Abstract
Introduction
Solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs) are commonly found in imaging technologies, but are plagued by high false-positive rates.
Objective
We aimed to identify metabolic alterations in SPN etiology and diagnosis using less invasive plasma metabolomics and lipidomics.
Methods
In total, 1160 plasma samples were obtained from healthy volunteers (n = 280), benign SPNs (n = 157) and malignant SPNs (stage I, n = 723) patients enrolled from 5 independent centers. Gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC‒MS) and liquid chromatography-Q Exactive Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry (LC‒MS) were used to analyze the samples for untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics.
Results and conclusion
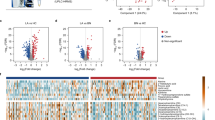
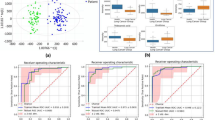
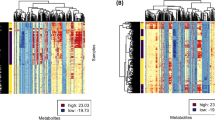
GC‒MS-based metabolomics revealed 1336 metabolic features, while LC‒MS-based lipidomics revealed 6088 and 2542 lipid features in the positive and negative ion modes, respectively. The metabolic and lipidic characteristics of healthy vs. benign or malignant SPNs exhibited substantial pattern differences. Of note, benign and malignant SPNs had no significant variations in circulating metabolic and lipidic markers and were validated in four other centers. This study demonstrates evidence of early metabolic alterations that can possibly distinguish SPNs from healthy controls, but not between benign and malignant SPNs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- LC–MS:
-
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- OPLS-DA:
-
Orthogonal partial least-squared discriminant analysis
- PCA:
-
Principal components analysis
- QC:
-
Quality control
- SPNs:
-
Solitary pulmonary nodules
- VIP:
-
Variable importance in the projection
References
Au-Yong, I. T. H., Hamilton, W., Rawlinson, J., & Baldwin, D. R. (2020). Pulmonary nodules. BMJ, 371, m3673. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3673
Baharum, S.N.; Azizan, K.A. (2018) Metabolomics in systems biology. In: Wan Mohd Aizat, Hoe-Han Goh, Syarul Nataqain Baharum (eds), Omics Applications for Systems Biologyed. Springer, cham https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98758-3_4
Calderon-Santiago, M. (2021). MetaboQC: Normalize metabolomic data using QC signal. r-project.org/web/packages/MetaboQC/MetaboQC.pdf.
Cruickshank, A., Stieler, G., & Ameer, F. (2019). Evaluation of the solitary pulmonary nodule. The Internal Medicine Journal, 49, 306–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.14219
Detterbeck, F. C., Boffa, D. J., Kim, A. W., & Tanoue, L. T. (2017). The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest, 151(1), 193–203.
Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D., Begley, P., Zelena, E., Francis-McIntyre, S., Anderson, N., et al. (2011). Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nature Protocol, 6, 1060–1083. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.335
Fahrmann, J. F., Grapov, D., DeFelice, B. C., Taylor, S., Kim, K., Kelly, K., et al. (2016). Serum phosphatidylethanolamine levels distinguish benign from malignant solitary pulmonary nodules and represent a potential diagnostic biomarker for lung cancer. Cancer Biomarkers, 16, 609–617. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160602
Gao, L., Wen, Z., Wu, C., Wen, T., & Ong, C. N. (2013). Metabolic profiling of plasma from benign and malignant pulmonary nodules patients using mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Metabolites, 3, 539–551. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030539
Gould, M. K., Tang, T., Liu, I. L., Lee, J., Zheng, C., Danforth, K. N., et al. (2015). Recent trends in the identification of incidental pulmonary nodules. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 192, 1208–1214. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201505-0990OC
Harris, F. T., Rahman, S. M., Hassanein, M., Qian, J., Hoeksema, M. D., Chen, H., et al. (2014). Acyl-coenzyme A-binding protein regulates Beta-oxidation required for growth and survival of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Prevention Research, 7, 748–757. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0057
Horeweg, N., van Rosmalen, J., Heuvelmans, M. A., van der Aalst, C. M., Vliegenthart, R., Scholten, E. T., et al. (2014). Lung cancer probability in patients with CT-detected pulmonary nodules: A prespecified analysis of data from the NELSON trial of low-dose CT screening. The Lancet Oncology, 15, 1332–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70389-4
Issaq, H. J., & Veenstra, T. D. (Eds.). (2013). Proteomic and metabolomic approaches to biomarker discovery. Cambridge: Elsevier Academic Press.
Li, W. W., Shan, J. J., Lin, L. L., Xie, T., He, L. L., Yang, Y., et al. (2017). Disturbance in plasma metabolic profile in different types of human cytomegalovirus-induced liver injury in infants. Scientific Reports, 7, 15696. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16051-8
Nasim, F., & Ost, D. E. (2019). Management of the solitary pulmonary nodule. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine, 25, 344–353. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcp.0000130322.11513.c8
Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2008). Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature, 455, 1054–1056. https://doi.org/10.1038/4551054a
Noreldeen, H. A. A., Liu, X., & Xu, G. (2020). Metabolomics of lung cancer: Analytical platforms and their applications. Journal of Separation Science, 43, 120–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900736
Ost, D., Fein, A. M., & Feinsilver, S. H. (2003). The solitary pulmonary nodule. The New England Journal of Medicine., 348, 2535–2542. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp012290
Tsugawa, H., Cajka, T., Kind, T., Ma, Y., Higgins, B., Ikeda, K., et al. (2015). MS-DIAL: data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nature Methods., 12, 523–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3393
van Klaveren, R. J., Oudkerk, M., Prokop, M., Scholten, E. T., Nackaerts, K., Vernhout, R., et al. (2009). Management of lung nodules detected by volume CT scanning. The New England Journal of Medicine, 361, 2221–2229. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0906085
Wehrens, R., Hageman, J. A., van Eeuwijk, F., Kooke, R., Flood, P. J., Wijnker, E., et al. (2016). Improved batch correction in untargeted MS-based metabolomics. Metabolomics, 12, 88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1015-8
Wishart, D. S. (2016). Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 15, 473–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.32
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81803694, 81904254), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2632020ZD07); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. BK20190808); Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. 19KJB360002); Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing university of Chinese medicine (NZY81904254); Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), No. 87 [2018]; the Open Projects of the Discipline of Chinese Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine Supported by the Subject of Academic priority discipline of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Grant No. ZYX03KF52). The authors also thank Dr. Raphael N. Alolga from China Pharmaceutical University and American Journal Experts (an editing company) for the editorial services rendered.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,81803694,81904254,Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities,2632020ZD07,Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province,BK20190808,Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province,19KJB360002,Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing university of Chinese medicine,NZY81904254,Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions,87 [2018],the Open Projects of the Discipline of Chinese Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine Supported by the Subject of Academic priority discipline of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, ZYX03KF52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ, L-yJ, LL, J-lW, JY, L-cD, Z-hZ and J-jS: conceptualization, Methodology and Writing- Original draft preparation. W-cX, YZ, M-jW, X-mC and H-qL: Data curation and Resources. WZ and J-jS: Investigation and Supervision. WZ and J-jS: Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest declared.
Ethical approval
The Affiliated Jiangyin Hospital of Southest University Medical College approved this study (2017-036), in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, approved use of the patient plasma samples. Patients gave written informed consent before enrolment.
Data availability
The mass spectrometry data have been deposited to the Metabolomics Workbench (https://www.metabolomicsworkbench.org/). The study named ST001937. Reviewer account details: Username: jshan12345678. Password: Shan85811329 (http://dev.metabolomicsworkbench.org:22222/data/DRCCMetadata.php?Mode=Study&StudyID=ST001937). Further details and other data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Wei Zhou, Lili Lin, Lian-yong Jiang and Jin-long Wu are the co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Lin, L., Jiang, Ly. et al. Comprehensive plasma metabolomics and lipidomics of benign and malignant solitary pulmonary nodules. Metabolomics 18, 71 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01929-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01929-0