Abstract
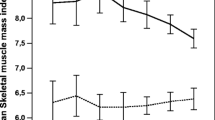
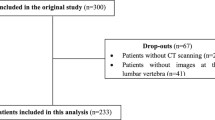
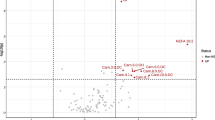
Cancer-associated muscle wasting is associated with reduction in functional status, in response to treatment and in life expectancy. Methods currently used to assess muscle loss involve diagnostic imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), which are costly, inconvenient, invasive, time consuming and have limited ability to detect early or slowly evolving wasting. We present a novel approach using single time-point urinary metabolite profiles to determine whether a patient is experiencing muscle wasting. We analyzed 93 random urine samples from patients with cancer using 1H-NMR. Using two successive CT images we assessed their lumbar skeletal muscle area (cm2) to estimate the rate of muscle change (% loss or gain over time) for each patient. The average muscle change over time was −4.71%/100 days in the muscle-losing group and +3.91%/100 days in the comparator group. Bivariate statistics identified metabolites related with muscle loss, including constituents and metabolites of muscle (creatine, creatinine, 3-OH-isovalerate), amino acids (Leu, Ile, Val, Ala, Thr, Tyr, Gln, Ser) and intermediary metabolites. We also applied machine-learning techniques to identify patterns of urinary metabolites that identify which patients are likely to lose muscle mass. We evaluated the predictive performance of 8 machine-learning approaches using fivefold cross validation and permutation testing, and found that SVM provided the best generalization accuracy (82.2%). These results suggest that 1H-NMR analysis of a single random urine sample may be a fast, cheap, safe and inexpensive tool to screen and monitor muscle loss, and that useful classifiers for predicting related metabolic conditions are possible with the methodology presented.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcay, M. N., Akcay, G., Solak, S., Balik, A. A., & Aylu, B. (2001). The effect of growth hormone on 24-h urinary creatinine levels in burned patients. Burns, 27, 42–45.
Antoun, S., Baracos, V. E., Birdsell, L., Escudier, B., & Sawyer, M. B. (2010). Low body mass index and sarcopenia associated with dose-limiting toxicity of sorafenib in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Annals of Oncology, 21, 1594–1598.
Asp, M. L., Tian, M., Wendel, A. A., & Belury, M. A. (2009). Evidence for the contribution of insulin resistance to the development of cachexia in tumor-bearing mice. International Journal of Cancer, 126, 756–763.
Bertini, I., Calabro, A., De Carli, V., Luchinat, C., Nepi, S., Porfirio, B., et al. (2009). The metabonomic signature of celiac disease. J Proteome Research, 8, 170–177.
Bidlingmeyer, B. A., Cohen, S. A., & Tarvin, T. L. (1984). Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatography, 336, 93–104.
Bollard, M. E., Stanley, E. G., Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2005). NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR in Biomedicine, 18, 143–162.
Cover, T. M., & Thomas, J. A. (2006). Elements of information theory. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience.
Craig, A., Cloarec, O., Holmes, E., Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2006). Scaling and normalization effects in NMR spectroscopic metabonomic data sets. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2262–2267.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4281–4290.
Eastman, T. (2010). A disease classifier for metabolic profiles based on metabolic pathway knowledge. MSc Thesis, University of Alberta.
Evans, W. J., Morley, J. E., Argiles, J., Bales, C., Baracos, V., Guttridge, D., et al. (2008). Cachexia: A new definition. Clinical Nutrition, 27, 793–799.
Friedman, N., Geiger, D., & Goldszmidt, M. (1997). Bayesian network classifiers. Machine Learning, 29, 131–163.
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. H. (2001). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction: With 200 full-color illustrations. New York: Springer.
Heymsfield, S. B., Wang, Z., Baumgartner, R. N., & Ross, R. (1997). Human body composition: Advances in models and methods. Annual Review of Nutrition, 17, 527–558.
Holmes, E., Foxall, P. J., Nicholson, J. K., Neild, G. H., Brown, S. M., Beddell, C. R., et al. (1994). Automatic data reduction and pattern recognition methods for analysis of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of human urine from normal and pathological states. Analytical Biochemistry, 220, 284–296.
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., et al. (2008). KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D480–D484.
Lieffers, J. R., Mourtzakis, M., Hall, K. D., Mccargar, L. J., Prado, C. M., & Baracos, V. E. (2009). A viscerally driven cachexia syndrome in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: Contributions of organ and tumor mass to whole-body energy demands. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89, 1173–1179.
Mahadevan, S., Shah, S. L., Marrie, T. J., & Slupsky, C. M. (2008). Analysis of metabolomic data using support vector machines. Analytical Chemistry, 80, 7562–7570.
Mitsiopoulos, N., Baumgartner, R. N., Heymsfield, S. B., Lyons, W., Gallagher, D., & Ross, R. (1998). Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. Journal of Applied Physiology, 85, 115–122.
Mourtzakis, M., Prado, C. M., Lieffers, J. R., Reiman, T., Mccargar, L. J., & Baracos, V. E. (2008). A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism, 33, 997–1006.
Pesarin, F. (2001). Multivariate permutation tests: With applications in biostatistics. Chichester, New York: J. Wiley.
Prado, C. M., Baracos, V. E., Mccargar, L. J., Mourtzakis, M., Mulder, K. E., Reiman, T., et al. (2007). Body composition as an independent determinant of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Clinical Cancer Research, 13, 3264–3268.
Prado, C. M., Lieffers, J. R., Mccargar, L. J., Reiman, T., Sawyer, M. B., Martin, L., et al. (2008). Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncology, 9, 629–635.
Prado, C. M., Baracos, V. E., Mccargar, L. J., Reiman, T., Mourtzakis, M., Tonkin, K., et al. (2009). Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving capecitabine treatment. Clinical Cancer Research, 15, 2920–2926.
Quinlan, J. R. (1993). C4.5: Programs for machine learning. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Ross, R. (2003). Advances in the application of imaging methods in applied and clinical physiology. Acta Diabetologica, 40(Suppl 1), S45–S50.
Saude, E. J., & Sykes, B. D. (2007). Urine stability for metabolomic studies: Effects of preparation and storage. Metabolomics, 3, 19–27.
Shen, W., Punyanitya, M., Wang, Z., Gallagher, D., St-Onge, M. P., Albu, J., et al. (2004a). Total body skeletal muscle and adipose tissue volumes: Estimation from a single abdominal cross-sectional image. Journal of Applied Physiology, 97, 2333–2338.
Shen, W., Punyanitya, M., Wang, Z., Gallagher, D., St-Onge, M. P., Albu, J., et al. (2004b). Visceral adipose tissue: Relations between single-slice areas and total volume. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 80, 271–278.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K. N., Wagner, J., Fu, H., Chang, D., Weljie, A. M., et al. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 6995–7004.
Tan, B. H., Birdsell, L. A., Martin, L., Baracos, V. E., & Fearon, K. C. (2009). Sarcopenia in an overweight or obese patient is an adverse prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(22), 6973–6979.
Wagner, A., & Fell, D. A. (2001). The small world inside large metabolic networks. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Biological Science, 268, 1803–1810.
Walsh, M. C., Brennan, L., Malthouse, J. P., Roche, H. M., & Gibney, M. J. (2006). Effect of acute dietary standardization on the urinary, plasma, and salivary metabolomic profiles of healthy humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 84(3), 531–539.
Wang, X., Hu, Z., Hu, J., Du, J., & Mitch, W. E. (2006). Insulin resistance accelerates muscle protein degradation: Activation of the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway by defects in muscle cell signaling. Endocrinology, 147, 4160–4168.
Weljie, A. M., Newton, J., Mercier, P., Carlson, E., & Slupsky, C. M. (2006). Targeted profiling: Quantitative analysis of 1H NMR metabolomics data. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4430–4442.
Westerhuis, J. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Smit, S., Vis, D. J., Smilde, A. K., Van Velzen, E. J. J., et al. (2008). Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics, 4, 81–89.
Wishart, D. S. (2007). Current progress in computational metabolomics. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 8, 275–284.
Wishart, D. S. (2008). Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27, 228–237.
Wishart, D. S., Tzur, D., Knox, C., Eisner, R., Guo, A. C., Young, N., et al. (2007). HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Research, 35(Database issue), D521–D526.
Witten, I. H., & Frank, E. (2005). Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Boston, MA: Morgan Kaufman.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Alberta Cancer Foundation (ACF), the Cross Cancer Institute, the Alberta Ingenuity Fund (AIF), the Alberta Advanced Education and Technology (AAET), the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR) and the Alberta Ingenuity Centre for Machine Learning (AICML) for financial support.
Financial or material support
This work was supported by grants from the Alberta Cancer Board and Alberta Cancer Foundation, the Alberta Ingenuity Fund, the Alberta Ingenuity Centre for Machine Learning, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and Genome Canada.
Author disclosures
R. Eisner, C. Stretch, T. Eastman, J. Xia, D. Hau, S. Damaraju, R. Greiner, D.S. Wishart and V.E. Baracos have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Roman Eisner and Cynthia Stretch contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eisner, R., Stretch, C., Eastman, T. et al. Learning to predict cancer-associated skeletal muscle wasting from 1H-NMR profiles of urinary metabolites. Metabolomics 7, 25–34 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0232-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0232-9