Abstract
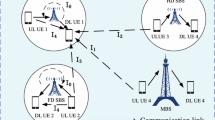
In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic point selection (DPS) and user scheduling method for improving the energy efficiency in distributed antenna systems without cell edge spectral efficiency degradation. When DPS is used, each user is served by a single transmission point that can be dynamically switched. The proposed method decreases the power consumption by switching off inactive radio frequency (RF) chains and additionally reduces the interference by a static inter-cell agreement on which transmission points are simultaneously active. The performance of the method is evaluated by computer simulations in a system that accurately models the LTE-Advanced (LTE-A) intra-cell coordinated multi-point scenario 4. Based on the performance simulations, the proposed method achieves a significant energy efficiency gain over closed-loop spatial multiplexing applied on localized or distributed transmitting antennas. In general, the proposed method performs well when the load-independent RF power consumption is high in the active mode and low in the sleep mode. When the proportion of the load-independent RF power consumption to the total load-independent power consumption exceeds a certain limit, which is 22 % in the case of ten users in the 3-sector layout, the proposed method brings always energy efficiency gain even when RF chain micro sleeping cannot be implemented. The usability of the method is not dependent on the traffic load. The same approach can be applied to any distributed antenna system.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L., Wang, W., Anpalagan, A., Vasilakos, A. V., Illanko, K., Wang, H., et al. (2013). Green cooperative cognitive communication and networking: A new paradigm for wireless networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 18(4), 524–534.
Alsharif, M. H., Nordin, R., & Ismail, M. (2014). Classification, recent advances and research challenges in energy efficient cellular networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 77(2), 1249–1269.
ITU-R Report M.2134. (2008). Requirements related to technical performance for IMT-Advanced radio interface(s).
Ghosh, A., Ratasuk, R., Mondal, B., Mangalvedhe, N., & Thomas, T. (2010). LTE-Advanced: Next-generation wireless broadband technology. IEEE Wireless Communication Magazine, 17(3), 10–22.
Chen, T., Yang, Y., Zhang, H., Kim, H., & Horneman, K. (2011). Network energy saving technologies for green wireless access networks. IEEE Wireless Communication Magazine, 18(5), 30–38.
Frenger, P., Moberg, P., Malmodin, J., Jading, Y., & Gódor, I. (2011). Reducing energy consumption in LTE with cell DTX. In Proceedings of IEEE VTC Spring. Budapest, Hungary.
Wang, R., Thompson, J., Haas, H., & Grant, P. (2011). Sleep mode design for green base stations. IET Communications, 5(18), 2606–2616.
Goldsmith, A., Jafar, S. A., Jindal, N., & Vishwanath, S. (2003). Capacity limits of MIMO channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 21(5), 684–702.
Kakitani, M. T., Brante, G., Souza, R. D., & Imran, M. A. (2013). Energy efficiency of transmit diversity systems under a realistic power consumption model. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(1), 119–122.
Cui, S., Goldsmith, A. J., & Bahai, A. (2004). Energy-efficiency of MIMO and cooperative MIMO techniques in sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 22(6), 1089–1098.
Héliot, F., Imran, M. A., & Tafazolli, R. (2012). On the energy efficiency-spectral efficiency trade-off over the MIMO Rayleigh fading channel. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60(5), 1345–1356.
Onireti, O., Heliot, F., & Imran, M. A. (2013). On the energy efficiency-spectral efficiency trade-off of distributed MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(9), 3741–3753.
Xu, J., & Qiu, L. (2013). Energy efficiency optimization for MIMO broadcast channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(2), 690–701.
Irmer, R., Droste, H., Marsch, P., Grieger, M., Fettweis, G., Brueck, S., et al. (2011). Coordinated multipoint: Concepts, performance, and field trial results. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(2), 102–111.
Lee, J., Kim, Y., Lee, H., Ng, B. L., Mazzarese, D., Liu, J., et al. (2012). Coordinated multipoint transmission and reception in LTE-Advanced systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(11), 44–50.
3GPP Technical Report TR 36.819. (2011). Coordinated multi-point operation for LTE physical layer aspects. V11.1.0.
Holtkamp, H., Auer, G., Bazzi, S., & Haas, H. (2014). Minimizing base station power consumption. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(2), 297–306.
Abdallah, K., Cerutti, I., & Castoldi, P. (2012). Energy-efficient coordinated sleep of LTE cells. In Proceedings of IEEE ICC. Ottawa, Canada.
ITU-R Report M.2135-1. (2009). Guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT-advanced.
Chhedda, A. & Bassirat, F. (1999). Enhanced cellular layout for CDMA networks having six-sectored cells. U.S. Patent 5,960,349.
Sheikh, M. U., & Lempiäinen, J. (2013). A flower tessellation for simulation purpose of cellular network with 12-sector sites. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2(3), 279–282.
3GPP Technical Specification TS 36.211. (2013). Physical channels and modulation. V11.5.0.
3GPP Technical Specification TS 36.213. (2013). Physical layer procedures. V11.5.0.
Schwarz, S., Mehlführer, C., & Rupp, M. (2010). Calculation of the spatial preprocessing and link adaptation feedback for 3GPP UMTS/LTE. In Proceedings of WiAD Conference. London, UK.
Nam, Y. H., Akimoto, Y., Kim, Y., il Lee, M., Bhattad, K., & Ekpenyong, A. (2012). Evolution of the reference signals for LTE-Advanced systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(2), 132–138.
Institute of Telecommunications. (2011). Vienna LTE simulators: Link level simulator documentation v1.7r1089. Vienna, Austria: Vienna University of Technology.
Ikuno, J. C., Wrulich, M., & Rupp, M. (2010). System level simulation of LTE networks. In Proceedings of IEEE VTC Spring. Taipei, Taiwan.
Berggren, F. & Jäntti, R. (2003). Multiuser scheduling over Rayleigh fading channels. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM. San Francisco, CA.
Etsi TR 103.117. (2012). Principles for mobile network level energy efficiency. V1.1.1
Varma, V. S., Elayoubi, S. E., Debbah, M., & Lasaulce, S. (2013). On the energy efficiency of virtual MIMO systems. In Proceedings of IEEE PIMRC. London, UK.
Joung, J., Ho, C. K., & Sun, S. (2014). Spectral efficiency and energy efficiency of OFDM systems: Impact of power amplifiers and countermeasures. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(2), 208–220.
Li, G. Y., Niu, J., Lee, D., Fan, J., & Fu, Y. (2014). Multi-cell coordinated scheduling and MIMO in LTE. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(2), 761–775.
Lasanen, M., Aubree, M., Cassan, C., Conte, A., David, J., Elayoubi, S. E., et al. (2013). Environmental friendly mobile radio networks: Approaches of the European OPERA-Net 2 project. In Proceedings of ICT. Casablanca, Morocco.
Holtkamp, H., Auer, G., Giannini, V., & Haas, H. (2013). A parameterized base station power model. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(11), 2033–2035.
Deruyck, M., Joseph, W., Lannoo, B., Colle, D., & Martens, L. (2013). Designing energy-efficient wireless access networks: LTE and LTE-Advanced. IEEE Internet Computing, 17(5), 39–45.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly funded by Tekes—the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation (Decision No. 40446/11) and Academy of Finland (Decision No. 284728). The work was done in the frameworks of the Celtic-Plus OPERA-Net2 project, which is funded by Tekes and the French Ministry of Industry, and the Academy of Finland TT5G project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apilo, O., Lasanen, M. & Mämmelä, A. Energy-Efficient Dynamic Point Selection and Scheduling Method for Intra-cell CoMP in LTE-A. Wireless Pers Commun 86, 705–726 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2953-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2953-6