, Wu S, Yang C, Zeng G (2020) Microalgal and duckweed based constructed wetlands for swine wastewater treatment: A review. Bioresour Technol 318:123858
Li Z, Xiao H, Cheng S, Zhang L, Xie X, Wu Z (2014) A comparison on the phytoremediation ability of triazophos by different macrophytes. J Environ Sci 26(2):315–322
Malik A (2007) Environmental challenge vis a vis opportunity: the case of water hyacinth. Environ Int 33(1):122–138
Liu C, Dai Z, Sun H (2017) Potential of duckweed (Lemna minor) for removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from water under salt stress. J Environ Manag 187:497–503
Mitsou K, Koulianou A, Lambropoulou D, Pappas P, Albanis T, Lekka M (2006) Growth rate effects, responses of antioxidant enzymes and metabolic fate of the herbicide Propanil in the aquatic plant Lemna minor. Chemosphere 62(2):275–284
Monteith JL (1965) Evaporation and environment. In Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology 19, 205-234. Cambridge University Press (CUP) Cambridge
Mustafa HM, Hayder G (2020) Recent studies on applications of aquatic weed plants in phytoremediation of wastewater: A review article. Ain Shams Eng J 12(1):355–365
Osti JAS, do Carmo CF, Cerqueira MAS, Giamas MTD, Peixoto AC, Vaz-dos-Santos AM, Mercante CTJ (2020) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from fish farming effluents using artificial floating islands colonized by Eichhornia crassipes. Aquac Rep 17:100324
Papadopoulos FH, Tsihrintzis VA (2011) Assessment of a full-scale duckweed pond system for septage treatment. Environ Technol 32(7):795–804
Papadopoulos FH, Tsihrintzis VA, Zdragas AG (2011) Removal of faecal bacteria from septage by treating it in a full-scale duckweed-covered pond system. J Environ Manag 92(12):3130–3135
Papadopoulos N, Zalidis G (2019) The use of Typha Latifolia L. in constructed wetland microcosms for the remediation of herbicide terbuthylazine. Environ Process 6(4):985–1003
Papaevangelou VA, Gikas GD, Tsihrintzis VA, Antonopoulou M, Konstantinou IK (2016) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in HSF and VF pilot-scale constructed wetlands. Chem Eng J 294:146–156
Papaevangelou VA, Gikas GD, Vryzas Z, Tsihrintzis VA (2017) Treatment of agricultural equipment rinsing water containing a fungicide in pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 101:193–200
Pavlidis G, Tsihrintzis VA (2018) Environmental benefits and control of pollution to surface water and groundwater by agroforestry systems: a review. Water Resour Manag 32(1):1–29
Pavlidis G, Karasali H (2020) Natural remediation techniques for water quality protection and restoration. Methods for Bioremediation of Water and Wastewater Pollution. Springer, Cham, pp 327–340
Pavlineri N, Skoulikidis NT, Tsihrintzis VA (2017) Constructed floating wetlands: a review of research, design, operation and management aspects, and data meta-analysis. Chem Eng J 308:1120–1132
Penman HL (1948) Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences 193(1032):120–145
Prasertsup P, Ariyakanon N (2011) Removal of chlorpyrifos by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.) and duckweed (Lemna minor L.). Int J Phytoremediation 13(4):383–395
Rezania S, Taib SM, Din MFM, Dahalan FA, Kamyab H (2016) Comprehensive review on phytotechnology: heavy metals removal by diverse aquatic plants species from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 318:587–599
Sarkheil M, Safari O (2020) Phytoremediation of nutrients from water by aquatic floating duckweed (Lemna minor) in rearing of African cichlid (Labidochromis lividus) fingerlings. Environ Technol Innov 18:100747
Sharma S, Singh B, Manchanda VK (2015) Phytoremediation: role of terrestrial plants and aquatic macrophytes in the remediation of radionuclides and heavy metal contaminated soil and water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:946–962
Stefanakis A, Akratos CS, Tsihrintzis VA (2014) Vertical flow constructed wetlands: eco-engineering systems for wastewater and sludge treatment. Elsevier, 378p. ISBN: 978-0-12-404612-2
Sudiarto SIA, Renggaman A, Choi HL (2019) Floating aquatic plants for total nitrogen and phosphorus removal from treated swine wastewater and their biomass characteristics. J Environ Manag 231:763–769
Tagun R, Boxall AB (2018) The Response of Lemna minor to mixtures of pesticides that are commonly used in Thailand. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100(4):516–523
Tsihrintzis VA (2017) The use of vertical flow constructed wetlands in wastewater treatment. Water Resour Manag 31(10):3245–3270
Wang F, Liu D, Qu H, Chen L, Zhou Z, Wang P (2016) A full evaluation for the enantiomeric impacts of lactofen and its metabolites on aquatic macrophyte Lemna minor. Water Res 101:55–63
Wang J, Wang W, Xiong J, Li L, Zhao B, Sohail I, He Z (2021) A constructed wetland system with aquatic macrophytes for cleaning contaminated runoff/storm water from urban area in Florida. J Environ Manag 280:111794
Wang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Yan S, Guo J (2013) Nitrogen removal from Lake Caohai, a typical ultra-eutrophic lake in China with large scale confined growth of Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 92(2):177–183
Xia H, Ma X (2006) Phytoremediation of ethion by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) from water. Bioresour Technol 97(8):1050–1054
Zhou X, He ZL, Jones KD, Li L, Stoffella PJ (2017) Dominating aquatic macrophytes for the removal of nutrients from waterways of the Indian River Lagoon basin, South Florida, USA. Ecol Eng 101:107–119
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out and funded in the context of the project "Investigation of the efficiency of natural treatment systems in the removal of pesticides and fertilizers" (MIS 5049184) under the call for proposals "Researchers' support with an emphasis on young researchers - 2nd Cycle". The project is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Programme Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014-2020.
Funding
The study was funded in the context of the project "Investigation of the efficiency of natural treatment systems in the removal of pesticides and fertilizers" (MIS 5049184) under the call for proposals "Researchers' support with an emphasis on young researchers - 2nd Cycle". The project is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Program Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014-2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. Pavlidis: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft; I. Zotou: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft; H. Karasali: Resources, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - Review & Editing; A. Marousopoulou: Data curation, Writing - Review & Editing; G. Bariamis: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing - Review & Editing; V.A. Tsihrintzis: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing - Review & Editing; I. Nalbantis: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing - Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The pollution abatement efficiency of constructed floating wetlands is tested
• The effect of lemna and hyacinth is examined in pilot-scale continuously loaded units
• Average nutrient and pesticide reductions varied from 27.4% to 83.6% and from 12.4% to 42.7%
• Temperature and solar radiation were significant parameters in pollutant removal
• No significant differences were observed in the performance of the two plants
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlidis, G., Zotou, I., Karasali, H. et al. Performance of Pilot-scale Constructed Floating Wetlands in the Removal of Nutrients and Pesticides. Water Resour Manage 36, 399–416 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03033-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03033-9