Abstract
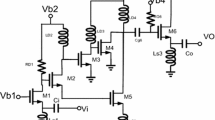
A new ultra-wideband common gate low noise amplifier (LNA) for 3–6 GHz WLAN and WPAN applications is presented in which a current reused noise canceling structure utilized in the first stage not only provides a suitable noise performance, but also enhances the linearity characteristics of the LNA in a power efficient manner needed by WLAN/WPAN applications. The overall structure of the proposed LNA, consisting of three stages, namely input matching common gate stage with noise canceling, gain stage, and buffer one, is designed, laid out, and analyzed in 0.18 µm RF CMOS process. The LNA has a noise figure of 3.5–3.6 dB, a high and flat power gain of 20.27 ± 0.13 dB, and input and output losses of better than −11 and −14 dB, respectively, over the entire frequency band of 3–5 GHz, while these parameters are 3.5 dB, 20.75 ± 0.25 dB, −15 and −9 dB for the frequency band of 5–6 GHz, respectively. IIP2 and IIP3 of the proposed topology are equal to 25.9 and −1.85 dBm, respectively, at 4 GHz frequency. The proposed LNA has 15.3 mW power dissipation from a 1.8 V supply.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siwiak, K., Withington, P., & Phelan, S. (2001). Ultra-wide band radio: The emergence of an important new technology. In Proceedings of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, (VTC'01) (Vol. 2, pp. 1169–1172).
Multi-Band OFDM Physical Layer Proposal for IEEE 802.15 Task Group 3a, ftp.802wirelessworld.com/15/Archive/2003/Jul03/03268r3P802-15TG3a-Multi-Band-CFPDocument.Doc
DS-UWB Physical Layer Submission to 802.15 Task Group 3a, ftp.802wirelessworld.com/15/04/15-04-0137-03-003a-merger2-proposal-ds-uwb-update.doc
IEEE 802.15 WPAN High Rate Alternative PHY Task Group 3a (TG3a). (2003). http://www.ieee802.org/15/pub/TG3a.html
Rashtian, H., & Mirabbasi, Sh. (2014). Applications of body biasing in multistage CMOS low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Transaction on Circuits and Systems I: Reg Papers, 61(6), 1638–1647.
Khurram, M., & Rezaul Hasan, S. M. (2012). A 3–5 GHz current-reuse Gm-boosted CG LNA for ultra wideband in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE Transaction on VLSI Systems, 20(3), 400–409.
Kim, C. W., Kang, M. S., Anh, P. T., Kim, H. T., & Lee, S. G. (2005). An ultra-wideband CMOS low noise amplifier for 3–5GHz UWB system. IEEE Journal of Solid-state Circuits, 40(2), 544–547.
Chang, C. P., & Choung, H. R. (2005). 0.18 µm 3–6 GHz CMOS broadband LNA for UWB radio. Electronics Letters, 41(12), 696–698.
Zhang, H., Fan, X., & Sinencio, E. S. (2009). A low power, linearized, ultra wideband LNA design technique. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 44(2), 320–330.
Shaeffer, D. K. & Lee, T. H. (1997). 1.5 V 1.5 GHz CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 32(5), 745–759.
Nga, T. T. T. (2012). Ultra low-power low-noise amplifier design for 2.4 GHz ISM band applications. Ph.D. dissertation, Nanyang Tech. Univ.
Lin, Y.-J., Hsu, S. H., Jin, J. D., & Chan, C. Y. (2007). A 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra wideband CMOS LNA with current-reused technique. IEEE Journal of Microwave and Wireless Component Letters, 17(3), 232–234.
Saghafi, A. & Nabavi, A. (2006). An ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier for 3–5 GHz wireless systems. In Proceeding IEEE International Conference of Microelectronics (ICM’06) (pp. 20–23).
Ziabakhsh, S., Alavi-Rad, H., & Yagoub, M. C. E. (2012). A high-gain low-power 2–14 GHz ultra-wide-band CMOS LNA for wireless receivers. International Journal of Electronics and Communications (AEÜ), 66(9), 727–731.
Khurram, M., & Rezaul Hasan, S. M. (2011). Novel analysis and optimization of gm-boosted common-gate UWB LNA. Microelectronics Journal, 42, 253–264.
Liao, C. F. & Liu, S. I. (2007). A broadband noise-canceling CMOS LNA for 3.1–10.6-GHz UWB receivers. IEEE Journal of Slid-State Circuits, 42(2), 329–339.
Asgaran, S., Jamal Deen, M., & Chen, C. H.(2007). Design of the input matching network of RF CMOS LNAs for low-power operation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Reg. Papers, 54(3), 544–554.
Wang, Y. S., & Lu, L. H. (2005). 5.7-GHz low-power variable gain LNA in 0.18-µm CMOS. Electronics Letters, 41(2), 66–68.
Shouxian, M., Guo, M., Seng, Y. K., & Anh, D. M. (2005). A modified architecture used for input matching in CMOS low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems II, Express Briefs, 52(11), 784–788.
Jin, X., Ou, J., Chen, C. H., Liu, W., Deen, M. J., Gray, P. R., & Hu, C. (1998). An effective gate resistance model for CMOS RF and noise modeling. Digital Technology papers IEDM (pp. 961–964).
Lee, T. H. (2004). The design of CMOS radio frequency integrated circuits (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Zhang, H., Fan, X., & Sinencio, E. S. (2009). A wideband CMOS low noise amplifier employing noise and IM2 distortion cancellation for a digital TV tuner. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(2), 320–330.
Moezzi, M., & Sharif Bakhtiar, M. (2012). Wideband LNA using active inductor with multiple feed-forward noise reduction paths. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Technology, 60(4), 1069–1078.
Im, D., Nam, I., Kim, H., & Lee, K. (2009). A wideband CMOS low noise amplifier employing noise and IM2 distortion cancellation for a digital TV tuner. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(3), 686–698.
Kim, N., Aparin, V., Barnett, K., & Persico, C. (2006). A cellular-band CDMA CMOS LNA linearized using active post-distortion. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(7), 1530–1534.
Geddada, H. M., Park, J. W., & Martinez, J. S. (2009). Robust derivative superposition method for linearizing broadband LNAs. IEEE Electronics Letters, 45(9), 435–436.
Alavi-Rad, H., Ziabakhsh, S., Ziabakhsh, S., & Yagoub, M. C. E. (2013). A 0.9 V CMOS 3–5 GHz broadband flat gain low-noise amplifier for ultra-wide band receivers. Canadian Journal of Electrical Computer Engineering, 36(2), 87–91.
Nouri, M., & Karimi, Gh. (2014). A novel 2.5–3.1 GHz wide-band low-noise amplifier in 0.18 µm CMOS. Wireless Personal Communications, 79(3), 1993–2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saberkari, A., Shirmohammadli, V. & Yagoub, M.C.E. A 3–6 GHz Current Reused Noise Canceling Low Noise Amplifier for WLAN and WPAN Applications. Wireless Pers Commun 86, 1359–1376 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2993-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2993-y