Abstract
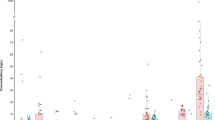
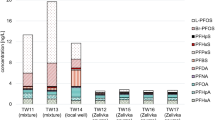
We examined per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in air from eight cities, and in water from six drinking-water treatment plants (DWTPs), in central eastern China. We analyzed raw and treated water samples from the DWTPs for 17 ionic PFASs with high-performance liquid chromatography/negative-electrospray-ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/(–)ESI-MS/MS), and analyzed the gas and particle phases of atmospheric samples for 12 neutral PFASs by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) were the dominant compounds in drinking water, and fluorotelomer alcohols (FTOHs) dominated in atmospheric samples. Of all the compounds in the treated water samples, the concentration of PFOA, at 51.0 ng L−1, was the highest. Conventional treatments such as coagulation (COA), flocculation (FOC), sedimentation (SED), and sand filtration (SAF) did not remove PFASs. Advanced treatments, however, including ultrafiltration (UF) and activated carbon (AC), removed the majority of PFASs except for shorter-chain PFASs such as perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) and perfluoropentanoic acid (PFPA). We also investigated human exposure to PFASs via drinking water and the atmosphere and found that the mean daily intake of PFASs was 0.43 ng kg−1 day−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 March 2018
The original publication of this paper contains a mistake.
References
Ahrens L, Plassmann M, Xie Z, Ebinghaus R (2009) Determination of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water and suspended particulate matter in the river Elbe and the North Sea, Germany. Front Environ Sci Eng China 3(2):152–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0021-8
Ahrens L, Taniyasu S, Yeung LWY, Yamashita N, Lam PKS, Ebinghaus R (2010) Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 79(3):266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.01.045
Appleman TD, Higgins CP, Quinones O, Vanderford BJ, Kolstad C, Zeigler-Holady JC, Dickenson ERV (2014) Treatment of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in US full-scale water treatment systems. Water Res 51:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.067
Bao J, Liu W, Liu L, Jin YH, Dai JY, Ran XR, Zhang ZX, Tsuda S (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in the environment and the blood of residents living near fluorochemical plants in Fuxin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8075–8080. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102610x
Barber JL, Berger U, Chaemfa C, Huber S, Jahnke A, Temme C, Jones KC (2007) Analysis of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J Environ Monit 9(6):530–541. https://doi.org/10.1039/b701417a
Benskin, J. P.; Ikonomou, M. G.; Gobas, F. A. P. C.; Begley, T. H.; Woudneh, M. B.; Cosgrove, J. R ( 2013) Biodegradation of N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamido ethanol (EtFOSE) and EtFOSE-based phosphate diester (SAmPAP diester) in marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol 47: 1381–1389, 3, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/es304336r
Beškoski VP, Takemine S, Nakano T, Beškoski LS, Gojgić-Cvijović G, Ilić M, Miletić S, Vrvić MM (2013) Perfluorinated compounds in sediment samples from the wastewater canal of Pančevo (Serbia) industrial area. Chemosphere 91(10):1408–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.079
Beškoski VP, Yamamoto K, Yamamoto A, Okamura H, Hayashi M, Nakano T, Inui H (2017) Distribution of perfluoroalkyl compounds in Osaka Bay and coastal waters of Western Japan. Chemosphere 170:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.028
Boiteux V, Dauchy X, Rosin C, Munoz J-F (2012) National screening study on 10 perfluorinated compounds in raw and treated tap water in France. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicology 63:1–12
Boiteux V, Dauchy X, Bach C, Colin A, Hemard J, Sagres V, Munoz JF (2017) Concentrations and patterns of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a river and three drinking water treatment plants near and far from a major production source. Sci Total Environ 583:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.079
Cai, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, H.Z.; Yin, Z.G.; Hong, Q.Q.; Sturm, R.; Ebinghaus, R.; Ahrens, L.; Cai, M.G.; He, J.F; Xie, Z.Y (2012b) Spatial distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds in coastal waters from the east to South China Sea. Environ Pollut 161: 162–169, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.09.045
Cai, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, Z.G.; Ahrens, L.; Huang, P.; Cai, M.G.; Yang, H.Z; He, J.F.; Sturm, R.; Ebinghaus, R.; Xie, Z.Y. (2011) Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl compounds in surface waters from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ Scie Technol 46: 661–668
Cai MH, Xie Z, Möller A, Yin Z, Huang P, Cai M, Yang H, Sturm R, He J, Ebinghaus R (2012a) Polyfluorinated compounds in the atmosphere along a cruise pathway from the Japan Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Chemosphere 87(9):989–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.010
De Solla SR, De Silva AO, Letcher RJ (2012) Highly elevated levels of perfluorooctane sulfonate and other perfluorinated acids found in biota and surface water downstream of an international airport, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Environ Int 39(1):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.09.011
Dreyer A, Ebinghaus R (2009) Polyfluorinated compounds in ambient air from ship- and land-based measurements in northern Germany. Atmos Environ 43:1527–1535
Eschauzier C, Beerendonk E, Scholte-Veenendaal P, De Voogt P (2012) Impact of treatment processes on the removal of perfluoroalkyl acids from the drinking water production chain. Environ. Sci. Technol 46(3):1708–1715. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201662b
Flores, C.; Ventura, F.; Martin-Alonso, J; Caixach, J. (2013) Occurrence of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in NE Spanish surface waters and their removal in a drinking water treatment plant that combines conventional and advanced treatments in parallel lines. Sci. Total Environ 461: 618–626
Fromme H, Tittlemier SA, Volkel W, Wilhelm M, Twardella D (2009) Perfluorinated compounds - exposure assessment for the general population in western countries. Int J Hyg Envir Heal 212(3):239–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.04.007
Geiger SD, Xiao J, Ducatman A, Frisbee S, Innes K, Shankar A (2014) The association between PFOA, PFOS and serum lipid levels in adolescents. Chemosphere 98:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.005
Genualdi S, Lee SC, Shoeib M, Gawor A, Ahrens L, Harner T (2010) Global pilot study of legacy and emerging persistent organic pollutants using sorbent-impregnated polyurethane foam disk passive air samplers. Environ. Sci. Technol 44(14):5534–5539. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1009696
Gorrochategui, E.; Perez-Albaladejo, E.; Casas, J.; Lacorte, S; Porte, C. (2014) Perfluorinated chemicals: differential toxicity, inhibition of aromatase activity and alteration of cellular lipids in human placental cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 277: 124–130, 2, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.03.012
Higgins CP, Luthy RG (2006) Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol 40(23):7251–7256. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061000n
Holzer J, Midasch O, Rauchfuss K, Kraft M, Reupert R, Angerer J, Kleeschulte P, Marschall N, Wilhelm M (2008) Biomonitoring of perfluorinated compounds in children and adults exposed to perfluorooctanoate-contaminated drinking water. Environ. Health Persp 116(5):651–657. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11064
Kim SK, Kho YL, Shoeib M, Kim KS, Kim KR, Park JE, Shin YS (2011) Occurrence of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate in the Korean water system: implication to water intake exposure. Environ Pollut 159(5):1167–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.004
Kim, S.K.; Shoeib, M.; Kim, K.S; Park, J.E. (2012) Indoor and outdoor poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Korea determined by passive air sampler. Environ Pollut 162:144–150, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.10.037
Knox SS, Jackson T, Javins B, Frisbee SJ, Shankar A, Ducatman AM (2011) Implications of early menopause in women exposed to perfluorocarbons. J Clin Endocr Metab 96(6):1747–1753. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-2401
Kunacheva C, Fujii S, Tanaka S, Kitpati Boontanon S, Poothong S, Wongwatthana T, Shivakoti BR (2010) Perfluorinated compounds contamination in tap water and bottled water in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.-Aqua 59:345
Kwok KY, Taniyasu S, Yeung LWY, Murphy MB, Lam PKS, Horii Y, Kannan K, Petrick G, Sinha RK, Yamashita N (2010) Flux of perfluorinated chemicals through wet deposition in Japan, the United States, and several other countries. Environ. Sci. Technol 44(18):7043–7049. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101170c
Li J, Del Vento S, Schuster J, Zhang G, Chakraborty P, Kobara Y, Jones KC (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in the Asian atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol 45(17):7241–7248. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201739t
Llorca M, Farre M, Pico Y, Muller J, Knepper TP, Barcelo D (2012) Analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances in waters from Germany and Spain. Sci. Total Environ 431:139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.011
Lundgren S. (2014) Evaluation of the efficiency of treatment techniques in removing perfluoroalkyl substances from water
Mak YL, Taniyasu S, Yeung LWY, Lu G, Jin L, Yang Y, Lam PKS, Kannan K, Yamashita N (2009) Perfluorinated compounds in tap water from China and several other countries. Environ Sci Technol 43(13):4824–4829. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900637a
Melzer D, Rice N, Depledge MH, Henley WE, Galloway TS (2010) Association between serum perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and thyroid disease in the US national health and nutrition examination survey. Environ. Health Persp 118(5):686–692. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901584
Muller CE, Gerecke AC, Bogdal C, Wang ZY, Scheringer M, Hungerbuhler K (2012) Atmospheric fate of poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs): I. Day-night patterns of air concentrations in summer in Zurich, Switzerland. Environ. Pollut 169:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.010
Naile JE, Khim JS, Wang T, Chen C, Luo W, Kwon B-O, Park J, Koh C-H, Jones PD, Lu Y, Giesy J (2010) P.Perfluorinated compounds in water, sediment, soil and biota from estuarine and coastal areas of Korea. Environ. Pollut 158(5):1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.023
Papadopoulou E, Sabaredzovic A, Namork E, Nygaard UC, Granum B, Haug LS (2016) Exposure of Norwegian toddlers to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): the association with breastfeeding and maternal PFAS concentrations. Environ Int 94:687–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.07.006
Piekarz AM, Primbs T, Field JA, Barofsky DF, Simonich S (2007) Semivolatile fluorinated organic compounds in Asian and western US air masses. Environ. Sci. Technol 41(24):8248–8255. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0713678
Post GB, Louis JB, Lippincott RL, Procopio NA (2013) Occurrence of perfluorinated compounds in raw water from New Jersey public drinking water systems. Environ. Sci. Technol 47(23):13266–13275. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402884x
Reagen WK, Ellefson ME, Kannan K, Giesy JP (2008) Comparison of extraction and quantification methods of perfluorinated compounds in human plasma, serum, and whole blood. Anal Chim Acta 628(2):214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.09.029
Rhoads, K. R.; Janssen, E. M.-L.; Luthy, R. G.; Criddle, C. S (2008) Aerobic biotransformation and fate of N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol (N-EtFOSE) in activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol 42:2873–2878, 8, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/es702866c
Shivakoti BR, Fujii S, Nozoe M, Tanaka S, Kunacheva C (2010) Perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) in water purification plants (WPPs) with advanced treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol.: Water Supply 10(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2010.707
Shoeib M, Vlahos P, Harner T, Peters A, Graustein M, Narayan J (2010) Survey of polyfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) in the atmosphere over the northeast Atlantic Ocean. Atmos Environ 44(24):2887–2893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.04.056
So MK, Miyake Y, Yeung WY, Ho YM, Taniyasu S, Rostkowski P, Yamashita N, Zhou BS, Shi XJ, Wang JX, Giesy JP, Yu H, Lam PKS (2007) Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl River and Yangtze river of China. Chemosphere 68(11):2085–2095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.008
So MK, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Giesy JP, Zheng J, Fang Z, Im SH, Lam PKS (2004) Perfluorinated compounds in coastal waters of Hong Kong, South China, and Korea. Environ. Sci. Technol 38(15):4056–4063. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049441z
Sun HW, Li FS, Zhang T, Zhang XZ, He N, Song Q, Zhao LJ, Sun LN, Sun TH (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters and WWTPs in Shenyang, China: mass flows and source analysis. Water Res 45(15):4483–4490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.036
Sun HW, Zhang XZ, Wang L, Zhang T, Li FS, He N, Alder A (2012) Perfluoroalkyl compounds in municipal WWTPs in Tianjin, China-concentrations, distribution and mass flow. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(5):1405–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0727-6
Takagi S, Adachi F, Miyano K, Koizumi Y, Tanaka H, Mimura M, Watanabe I, Tanabe S, Kannan K (2008) Perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in raw and treated tap water from Osaka, Japan. Chemosphere 72(10):1409–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.034
Takagi S, Adachi F, Miyano K, Koizumi Y, Tanaka H, Watanabe I, Tanabe S, Kannan K (2011) Fate of perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in drinking water treatment processes. Water Res 45(13):3925–3932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.04.052
Takemine S, Matsumura C, Yamamoto K, Suzuki M, Tsurukawa M, Imaishi H, Nakano T, Kondo A (2014) Discharge of perfluorinated compounds from rivers and their influence on the coastal seas of Hyogo prefecture. Japan Environ Pollut 184:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.016
Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Moon H-B, Kwok KY, Lam PKS, Horii Y, Petrick G, Kannan K (2013) Does wet precipitation represent local and regional atmospheric transportation by perfluorinated alkyl substances? Environ. Int 55:25–32
Thompson J, Eaglesham G, Reungoat J, Poussade Y, Bartkow M, Lawrence M, Mueller JF (2011) Removal of PFOS, PFOA and other perfluoroalkyl acids at water reclamation plants in south East Queensland Australia. Chemosphere 82(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.040
USEPA, 2011a. Exposure factors handbook: 2011 edition. Washington, DC. Federal Register Notice, Oct 3
USEPA (2011b) Revisions to the unregulated contaminants monitoring regulations (UCMR3) for public water systems. Fed Regist 76:1113–11737
USEPA, 2013. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and fluorinated telomers. Available from http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pfoa/index.html
USEPA, 2016. Fact sheet PFOA and PFOS drinking water health advisories
Vierke L, Ahrens L, Shoeib M, Palm W-U, Webster EM, Ellis DA, Ebinghaus R, Harner T (2013) In situ air–water and particle–water partitioning of perfluorocarboxylic acids, perfluorosulfonic acids and perfluorooctyl sulfonamide at a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 92(8):941–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.067
www.tianqi.com. (2011) The weather trend and statistical data of weather conditions in June, 2011. Available from: http://lishi.tianqi.com/shanghai/201106.html
Xiao F, Simcik MF, Gulliver JS (2013) Mehanisms for removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) from drinking water by conventional and enhanced coagulation. Water Res 47(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.024
Yeung LWY, Miyake Y, Taniyasu S, Wang Y, Yu HX, So MK, Jiang GB, Wu YN, Li JG, Giesy JP, Yamashita N, Lam PKS (2008) Perfluorinated compounds and total and extractable organic fluorine in human blood samples from China. Environ. Sci. Technol 42(21):8140–8145. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800631n
Zhang T, Sun HW, Wu Q, Zhang XZ, Yun SH, Kannan K (2010a) Perfluorochemicals in meat, eggs and indoor dust in China: assessment of sources and pathways of human exposure to perfluorochemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol 44(9):3572–3579. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1000159
Zhang T, Sun HW, Lin Y, Wang L, Zhang XZ, Liu Y, Geng X, Zhao LJ, Li FS, Kannan K (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in human blood, water, edible freshwater fish, and seafood in China: daily intake and regional differences in human exposures. J. Agric. Food Chem 59(20):11168–11176. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2007216
Zhang T, Wu Q, Sun HW, Zhang XZ, Yun SH, Kannan K (2010b) Perfluorinated compounds in whole blood samples from infants, children, and adults in China. Environ. Sci. Technol 44(11):4341–4347. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1002132
Zhang Y, Meng W, Guo CS, Xu J, Yu T, Fan WH, Li L (2012) Determination and partitioning behavior of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids and perfluorooctanesulfonate in water and sediment from Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere 88(11):1292–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.103
Zushi Y, Ye F, Motegi M, Nojiri K, Hosono S, Suzuki T, Kosugi Y, Yaguchi K, Masunaga S (2011) Spatially detailed survey on pollution by multiple perfluorinated compounds in the Tokyo Bay basin of Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol 45(7):2887–2893. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103917r
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41406213, 41376189, 41776202) and the Chinese Polar Environment Comprehensive Investigation and Assessment Program (Grant No. CHINARE2016-02-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Peter Kallenborn
The original publication of this paper contains a mistake. The correct presentation of the 7th Author is shown in this paper.
The original version of this article was revised.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1195 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Lu, R., Zheng, H. et al. Risk exposure assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water and atmosphere in central eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 9311–9320 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0950-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0950-x