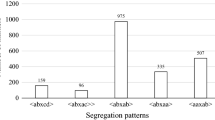
Abstract
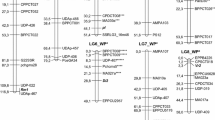
Two populations (Pop) segregating quantitatively for resistance to downy mildew (DM), caused by Plasmopara viticola, were used to construct genetic maps and to carry out quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis. Pop1 comprised of 174 F1 individuals from a cross of ‘Moscato Bianco’, a susceptible Vitis vinifera cultivar, and a resistant individual of Vitis riparia. Pop2 consisted of 94 progeny from a cross of two interspecific hybrids, ‘VRH3082 1-42’ and ‘SK77 5/3’, with resistance traits inherited from Vitis rotundifolia and Vitis amurensis, respectively. Resistance of progeny was measured in field and greenhouse conditions by visual evaluation of disease symptoms on leaves. Linkage maps of 1037.2 and 651 cM were built essentially with simple sequence repeat markers and were enriched with gene-derived single-strand conformational polymorphism and single-nucleotide polymorphism markers. Simple interval mapping and Kruskall–Wallis analysis detected a stable QTL involved in field resistance to DM on linkage group (LG) 7 of the Pop1 integrated map co-localized with a putative Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase-derived marker. Additional QTLs were detected on LGs 8, 12 and 17. We were able to identify genetic factors correlated with resistance to P. viticola with lower statistical significance on LGs 1, 6 and 7 of the Pop2 map. Finally, no common QTLs were found between the two crosses analyzed. A search of the grapevine genome sequence revealed either homologues to non-host-, host- or defense-signalling genes within the QTL intervals. These positional candidate genes may provide new information about chromosomal regions hosting phenotypic loci.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam-Blondon AF, Roux C, Claux D, Butterlin G, Merdinoglu D, This P (2004) Mapping 245 SSR markers on the Vitis vinifera genome: a tool for grape genetics. Theor Appl Genet 109:1017–1027
Allegre M, Daire X, Heloir MC, Trouvelot S, Mercier L, Adrian M, Pugin A (2007) Stomatal deregulation in Plasmopara viticola-infected grapevine leaves. New Phytol 173:832–840
Alleweldt G, Possingham JV (1988) Progress in grapevine breeding. Theor Appl Genet 75:669–673
Barker CL, Donald T, Pauquet J, Ratnaparkhe MB, Bouquet A, Adam-Blondon AF, Thomas MR, Dry I (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of the grapevine powdery mildew resistance gene, Run1, using a bacterial artificial chromosome library. Theor Appl Genet 111:370–377
Bellin D, Peressotti E, Merdinoglu D, Weidemann-Merdinoglu S, Adam-Blondon AF, Cipriani G, Morgante M, Testolin R, Di Gaspero G (2009) Resistance to Plasmopara viticola in grapevine ‘Bianca’ is controlled by a major dominant gene causing localised necrosis at the infection site. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1167-2
Bishop DT, Cannings C, Skolnick M, Williamson JA (1983) The number of polymorphic DNA clones required to map the human genome. In: Weir BC (ed) Statistical analysis of DNA sequence data. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 181–200
Bouquet A, Pauquet J, Adam-Blondon AF, Torregrosa L, Merdinoglu D, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S (2000) Vers l’obtention de variétés de vigne résistantes à l’oidium et au mildou par les methodes conventionelles et biotechnologiques. Progrès Agric Vitic 117(18):383–389
Bowers JE, Dangl GS, Vignani R, Meredith CP (1996) Isolation and characterization of new polymorphic simple sequence repeat loci in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Genome 39:628–633
Bowers JE, Dangl GS, Meredith CP (1999) Development and characterization of additional microsatellite DNA markers for grape. Am J Enol Vitic 50:243–246
Busam C, Kassemeyer HH, Matern U (1997) Characterization and expression of caffeoyl-Coenzyme A 3-O-methyltransferase proposed for the induced resistance response of Vitis vinifera L. Plant Physiol 11(5):1039–1048
Cadle Davidson LE (2008) Variation within and between Vitis species for foliar resistance to the downy mildew pathogen Plasmopara viticola. Plant Dis 92:1577–1584
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PM, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1994) Satured molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics 138:1251–1274
Chakravarti A, Lasher LK, Reefer JE (1991) A maximum likelihood method for estimating genome length using genetic linkage data. Genetics 128:175–182
Dalbò MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Steinkellner H, Sefc KM, Reisch BI (2000) Gene controlling sex in grapevines placed on a molecular marker-based genetic map. Genome 43:333–340
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G (2003) Nucleotide binding site/leucine-rich repeats, Pto-like and receptor-like kinases related to disease resistance in grapevine. Mol Genet Genomics 269:612–623
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G, Adam-Blondon A-F, Testolin R (2007) Linkage maps of grapevine displaying the chromosomal locations of 420 microsatellite markers and 82 markers for R-gene candidates. Theor Appl Genet 114:1249–1263
Díez-Navajas AM, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Greif C, Merdinoglu D (2008) Non-host versus host resistance to the grapevine downy mildew, Plasmopara viticola, studied at the tissue level. Phytopathology 98:776–780
Eibach R, Diehl H, Alleweldt G (1989) Untersuchungen zur verebung von resistenzeigenschaften bei reben gegen oidium tuckeri, Plasmopara viticola, und Botrytis cinerea. Vitis 28:209–228
Fischer BM, Salakhutdinov I, Akkurt M, Eibach R, Edwards KJ, Töpfer R, Zyprian EM (2004) Quantitative trait locus analysis of fungal disease resistance factors on a molecular map of grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 108:501–515
Gerber S, Rodolphe F (1994) An estimation of the genome length of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ati). Theor Appl Genet 88:289–292
Grando MS, Bellin D, Edwards KJ, Pozzi C, Stefanini M, Velasco R (2003) Molecular linkage maps of Vitis vinifera L. and V. riparia Mchx. Theor Appl Genet 106:1213–1224
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Greenberg JT, Yao N (2004) The role and regulation of programmed cell death in plant–pathogen interactions. Cell Microbiol 6:201–211
Heath MC, Skalamera D (1997) Cellular interactions between plants and biotrophic fungal parasites. Adv Bot Res 24:195–225
Hulbert SH, Ilott TW, Legg EJ, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Michelmore RW (1988) Genetic analysis of the fungus Bremia lactucae, using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics 120:947–958
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C, Casagrande A, Choisne N, Aubourg S, Vitulo N, Jubin C, Vezzi A, Legeai F, Hugueney P, Dasilva C, Horner D, Mica E, Jublot D, Poulain J, Bruyere C, Billault A, Segurens B, Gouyvenoux M, Ugarte E, Cattonaro F, Anthouard V, Vico V, Del Fabbro C, Alaux M, Di Gaspero G, Dumas V, Felice N, Paillard S, Juman I, Moroldo M, Scalabrin S, Canaguier A, Le Clainche I, Malacrida G, Durand E, Pesole G, Laucou V, Chatelet P, Merdinoglu D, Delledonne M, Pezzotti M, Lecharny A, Scarpelli C, Artiguenave F, Pe ME, Valle G, Morgante M, Caboche M, Adam-Blondon AF, Weissenbach J, Quetier F, Wincker P (2007) French–Italian public consortium for grapevine genome characterization: the grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–467
Kortekamp A (2006) Expression analysis of defense-related genes in grapevine leaves after inoculation with a host and a non-host pathogen. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:58–67
Kortekamp A, Zyprian E (2003) Characterization of Plasmopara resistance in grapevine using in vitro plants. J Plant Physiol 160:1393–1400
Kortekamp A, Wind R, Zyprian E (1998) Investigation of the interaction of Plasmopara viticola with susceptible and resistant grapevine cultivars. J Plant Dis Protec 105:475–488
Kozma P, Dula T (2003) Inheritance of resistance to downy mildew and powdery mildew of hybrid family Muscadinia x V. vinifera x V. amurensis x Franco-American hybrid. Acta Hortic 603:457–463
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lawton K, Uknes S, Friedrich L, Gaffney T, Alexander D, Goodman R, Metraux JP, Kessmann H, Ahlgoy P, Gutrella M et al (1993) The molecular biology of systemic acquired resistance. In: Fritig B, Legrand M (eds) Mechanisms of plant defense responses. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 422–432
Levadoux L (1956) Les populations sauvages et cultivées de Vitis vinifera L. Ann Amélior Plant 6:59–117
Lodhi MA, Daly MJ, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1995) A molecular marker based linkage map of Vitis. Genome 38:786–794
Marguerit E, Boury C, Manicki A, Donnart M, Butterlin G, Némorin A, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Merdinoglu D, Ollat N, Decroocq S (2009) Genetic dissection of sex determinism, inflorescence morphology and downy mildew resistance in grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 118(7):1261–1278
Marino R, Sevini F, Madini A, Vecchione A, Pertot I, Dalla Serra A, Versini G, Velasco R, Grando MS (2003) QTL mapping for disease resistance and fruit quality in grape. Acta Hortic 603(2):527–533
Merdinoglu D, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Coste P, Dumas V, Haetty S, Butterlin G, Greif C (2003) Genetic analysis of downy mildew resistance derived from Muscadinia rotundifolia. Acta Hortic 603:451–456
Merdinoglu D, Butterlin G, Bevilacqua L, Chiquet V, Adam-Blondon AF, Decroocq S (2005) Development and characterization of a large set of microsatellite markers in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) suitable for multiplex PCR. Mol Breed 15:349–366
Moroldo M, Paillard S, Marconi R, Fabrice L, Canaguier A, Cruaud C, De Berardinis V, Guichard C, Brunaud V, Le Clainche I, Scalabrin S, Testolin R, Di Gaspero G, Morgante M, Adam-Blondon AF (2008) A physical map of the heterozygous grapevine ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ allows mapping candidate genes for disease resistance. BMC Plant Biol 8:66
Moser C, Segala C, Fontana P, Salakhudtinov I, Gatto P, Pindo M, Zyprian E, Toepfer R, Grando MS, Velasco R (2005) Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags from different organs of Vitis vinifera L. Funct Integr Genomics 5(4):208–217
Musetti R, Vecchione A, Stringher L, Borselli S, Zulini L, Marzani C, D’Ambrosio M, Sanita di Toppi L, Pertot I (2006) Inhibition of sporulation and ultrastructural alterations of grapevine downy mildew by the endophytic fungus Alternaria alternata. Phytopathology 96(7):689–698
Paterson AH, de Verna JW, Lanini B, Tanksley SD (1990) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes in an interspecific cross of tomato. Genetics 124:735–742
Pauquet J, Bouquet A, This P, Adam-Blondon AF (2001) Establishment of a local map of AFLP markers around the powdery mildew resistance gene Run1 in grapevine and assessment of their usefulness for marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 103:1201–1210
Polesani M, Desario F, Ferrarini A, Zamboni A, Pezzetti M, Kortekamp A, Polverari A (2008) cDNA-AFLP analysis of plant and pathogen genes expressed in grapevine infected with Plasmopara viticola. BMC Genomics 9:142
Riaz S, Dangl GS, Edwards KJ, Meredith CP (2004) A microsatellite marker based framework linkage map of Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 108:864–872
Salmaso M, Malacarne G, Troggio M, Faes G, Stefanini M, Grando MS, Velasco R (2008) A grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) genetic map integrating the position of 139 expressed genes. Theor Appl Genet 116:1129–1143
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias Neto E, Simpson AJG (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17(5):915–919
Scott KD, Eggler P, Seaton G, Rossetto M, Ablett EM, Lee LS, Henry RJ (2000) Analysis of SSRs derived from grape ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 100:723–726
Sefc KM, Regner F, Turetschek E, Glössl J, Steinkellner H (1999) Identification of microsatellite sequences in Vitis riparia and their applicability for genotyping of different Vitis species. Genome 42:367–373
Sevini F, Marino R, Segala C, Grando MS (2003) Development and transferability of grape EST–SSR markers suitable for mapping in Vitis spp. In: XLVII Italian society of agricultural genetics—SIGA annual congress: proceedings, Verona, Italy, 24–27 September 2003: 5.57. ISBN 88-900622-4-X
Thomas MR, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphisms when analysed as sequence-tagged sites (STSs). Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Troggio M, Malacarne G, Coppola G, Segala C, Cartwright DA, Pindo M, Stefanini M, Mank R, Moroldo M, Morgante M, Grando MS, Velasco R (2007) A dense single-nucleotide polymorphism-based genetic linkage map of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) anchoring ‘Pinot Noir’ bacterial artificial chromosome contigs. Genetics 176:2637–2650
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MapQTL® 4.0, software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Troggio M, Cartwright DA, Cestaro A, Pruss D, Pindo M, FitzGerald LM, Vezzulli S, Reid J, Malacarne G, Iliev D, Coppola G, Wardell B, Micheletti D, Macalma T, Facci M, Mitchell JT, Perazzolli M, Eldredge G, Gatto P, Oyzerski R, Moretto M, Gutin N, Stefanini M, Chen Y, Segala C, Davenport C, Dematte L, Mraz A, Battilana J, Stormo K, Costa F, Tao Q, Si-Ammour A, Harkins T, Lackey A, Perbost C, Taillon B, Stella A, Solovyev V, Fawcett JA, Sterck L, Vandepoele K, Grando MS, Toppo S, Moser C, Lanchbury J, Bogden R, Skolnick M, Sgaramella V, Bhatnagar SK, Fontana P, Gutin A, Van de Peer Y, Salamini F, Viola R (2007) A high quality draft consensus sequence of the genome of a heterozygous grapevine variety. PLoS ONE, 2(12):e1326. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0001326
Vezzulli S, Micheletti D, Riaz S, Pindo M, Viola R, This P, Walker MA, Troggio M, Velasco R (2008) A SNP transferability survey within the genus Vitis. BMC Plant Biol 16:8–128
Welter L, Gokturk-Baydar N, Akkurt M, Maul E, Eibach R, Topfer R, Zyprian EM (2007) Genetic mapping and localization of quantitative trait loci affecting fungal disease resistance and leaf morphology in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L). Mol Breed 20:359–374
Zhang J, Hausmann L, Eibach R, Welter LJ, Töpfer R, Zyprian EM (2009) A framework map from grapevine V3125 (Vitis vinifera ‘Schiava grossa’ x ‘Riesling’) x rootstock cultivar ‘Börner’ (Vitis riparia x Vitis cinerea) to localize genetic determinants of phylloxera root resistance. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1107-1
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Silvia Lorenzi, Jessica Zambanini and Giuseppina Coppola for excellent technical assistance and to Federica Sevini for the EST–SSR characterization. We also thank Ilaria Pertot for her advice in Plasmopara viticola resistance phenotyping. This work was supported by the National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Brasìlia/Brazil (Ph.D. fellowship awarded to F.M.M) and by funds from the Fondazione Cassa Di Risparmio Di Trento E Rovereto (Advanced Biology Project) and the Autonomous Province of Trento.
The author thanks the comments and suggestions of an anonymous reviewer, which critically contributed to improve the original version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. González-Martínez
Eletronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Distribution of the level of resistance to downy mildew in: A ‘Moscato Bianco’ x Vitis riparia mapping population, where F field, G greenhouse, D diameter of infection spot and S infected leaf surface; B ‘VRH3082 1-42’ x ‘SK77 5/3’ mapping population (DOC 334 kb)
Table S1
List of ESTs analysed as SSCP markers and putative function (XLS 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, F.M., Madini, A., Marino, R. et al. Genetic linkage maps of two interspecific grape crosses (Vitis spp.) used to localize quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance. Tree Genetics & Genomes 7, 153–167 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0322-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0322-x