Abstract
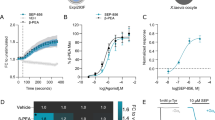
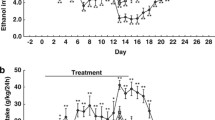
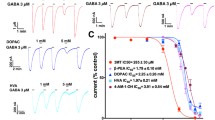
ATP-gated purinergic P2X4 receptors (P2X4Rs) are the most alcohol-sensitive P2XR subtype. We recently reported that ivermectin (IVM), an antiparasitic used in animals and humans, antagonized ethanol inhibition of P2X4Rs. Furthermore, IVM reduced ethanol intake in mice. The first molecular model of the rat P2X4R, built onto the X-ray crystal structure of zebrafish P2X4R, revealed an action pocket for both ethanol and IVM formed by Asp331, Met336 in TM2 and Trp46, and Trp50 in TM1 segments. The role of Asp331 and Met336 was experimentally confirmed. The present study tested the hypothesis that Trp46 plays a role in ethanol and IVM modulation of P2X4Rs. Trp46 was mutated to residues with different physicochemical properties and the resultant mutants tested for ethanol and IVM responses using Xenopus oocyte expression system and two-electrode voltage clamp. Nonaromatic substitutions at position 46 reduced ethanol inhibition at higher concentrations and switched IVM potentiation to inhibition. Simultaneous substitution of alanine at positions Trp46 and Met336 also resulted in similar changes in ethanol and IVM responses. Furthermore, a new molecular model based on the open pore conformation of zebrafish P2X4R suggested a role for Tyr42 that was further supported experimentally. Our previous and current findings, combined with our preliminary evidence of increased ethanol consumption in P2X4R knockout mice, suggest that the ethanol and IVM action pocket in P2X4Rs formed by positions 42, 46, 331, and 336 presents a potential target for medication development for alcohol use disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchery EE, Harwood HJ, Sacks JJ, Simon CJ, Brewer RD (2011) Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the US, 2006. Am J Prev Med 41(5):516–524. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.06.045
Khakh BS, Burnstock G, Kennedy C, King BF, North RA, Seguela P, Voigt M, Humphrey PA (2001) International union of pharmacology. XXIV. Current status of the nomenclature and properties of P2X receptors and their subunits. Pharmacol Rev 53:107–118
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Burnstock G (2008) Unresolved issues and controversies in purinergic signalling. J Physiol Online 586(14):3307–3312
Kawate T, Michel JC, Birdsong WT, Gouaux E (2009) Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state. Nature 460(7255):592–598
Hattori M, Gouaux E (2012) Molecular mechanism of ATP binding and ion channel activation in P2X receptors. Nature 485(7397):207–212. doi:10.1038/nature11010
Buell G, Lewis C, Collo G, North RA, Suprenant A (1996) An antagonist insensitive P2X receptor expressed in epithelia and brain. EMBO J 15(1):55–62
Soto F, Garcia-Guzman M, Gomez-Hernandez JM, Hollmann M, Karschin C, Stuhmer W (1996) P2X4: an ATP-activated ionotropic receptor clonned from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3684–3688
Amadio S, Montilli C, Picconi B, Calabrei PCV (2007) Mapping P2X and P2Y receptor proteins in striatum and substantia nigra: an immunohistological study. Purinergic Signal 3:389–398
Krügel U, Kittner H, Franke H, Illes P (2003) Purinergic modulation of neuronal activity in the mesolimbic dopaminergic system in vivo. Synapse 47:134–142
Davies DL, Kochegarov AA, Kuo ST, Kulkarni AA, Woodward JJ, King BF, Alkana RL (2005) Ethanol differentially affects ATP-gated P2X(3) and P2X(4) receptor subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuropharmacol 49:243–253
Asatryan L, Popova M, Perkins DI, Trudell JR, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2010) Ivermectin antagonizes ethanol inhibition in P2X4 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:720–728
Davies DL, Machu TK, Guo Y, Alkana RL (2002) Ethanol sensitivity in ATP-gated P2X receptors is subunit dependent. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:773–778
Popova M, Asatryan L, Ostrovskaya O, Wyatt RL, Li K, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2010) A point mutation in the ectodomain-transmembrane 2 interface eliminates the inhibitory effects of ethanol in P2X4 receptors. J Neurochem 112:307–317
Xiong K, Peoples RW, Montgomery JP, Chiang Y, Stewart RR, Weight FF, Li C (1999) Differential modulation by copper and zinc of P2X2 and P2X4 receptor function. J Neurophysiol 81:2088–2094
Xiong K, Li C, Weight FF (2000) Inhibition by ethanol of rat P2X4 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 130:1394–1398
Xiong K, Hu XQ, Stewart RR, Weight FF, Li C (2005) The mechanism by which ethanol inhibits rat P2X4 receptors is altered by mutation of histidine 241. Br J Pharmacol 145:576–586
Kimpel MW, Strother WN, McClintick JN, Carr LG, Liang T, Edenberg HJ, McBride WJ (2007) Functional gene expression differences between inbred alcohol-preferring and -non-preferring rats in five brain regions. Alcohol 41(2):95–132. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2007.03.003
Tabakoff B, Saba L, Printz M, Flodman P, Hodgkinson C, Goldman D, Koob G, Richardson H, Kechris K, Bell RL, Hübner N, Heinig M, Pravenec M, Mangion M, Legault L, Dongier M, Conigrave KM, Whitfield JB, Saunders JB, Grant B, Hoffman PL (2009) Genetical genomic determinants of alcohol consumption in rats and humans BMC. Biology 7:70
Khakh BS, Proctor WR, Dunwiddie TV, Labarca C, Lester HA (1999) Allosteric control of gating and kinetics at P2X4 receptor channels. J Neurosci 19:7289–7299
Norenberg W, Sobottka H, Hempel C, Plotz T, Fischer W, Schmalzing G, Schaefer M (2012) Positive allosteric modulation by ivermectin of human but not murine P2X7 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 167(1):48–66. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01987.x
Yardley MM, Wyatt L, Khoja S, Asatryan L, Ramaker MJ, Finn DA, Alkana RL, Huynh N, Louie SG, Petasis NA, Bortolato M, Davies DL (2012) Ivermectin reduces alcohol intake and preference in mice. Neuropharmacol 63. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.03.014
Asatryan L, Popova M, Woodward JJ, King BF, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2008) Roles of ectodomain and transmembrane regions in ethanol and agonist action in purinergic P2X2 and P2X3 receptors. Neuropharmacol 55(5):835–843
Yi CL, Liu YW, Xiong KM, Stewart RR, Peoples RW, Tian X, Zhou L, Ai YX, Li ZW, Wang QW, Li CY (2009) Conserved extracellular cysteines differentially regulate the inhibitory effect of ethanol in rat P2X4 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:102–106
Silberberg SD, Li M, Swartz KJ (2007) Ivermectin interaction with transmembrane helices reveals widespread rearrangements during opening of P2X receptor channels. Neuron 54(2):263–274
Jelinkova I, Vavra V, Jindrichova M, Obsil T, Zemkova HW, Zemkova H, Stojilkovic SS (2008) Identification of P2X(4) receptor transmembrane residues contributing to channel gating and interaction with ivermectin. Pflugers Arch 456:939–950
Jiang R, Taly A, Grutter T (2013) Moving through the gate in ATP-activated P2X receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 38(1):20–29. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2012.10.006
Samways DS, Khakh BS, Egan TM (2012) Allosteric modulation of Ca2+ flux in ligand-gated cation channel (P2X4) by actions on lateral portals. J Biol Chem 287(10):7594–7602. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111
King BF, Pintor J, Wang S, Ziganshin AU, Ziganshina LE, Burnstock G (1996) A novel P1 purinoceptor activates an outward K + current in follicular oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:93–100
King BF, Wang S, Burnstock G (1996) P2 purinoceptor-activated inward currents in follicular oocytes of Xenopus laveis. J Physiol (Lond) 494:17–28
Perkins DI, Trudell JR, Crawford DK, Asatryan L, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2009) Loop 2 structure in glycine and GABAA receptors plays a key role in determining ethanol sensitivity. J Biol Chem 284:27304–27314
Hibbs RE, Gouaux E (2011) Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor. Nature 474(7349):54–60. doi:10.1038/nature10139
Wimley WC, White SH (1996) Experimentally determined hydrophobicity scale for proteins at membrane interfaces. Nat Struct Biol 3(10):842–848
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Wildman SS, King BF, Burnstock G (1999) Modulation of ATP-responses at recombinant rP2X4 receptors by extracellular pH and zinc. Br J Pharmacol 126:762–768
Jelinkova I, Yan Z, Liang Z, Moonat S, Teisinger J, Stojilkovic SS, Zemkova H (2006) Identification of P2X4 receptor-specific residues contributing to the ivermectin effects on channel deactivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:619–625
Sattelle DB, Buckingham SD, Akamatsu M, Matsuda K, Pienaar I, Jones AK, Sattelle BM, Almond A, Blundell CD (2009) Comparative pharmacology and computational modelling yield insights into allosteric modulation of human [alpha]7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 78(7):836–843
Borghese CM, Henderson LA, Bleck V, Trudell JR, Harris RA (2003) Sites of excitatory and inhibitory actions of alcohols on neuronal alpha2beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:42–52
Crawford DK, Trudell JR, Bertaccini E, Li KX, Davies DL, Alkana RL (2007) Evidence that ethanol acts on a target in Loop 2 of the extracellular domain of alpha1 glycine receptors. J Neurochem 102(6):2097–2109
Mihic SJ, Ye Q, Wick MJ, Koltchine VV, Krasowski MD, Finn SE, Mascia MP, Valenzuela CF, Hanson KK, Greenblatt EP, Harris RA, Harrison NL (1997) Sites of alcohol and volatile anaesthetic action on GABA A and glycine receptors. Nature 389:385–389
Perkins DI, Trudell JR, Crawford DK, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2008) Targets for ethanol action and antagonism in loop 2 of the extracellular domain of glycine receptors. J Neurochem 106:1337–1349
Wang J, Lester HA, Dougherty DA (2007) Establishing an ion pair interaction in the homomeric rho1 gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor that contributes to the gating pathway. J Biol Chem 282(36):26210–26216
Ye Q, Koltchine VV, Mihic SJ, Mascia MP, Wick MJ, Finn SE, Harrison NL, Harris RA (1998) Enhancement of glycine receptor function by ethanol is inversely correlated with molecular volume at position à267. J Biol Chem 273:3314–3319
Dougherty DA (1996) Cation–pi interactions in chemistry and biology: a new view of benzene, Phe, Tyr, and Trp. Science 271(5246):163–168
Tatko CD, Waters ML (2004) Investigation of the nature of the methionine–pi interaction in beta-hairpin peptide model systems. Protein Sci 13(9):2515–2522. doi:10.1110/ps
Ma B, Nussinov R (2007) Trp/Met/Phe hot spots in protein–protein interactions: potential targets in drug design. Curr Topics Medicin Chem 7(10):999–1005
Bortolato M, Yardley M, Khoja S, Godar SC, Asatryan L, Finn DA, Huynh N, Alkana RL, Louie SG, Davies DL (2013) Pharmacological insights into the role of P2X4 receptors in behavioral regulation: lessons from ivermectin. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16(5):1059–1070. doi:10.1017/S1461145712000909
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Miriam Fine, Sylvia Nguyen, and Angeline Chen for technical and laboratorial assistance. This work was supported, in part, by research grants NIAAA/NIH F31 AA017029 (M.P.), KO1 AA017243 (L.A.), AA03972 (R.L.A.), AA013922 (D.L.D.), and AA013378 (J.R.T.) and the USC School of Pharmacy. This work was conducted as partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Southern California (M.P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popova, M., Trudell, J., Li, K. et al. Tryptophan 46 is a site for ethanol and ivermectin action in P2X4 receptors. Purinergic Signalling 9, 621–632 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-013-9373-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-013-9373-4