Abstract
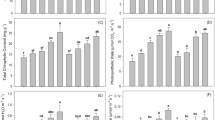
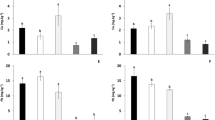
In two soils from Central Greece, a pot experiment was conducted with the addition of mixture at various ratios of zeolite and compost (based on Posidonia oceanica (L.) leaves) applied at a rate of 5% w/w (calculated on a soil dry weight basis). Three varieties of tobacco (Burley, Virginia, and Oriental) were cultivated, and Cu, Zn, and Cd concentrations in tobacco leaves were measured at first, second, and third primings. We found that the addition of zeolite in the soil1 led to a significant reduction of metal concentration in all three tobacco varieties compared to the control. Also, zeolite addition reduced significantly the water-soluble, as well as, DTPA-extractable metal concentrations, compared to the other treatments. Our results suggest that the most effective amendment in soil 1 was the mixture consisting of 20% compost and 80% zeolite; this mixture led to higher reduction of metal concentration in all tobacco varieties. As for soil 2, which had almost twice as high Cd concentrations as than in soil 1, Posidonia compost was more effective in reducing Cd concentrations from all three tobacco varieties. In all cases studied, both in soils 1 and 2, Cd concentration was higher in Burley tobacco leaves. The results indicate that a mixture of zeolite and compost consisting of Posidonia oceanica (L.) is a low-cost soil conditioner that is effective in reducing tobacco Cu, Zn, and Cd uptake.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Mamun, S., Chanson, G., Muliadi, Benyas, E., Aktar, M., Lehto, N., McDowell, R., Cavanagh, J., Kellermann, L., Clucas, L., & Robinson, B. (2016). Municipal composts reduce the transfer of Cd from soil to vegetables. Environmental Pollution, 213, 8–15.
Alloway, B. (1990). Heavy metals in soils. Glasgow: Blackie.
Alloway, B. J., & Steinnes, E. (1999). Anthropogenic additions of cadmium to soils. In M.J. McLaughlin, B.R. Singh (Eds.), Cadmium in Soils and Plants. Netherlands: Springer.
AOAC. (1984). Official method of analysis 14th Ed. Sidney Williams. Virginia: Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Inc..
Calkins, W. H. (1994). The chemical forms of sulfur in coal: a review. Fuel, 73, 475–484.
Castaldi, P., & Melis, P. (2004). Growth and yield characteristics and heavy metal content on tomatoes grown in different growing media. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 35(1 & 2), 85–98.
Cheng, F. S., & Hseu, Z. Y. (2002). In-situ immobilization of cadmium and lead by different amendments in two contaminated soils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 140, 73–84.
Golia, E. E., Dimirkou, A., & Mitsios, I. K. (2007a). Accumulation of heavy metals on Burley, Virginia and Oriental tobacco leaves grown in an agricultural area in relation to soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology, 79, 158–162.
Golia, E. E., Tsiropoulos, N. G., Dimirkou, A., & Mitsios, I. K. (2007b). Distribution of heavy metals of agricultural soils of central Greece using the modified BCR sequential extraction method. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 87, 1053–1063.
Golia, E. E., Floras, S. A., & Dimirkou, A. (2009). Monitoring the variability of zinc and copper in surface soils from Central Greece. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 82, 6–10.
Golia, E.E., Fuleky, G., Dimirkou, A., & Gizas, G. (2016) Influence of zeolite and Posidonia oceanica (L.) in reduction of Cadmium uptake by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants of Central Greece. Book of Proceedings of the Cyprus 2016 International Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management, Limassol, Cyprus, 24–25 June 2016.
Gworek, B. (1992). Lead inactivation in soils by zeolites. Plant and Soil, 143, 71–74.
Haidouti, C. (1997). Inactivation of mercury in contaminated soils using natural zeolites. Science of the Total Environment, 208, 105–109.
He, Q. B., & Singh, B. R. (1994). Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizers: I. Yield and cadmium content. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 74, 251–265.
ISO/DIS 11466. (1994). In environment soil quality. Geneva, Switzerland: ISO standards compendium.
James, R., & Sampath, K. (1999). Effect of zeolite on the reduction of cadmium toxicity in water and a freshwater fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62, 222–229.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Mukherjee, A. B. (2007). Trace elements from soil to human. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, A. K. (1992). Trace elements in soils and plants (2nd ed.). Ann Arbor: CRC.
Karyotis, T., Orfanidis, S., & Reizopoulou, S. (2006). Marine benthic macrophytes as possible nitrogen source in agriculture. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 169, 557–563.
Keller, C., Marchetti, M., Rossi, L., & Lugon-Moulin, N. (2005). Reduction of cadmium availability to tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants using soil amendments in low cadmium-contaminated agricultural soils: a pot experiment. Plant and Soil, 276, 69–84.
Kljakovic-Gaspic, Z., Antolic, B., Zvonaric, T., & Baric, A. (2004). Distribution of cadmium and lead in Posidonia oceanica (L.) delile from the middle Adriatic Sea. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 13(11), 1210–1215.
Kwon-Rae, K., Jeong-Gyu, K., Jeong-Sik, P., Min-Suk, K., Gary, O., Gyu-Hoon, Y., & Jin-Su, L. (2012). Immobilizer-assisted management of metal-contaminate agricultural soils for safer food production. Journal of Environmental Management, 102, 88–95.
Lajunen, L. H. G. (1992). Spectrochemical analysis by atomic absorption and emission. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Latihaf, O., Ahmed, O. H., Susilawati, K., & Mjid, N. M. (2015). Compost maturity and nitrogen availability by co-composting of paddy husk and chicken manure amended with clinoptilolite zeolite. Waste Management & Research, 33(4), 322–331.
Lin, D., & Zhou, Q. (2009). Effects of soil amendments on the extractability and speciation of Cd, Pb and Cu in a contaminated soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 83, 136–140.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Journal of American Soil Science Society, 42, 421–428.
Lugon-Moulin, N., Zhang, M., Gadani, F., Rossi, L., Koller, D., Krauss, M., & Wagner, G. J. (2004). Critical review of the science and options for reducing cadmium in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) and other plants. Advances in Agronomy, 83, 111–180.
Malea, P., Haritonidis, S., & Kervekidis, T. (1994). Seasonal and local variations of metal concentrations in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in the Antikyra Gulf, Greece. Science of the Total Environment, 153, 225–235.
McLaren, R. G., & Cameron, K. C. (1996). Soil science: sustainable production and environmental protection. Auckland: Oxford University Press.
Mininni, C., Grassi, F., Traversa, A., Cocozza, C., Parente, A., Miano, T., & Santamaria, P. (2014). Posidonia oceanica (L.) based compost as substrate for potted basil production. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 95, 2041–2046.
Page, A. L., Miller, H. R., & Keeney, R. D. (1982). Methods of soil analysis part ΙΙ—chemical and microbiological properties. Madison: Inc. Soil Science of America.
Richir, J., Salivas-Decaux, M., Lafarbie, C., Lopez y Royo, C., Gobert, S., Pergent, G., & Pergent-Martini, C. (2015). Bioassessment of trace element contamination of Mediterranean coastal waters using the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 486–499.
Shaheen, S. M., Tsadilas, C. D., & Rinklebe, J. (2015). Immobilization of soil copper using organic and inorganic amendments. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 178, 112–117.
Witter, E., & Lopez-Real, J. (1988). Nitrogen losses during the composting of sewage sludge, and the effectiveness of clay soil, zeolite, and compost in adsorbing the volatilized ammonia. Biological Wastes, 23, 279–294.
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author would like to thank Prof Fuleky, the administrator of the Laboratory of Soil Science and Agrochemistry of Szent István University, for his valuable contribution throughout her post-doctoral dissertation. Also, she wishes to thank the administration of the Laboratory of Soil Science, University of Thessaly, for the financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golia, E.E., Füleky, G., Dimirkou, A. et al. Influence of Zeolite and Posidonia oceanica (L.) in the Reduction of Heavy Metal Uptake by Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Plants of Central Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 324 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3522-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3522-2