Abstract
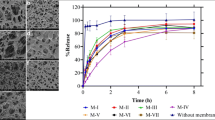
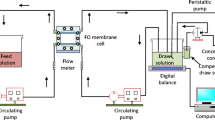
Adsorption together with size exclusion and charge attraction/repulsion has to be taken into account when considering removal of pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants from water by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. Glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone (HYDRO), dexamethasone (DEXA)), anesthetics (procaine, lidocaine) with relatively weak hydrophobicities (1 < log K O/W < 3), and membranes (XLE, LFC–1, CPA3, SWC1, NF90, and NF270) have been investigated in this study. Adsorption was studied by measuring the concentration of compounds in feed and permeate and by monitoring changes in membrane flux in the batch mode operation during 24 h. A decrease in the feed concentrations for HYDRO and DEXA (log K O/W < 2) was observed. The loss of these compounds in feed was associated with irreversible adsorption onto an NF270 and a CPA3 membrane. Therefore, when considering removal of pharmaceuticals with lower hydrophobicity, adsorption has to be particularly taken into account for membranes with bigger pores in the selective layer. Also, a high dipole moment and low water solubility affected adsorption on the membranes. For smaller and slightly more hydrophobic pharmaceuticals (log K O/W > 2), an increase in the feed concentration was obtained. Firstly, these compounds instantly adsorbed to the membrane. Secondly, the compounds diffused through the polymer matrix and desorbed to the permeate side after equilibrium had been reached.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alturki, A. A., Tadkaew, N., McDonald, J. A., Khan, S. J., Price, W. E., & Nghiem, L. D. (2010). Combining MBR and NF/RO membrane filtration for the removal of trace organics in indirect potable water reuse applications. Journal of Membrane Science, 365(1–2), 206–215. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2010.09.008.
Arsuaga, J. M., López-Muñoz, M. J., Aguado, J., & Sotto, A. (2008). Temperature, pH and concentration effects on retention and transport of organic pollutants across thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes. Desalination, 221(1–3), 253–258. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.081.
Bartelt-Hunt, S., Snow, D. D., Damon-Powell, T., & Miesbach, D. (2011). Occurrence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in shallow groundwater impacted by livestock waste control facilities. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 123(3–4), 94–103. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.12.010.
Behera, S. K., Kim, H. W., Oh, J.-E., & Park, H.-S. (2011). Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, hormones and several other pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants of the largest industrial city of Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20), 4351–4360. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.015.
Bellona, C., Drewes, J. E., Xu, P., & Amy, G. (2004). Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment—a literature review. Water Research, 38(12), 2795–2809. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.03.034.
Combe, C., Molis, E., Lucas, P., Riley, R., & Clark, M. M. (1999). The effect of CA membrane properties on adsorptive fouling by humic acid. Journal of Membrane Science, 154(1), 73–87. doi:10.1016/s0376-7388(98)00268-3.
Comerton, A. M., Andrews, R. C., Bagley, D. M., & Hao, C. (2008). The rejection of endocrine disrupting and pharmaceutically active compounds by NF and RO membranes as a function of compound and water matrix properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 313(1–2), 323–335. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2008.01.021.
Darvishmanesh, S., Vanneste, J., Tocci, E., Jansen, J., Tasseli, F., Degrève, J., et al. (2011). Physicochemical characterization of solute retention in solvent resistant nanofiltration: the effect of solute size, polarity, dipole moment, and solubility parameter. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 115(49), 14507–14517.
Dolar, D., Vuković, A., Ašperger, D., & Košutić, K. (2011). Effect of water matrices on removal of veterinary pharmaceuticals by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(8), 1299–1307. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(10)60545-1.
Dolar, D., Zokić, T. I., Košutić, K., Ašperger, D., & Pavlović, D. M. (2012). RO/NF membrane treatment of veterinary pharmaceutical wastewater: comparison of results obtained on a laboratory and a pilot scale. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(4), 1033–1042.
Dražević, E., Košutić, K., Finglerb, S., & Drevenkar, V. (2011). Removal of pesticides from the water and their adsorption on the reverse osmosis membranes of defined porous structure. Desalination and Water Treatment, 30(1–3), 161–170.
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., & Schlegel, H. B., (2009). Gaussian 09, Revision A.02. Wallingford, CT: Gaussian, Inc.
Gallenkemper, M., Wintgens, T., & Melin, T. (2003). Nanofiltration of endocrine disrupting compounds. Water Science & Technology: Water Supply, 3, 321–327.
Jelic, A., Gros, M., Ginebreda, A., Cespedes-Sánchez, R., Ventura, F., Petrovic, M., et al. (2011). Occurrence, partition and removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage water and sludge during wastewater treatment. Water Research, 45(3), 1165–1176. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.010.
Kim, N., Shin, D. H., & Lee, Y. T. (2007). Effect of silane coupling agents on the performance of RO membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 300(1–2), 224–231. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2007.05.039.
Kimura, K., Amy, G., Drewes, J., & Watanabe, Y. (2003). Adsorption of hydrophobic compounds onto NF/RO membranes: an artifact leading to overestimation of rejection. Journal of Membrane Science, 221(1–2), 89–101. doi:10.1016/s0376-7388(03)00248-5.
Košutić, K., Dolar, D., & Kunst, B. (2006). On experimental parameters characterizing the reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes’ active layer. Journal of Membrane Science, 282(1–2), 109–114. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2006.05.010.
Kuch, H. M., & Ballschmiter, K. (2001). Determination of endocrine-disrupting phenolic compounds and estrogens in surface and drinking water by HRGC-(NCI)-MS in the picogram per liter range. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(15), 3201–3206.
Lin, A. Y.-C., & Tsai, Y.-T. (2009). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in Taiwan's surface waters: impact of waste streams from hospitals and pharmaceutical production facilities. Science of the Total Environment, 407(12), 3793–3802. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.03.009.
Loos, R., Locoro, G., Comero, S., Contini, S., Schwesig, D., Werres, F., et al. (2010). Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Research, 44(14), 4115–4126. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.032.
Loraine, G. A., & Pettigrove, M. E. (2006). Seasonal variations in concentrations of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in drinking water and reclaimed wastewater in Southern California. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(3), 687–695.
Nghiem, L. D., & Coleman, P. J. (2008). NF/RO filtration of the hydrophobic ionogenic compound triclosan: transport mechanisms and the influence of membrane fouling. Separation and Purification Technology, 62(3), 709–716. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2008.03.027.
Nghiem, L. D., & Hawkes, S. (2007). Effects of membrane fouling on the nanofiltration of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs): mechanisms and role of membrane pore size. Separation and Purification Technology, 57(1), 176–184. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.04.002.
Nghiem, L. D., & Schäfer, A. I. (2006). Critical risk points of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes in water recycling applications. Desalination, 187(1–3), 303–312. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.089.
Nghiem, L. D., Schäfer, A. I., & Elimelech, M. (2004). Removal of natural hormones by nanofiltration membranes: measurement, modeling and mechanisms. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(6), 1888–1896.
Sim, W.-J., Lee, J.-W., & Oh, J.-E. (2010). Occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants and rivers in Korea. Environmental Pollution, 158(5), 1938–1947. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.036.
Tang, C. Y., Kwon, Y.-N., & Leckie, J. O. (2009). Effect of membrane chemistry and coating layer on physiochemical properties of thin film composite polyamide RO and NF membranes: II. Membrane physiochemical properties and their dependence on polyamide and coating layers. Desalination, 242(1–3), 168–182. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.004.
Van De Steene, J. C., Stove, C. P., & Lambert, W. E. (2010). A field study on 8 pharmaceuticals and 1 pesticide in Belgium: removal rates in waste water treatment plants and occurrence in surface water. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16), 3448–3453. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.04.037.
van den Berg, G. B., & Smolders, C. A. (1992). Diffusional phenomena in membrane separation processes. Journal of Membrane Science, 73(2–3), 103–118. doi:10.1016/0376-7388(92)80121-y.
Williams, M. E., Hestekin, J. A., Smothers, C. N., & Bhattacharyya, D. (1999). Separation of organic pollutants by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes: mathematical models and experimental verification. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 38(10), 3683–3695. doi:10.1021/ie990140l.
Wintgens, T., Gallenkemper, M., & Melin, T. (2003). Occurrence and removal of endocrine disrupters in landfill leachate treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 48, 127–134.
Xu, P., Drewes, J. E., Kim, T.-U., Bellona, C., & Amy, G. (2006). Effect of membrane fouling on transport of organic contaminants in NF/RO membrane applications. Journal of Membrane Science, 279(1–2), 165–175. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.001.
Yoon, Y., Westerhoff, P., Yoon, J., & Snyder, S. A. (2004). Removal of 17 beta estradiol and fluoranthene by nanofiltration and ultrafiltration. Journal of Environmental Engineering-ASCE, 130(12), 1460–1467.
Yoon, Y., Westerhoff, P., Snyder, S. A., & Wert, E. C. (2006). Nanofiltration and ultrafiltration of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Journal of Membrane Science, 270(1–2), 88–100. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2005.06.045.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Croatian Ministry of Science, Education and Sports Projects: 125-1253008-3009, Membrane and adsorption processes for removal of organic compounds in water treatment; 125-1253008-1350, Advanced analytical methods for pharmaceuticals determination in the environment; and Bilateral project HR-SLO, Determination of toxicity and physico-chemical properties of pharmaceuticals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolar, D., Košutić, K. & Ašperger, D. Influence of Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals onto RO/NF Membranes on Their Removal from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1377 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1377-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1377-0