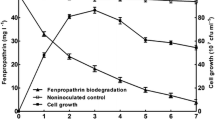
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain GF31, isolated from a contaminated soil, can effectively degrade β-cypermethrin (β-CP), as well as fenpropathrin, fenvalerate, and cyhalothrin. The highest level of degradation (81.2 %) was achieved with the addition of peptone. Surprisingly, the enzyme responsible for degradation was mainly localized to the extracellular areas of the bacteria, in contrast to the other known pyrethroid-degrading enzymes, which are intracellular. Although intact bacterial cells function at about 30 °C for biodegradation, similar to other degrading strains, the crude extracellular extract of strain GF31 remained biologically active at 60 °C. Moreover, the extract fraction showed good storage stability, maintaining >50 % of its initial activity following storage at 25 °C for at least 20 days. Significant differences in the characteristics of the crude GF31 extracellular extract compared with the known pyrethroid-degrading enzymes indicate the presence of a novel pyrethroid-degrading enzyme. Furthermore, the identification of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid and 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate from the degradation products suggests the possibility that β-CP degradation by both the strain and the crude extracellular fraction is achieved through a hydrolysis pathway. Further degradation of these two metabolites may lead to the development of an efficient method for the mineralization of these types of pollutants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Hussain I, Khan A, Najib ur R (2009) Deleterious effects of cypermethrin on semen characteristics and testes of dwarf goats (Capra hircus). Exp Toxicol Pathol 61(4):339–346
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Chen SH, Yang L, Hu M, Liu J (2010) Biodegradation of fenvalerate and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Stenotrophomonas sp. strain ZS-S-01 and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(2):755–767
Chen SH, Hu M, Liu J, Zhong G, Yang L, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Han H (2011) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Ochrobactrum lupini DG-S-01. J Hazard Mater 187(1–3):433–440
Chen SH, Dong YH, Chang C, Deng Y, Zhang XF, Zhong G, Song H, Hu M, Zhang LH (2013) Characterization of a novel cyfluthrin-degrading bacterial strain Brevibacterium aureum and its biochemical degradation pathway. Bioresour Technol 132:16–23
Fan XJ, Liu XL, Huang R, Liu YH (2012) Identification and characterization of a novel thermostable pyrethroid-hydrolyzing enzyme isolated through metagenomic approach. Microb Cell Factories 11(1):33–43
Galera M, Vidal JLM (1996) Determination of cypermethrin, fenvalerate and cis-and trans-permethrin in soil and groundwater by high-performance liquid chromatography using partial least-squares regression. J Chromatogr A 727(1):39–46
Guo P, Wang B, Hang B et al (2009) Pyrethroid-degrading Sphingobium sp. JZ-2 and the purification and characterization of a novel pyrethroid hydrolase. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63(8):1107–1112
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, USA
Kwak YY, Rhee IK, Shin JH (2013) Expression pattern of recombinant organophosphorus hydrolase from Flavobacterium sp. ATCC 27551 in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8097–8105
Lanzon JB, Brown DG (2013) Partitioning of phenanthrene into surfactant hemi-micelles on the bacterial cell surface and implications for surfactant-enhanced biodegradation. Water Res 47(13):4612–4620
Li G, Wang K, Liu YH (2008) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing esterase originating from the metagenome. Microb Cell Factories 7(1):38–47
Li QY, Gu BQ, Liu YY, Zhou MZ, Li C, Qin YM, Zhong SJ (2009) Isolation, identification and characteristics of a cypermethrin-degrading bacterium GF31. Microbiology 36(9):1334–1339 (in Chinese)
Li H, Mehler TW, Lydy MJ, You J (2011) Occurrence and distribution of sediment-associated insecticides in urban waterways in the Pearl River Delta, China. Chemosphere 82(10):1373–1379
Liang WQ, Wang ZY, Li H, Wu PC, Hu JM, Luo N, Cao LX, Liu YH (2005) Purification and characterization of a novel pyrethroid hydrolase from Aspergillus niger ZD11. J Agric Food Chem 53(19):7415–7420
Lin QS, Chen SH, Hu MY, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Yang L, Li H (2011) Biodegradation of cypermethrin by a newly isolated actinomycetes HU-S-01 from wastewater sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(1):45–56
Liu P, Liu Y, Liu Q, Liu J (2010) Photodegradation mechanism of deltamethrin and fenvalerate. J Environ Sci 22(7):1123–1128
Maloney SE, Maule A, Smith AR (1993) Purification and preliminary characterization of permethrinase from a pyrethroid-transforming strain of Bacillus cereus. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(7):2007–2013
Mazotto AM, de Melo ACN, Macrae A et al (2010) Biodegradation of feather waste by extracellular keratinases and gelatinases from Bacillus spp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(6):1355–1365
Meeker JD, Barr DB, Hauser R (2009) Pyrethroid insecticide metabolites are associated with serum hormone levels in adult men. Reprod Toxicol 27(2):155–160
Mehler WT, Li H, Lydy MJ, You J (2011) Identifying the causes of sediment-associated toxicity in urban waterways of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci Technol 45(5):1812–1819
Nannipier P, Bollag JM (1991) Use of enzymes to detoxify pesticide-contaminated soils and waters. J Environ Qual 20:510–517
Neu HC, Heppel LA (1965) The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem 204(9):3685–3692
Niebisch CH, Malinowski AK, Schadeck R et al (2010) Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive blue 220 textile dye by Lentinus crinitus extracellular extract. J Hazard Mater 180(1–3):316–322
Saikia N, Gopal M (2004) Biodegradation of α-cyfluthrin by fungi. J Agric Food Chem 52(5):1220–1223
Shafer TJ, Meyer DA, Crofton KM (2005) Developmental neurotoxicity of pyrethroid insecticides: critical review and future research needs. Environ Health Perspect 113(2):123–136
Sogorb MA, Vilanova E (2002) Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol Lett 128:215–228
Tallur P, Megadi V, Ninnekar H (2008) Biodegradation of cypermethrin by micrococcus sp. strain CPN 1. Biodegradation 19(1):77–82
Thouand G (2014) Biodegradability assessments of organic substances and polymers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9443–9444
Wang BZ, Ma Y, Zhou WY et al (2011) Biodegradation of synthetic pyrethroids by Ochrobactrum tritici strain pyd-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(10):2315–2324
Wolansky MJ, Harrill JA (2008) Neurobehavioral toxicology of pyrethroid insecticides in adult animals: a critical review. Neurotoxicol Teratol 30(2):55–78
Xu G, Zheng W, Li Y et al (2008) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by a newly isolated Paracoccus sp. strain TRP. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62(1):51–56
Yu Y, Fan D (2003) Preliminary study of an enzyme extracted from Alcaligenes sp. strain YF11 capable of degrading pesticides. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70(2):367–371
Zhang C, Jia L, Wang S, Qu J, Li K, Xu L, Shi Y, Yan Y (2010a) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by two Serratia spp. with different cell surface hydrophobicity. Bioresour Technol 101(10):3423–3429
Zhang SB, Yin L, Liu Y, Zhang D, Luo X, Je C, Cheng F, Dai J (2010b) Cometabolic biotransformation of fenpropathrin by Clostridium species strain ZP3. Biodegradation 22(5):869–875
Zhang C, Wang S, Yan Y (2011) Isomerization and biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa CH7 with biosurfactant production. Bioresour Technol 102(14):7139–7146
Zita A, Hermansson M (1997) Effects of bacterial cell surface structures and hydrophobicity on attachment to activated sludge flocs. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1168–1170
Acknowledgments
This work was support in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51108098), the Graduate Student Innovation Projects of Guangxi (No. GXU11T31090), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (No. XJZ120278).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, A., Wang, B., Liu, Y. et al. Biodegradation and extracellular enzymatic activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain GF31 on β-cypermethrin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 13049–13057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4545-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4545-0