Abstract
Background
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are highly prevalent in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and dyslipidemia is an important factor. Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP, log[TG/HDL-C]) and apolipoproteinB to apolipoproteinAI ratio (apoB/apoAI ratio) are considered high quality predictors of cardiovascular risk. However, the associations between OSA severity and AIP and apoB/apoAI ratio remained unclear.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed in 284 patients. Subjects were assessed with polysomnography (PSG) test, and OSA severity was defined by AHI. Data collected included anthropometric measurements, medical history, sleep parameters, fasting plasma lipids, fasting blood glucose, and insulin.
Results
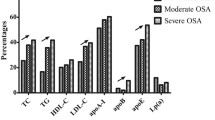
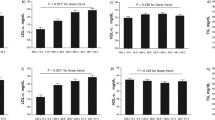
Participants were classified based on AHI into the following groups: control group (n = 28), mild group (n = 52), moderate group (n = 53), and severe group (n = 151). Triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apoAI, AIP, apoB/apoAI ratio (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, and HDL-C/apoAI ratio showed statistical significance among AHI subgroups (P < 0.05). The Pearson correlation analysis revealed that AIP (r = 0.32, P < 0.001) and apoB/apoAI ratio (r = 0.24, P < 0.001) were positively related to AHI. By multivariate linear regression analysis, we found that AHI was independently related to AIP (β = 0.24, P = 0.001), apoB/apoAI ratio (β = 0.24, P<0.001).
Conclusion
AHI was independently correlated with AIP and apoB/apoAI ratio in OSA. Our findings suggested that AIP and apoB/apoAI ratio increased with OSA severity, which might be partly responsible for the high risk of CVDs in OSA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Coughlin S (2004) Obstructive sleep apnoea is independently associated with an increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Eur Heart J 25:735–741
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigos J, Lisheng L (2004) Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. LANCET 364:937–952
Millan J, Pinto X, Munoz A, Zuniga M, Rubies-Prat J, Pallardo LF, Masana L, Mangas A, Hernandez-Mijares A, Gonzalez-Santos P, Ascaso JF, Pedro-Botet J (2009) Lipoprotein ratios: physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular prevention. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:757–765
Cai G, Shi G, Xue S, Lu W (2017) The atherogenic index of plasma is a strong and independent predictor for coronary artery disease in the Chinese Han population. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e8058
Wu T, Gao Y, Zheng Y, Ma Y, Xie X (2018) (AIP-AI ) Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP): a novel predictive indicator for the coronary artery disease in postmenopausal women. LIPIDS HEALTH DIS 17:197
Kaneva AM, Potolitsyna NN, Bojko ER, Odland JØ (2015) The Apolipoprotein B/Apolipoprotein A-I ratio as a potential marker of plasma atherogenicity. Dis Markers 2015:1–7
Dobiásová M, Frohlich J (2001) The plasma parameter log (TG/HDL-C) as an atherogenic index: correlation with lipoprotein particle size and esterification rate in apoB-lipoprotein-depleted plasma (FER(HDL)). Clin Biochem 34:583
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. DIABETOLOGIA 28:412–419
Roche F, Sforza E, Pichot V, Maudoux D, Garcin A, Celle S, Picard-Kossovsky M, Gaspoz J, Barthélémy JC (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnea influences high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the elderly. Sleep Med 10:882–886
Nadeem R, Singh M, Nida M, Waheed I, Khan A, Ahmed S, Naseem J, Champeau D (2014) Effect of obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome on lipid profile: a meta-regression analysis. J Clin Sleep Med 10:475–489
Newman AB, Nieto FJ, Guidry U, Lind BK, Redline S, Pickering TG, Quan SF (2001) (TG)relation of sleep-disordered breathing to cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 154:50–59
Adedayo AM, Olafiranye O, Smith D, Hill A, Zizi F, Brown C, Jean-Louis G (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea and dyslipidemia: evidence and underlying mechanism. Sleep Breath 18:13–18
Kawano Y, Tamura A, Kadota J (2012) Association between the severity of obstructive sleep apnea and the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. METABOLISM 61:186–192
Marotta T, Ferrara LA, Di Marino L, Mancini M, Annuzzi G, Russo O, D’Orta G, Lucarelli C, Rossi F (1995) Factors affecting lipoprotein lipase in hypertensive patients. METABOLISM 44:712–718
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Zhan Y, Xu T, Tan X (2016) Two parameters reflect lipid-driven inflammatory state in acute coronary syndrome: atherogenic index of plasma, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 16:96
Niroumand S, Khajedaluee M, Khadem-Rezaiyan M, Abrishami M, Juya M, Khodaee G, Dadgarmoghaddam M (2015) Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP): a marker of cardiovascular disease. Med J Islam Repub Iran 29:240
Wu TT, Gao Y, Zheng YY, Ma YT, Xie X (2018) Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP): a novel predictive indicator for the coronary artery disease in postmenopausal women. Lipids Health Dis 17:197
Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Vicente E, Agusti AG (2005) Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: an observational study. LANCET 365:1046–1053
Walldius G, Jungner I (2004) Apolipoprotein B and apolipoprotein A-I: risk indicators of coronary heart disease and targets for lipid-modifying therapy. J Intern Med 255:188–205
Walldius G, Jungner I (2006) The apoB/apoA-I ratio: a strong, new risk factor for cardiovascular disease and a target for lipid-lowering therapy--a review of the evidence. J Intern Med 259:493–519
Xu H, Guan J, Yi H, Zou J, Meng L, Tang X, Zhu H, Yu D, Zhou H, Su K, Wang Y, Wang J, Yin S, Shanghai SHSR, The SSHS (2016) Elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is independently associated with obstructive sleep apnea: evidence from a large-scale cross-sectional study. Sleep Breath 20:627–634
Sierra-Johnson J, Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Lopez-Jimenez F, Walldius G, Hamsten A, Hellenius ML, Fisher RM (2007) ApoB/apoA-I ratio: an independent predictor of insulin resistance in US non-diabetic subjects. Eur Heart J 28:2637–2643
Sniderman AD, Faraj M (2007) Apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein A-I, insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Lipidol 18:633–637
Seetho IW, Wilding JP (2014) Sleep-disordered breathing, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. ChroN Resp Dis 11:257–275
Walldius G, Jungner I, Aastveit AH, Holme I, Furberg CD, Sniderman AD (2004) The apoB/apoA-I ratio is better than the cholesterol ratios to estimate the balance between plasma proatherogenic and antiatherogenic lipoproteins and to predict coronary risk. Clin Chem Lab Med 42:1355–1363
Rasouli M, Kiasari AM, Mokhberi V (2006) The ratio of apoB/apoAI, apoB and lipoprotein(a) are the best predictors of stable coronary artery disease. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM) 44
Lin Q, Zhang X, Chen G, Huang D, Din H, Tang A (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with some components of metabolic syndrome in nonobese adults. Sleep Breath 16:571–578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, B., Fan, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Independent association of severity of obstructive sleep apnea with lipid metabolism of atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) and apoB/apoAI ratio. Sleep Breath 24, 1507–1513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02016-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02016-1