Abstract
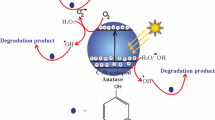
In this work, TiO2 (B) nano-belts were synthesized by hydrothermal method under stirring, and static conditions and preparation conditions were optimized. The prepared materials were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), and N2 adsorption/desorption measurement. The photocatalytic performance was evaluated by removing synthetic estrogen 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2), which is the most potent endocrine-disrupting chemical. The results show that the TiO2 nano-belt possesses pure metastable monoclinic TiO2 (B) and has uniform nano-belt shape with 80~120-nm diameters and 62.904 m2 g−1 of specific surface area. Under the best optimal preparation conditions (0.5 g P25, 20 mL 10 mol L−1 NaOH, hydrothermal temperature 180 °C for 18 h under stirring, 400 °C calcination for 2 h), the TiO2 (B) has better catalytic activity with 100.00% removal rate towards 3 mg L−1 EE2 in 120 min. The removal rates of EE2 over catalyst which was prepared under static condition and P25 are 74.66% and 70.71%, respectively. The photocatalytic degradation rate constant of TiO2 (B) prepared under stirring condition (0.0379 min−1) is 4.51 times and 8.42 times than those of TiO2 prepared under static condition (0.0084 min−1) and P25 (0.0045 min−1). The excellent photocatalytic activity is mainly ascribed to longer one-dimensional nano-belt structure and effective suppression of photo-produced electron-hole.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bavykin DV, Parmon VN, Lapkin AA, Walsh FC (2004) The effect of hydrothermal conditions on the mesoporous structure of TiO2 nanotubes. J Mater Chem 14:3370–3377
Bavykin DV, Carravetta M, Kulak AN, Walsh FC (2010) Application of magic-angle spinning NMR to examine the nature of protons in titanate nanotubes. Chem Mater 22:2458–2465
Belgiorno V, Rizzo L, Fatta D, Rocca DC, Lofrano G, Nikolaou A, Naddeo V, Meric S (2007) Review on endocrine disrupting-emerging compounds in urban wastewater: occurrence and removal by photocatalysis and ultrasonic irradiation for wastewater reuse. Desalination 215:166–176
Caldwell DJ, Mastrocco F, Anderson PD, Lange R, Sumpter JP (2012) Predicted-no-effect concentrations for the steroid estrogens estrone, 17beta-estradiol, estriol, and 17alpha-ethinylestradiol. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1396–1406
Chakraborty AK, Qi Z, Chai SY, Lee C, Park SY, Jang DJ, Lee WI (2010) Formation of highly crystallized TiO2(B) and its photocatalytic behavior. Appl Catal B Environ 93:368–375
Fagan R, McCormack DE, Dionysiou DD, Pillai SC (2016) A review of solar and visible light active TiO2 photocatalysis for treating bacteria, cyanotoxins and contaminants of emerging concern. Mater Sci Semicond Process 42:2–14
Ge MZ, Cao CY, Huang JJ, Li SH, Chen Z, Zhang KQ, Al-Deyab SS, Lai YK (2016) A review of one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructured materials for environmental and energy applications. J Mater Chem A 4:6772–6801
Jian T, Zhao ZH, Anil K, Boughton RI, Liu H (2014) Recent progress in design, synthesis, and applications of one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructured surface heterostructures: a review. Chem Soc Rev 43:6920–6937
León-Ríos S, González RE, Fuentes S, Ángel EC, Echeverría A, Serrano AE, Demergasso CS, Zárate RA (2016) One-dimensional TiO2-B crystals synthesised by hydrothermal process and their antibacterial behaviour on escherichia coli. J Nanomater 2016:1–8
Linsebigler AL, Lu GQ, Yates JT (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces—principles, mechanism, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758
Liu N, Chen XY, Zhang JL, Schwank JW (2014) A review on TiO2-based nanotubes synthesized via hydrothermal method: formation mechanism, structure modification, and photocatalytic applications. Catal Today 225:34–51
Menzel R, Peiro AM, Durrant JR, Shaffer MSP (2006) Impact of hydrothermal processing conditions on high aspect ratio titanate nanostructures. Chem Mater 18:6059–6068
Pessoa GP, de Souza NC, Vidal CB, Alves JA, Firmino PI, Nascimento RF, dos Santos AB (2014) Occurrence and removal of estrogens in Brazilian wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 490:288–295
Seo HK, Kim GS, Ansari SG, Kim YS, Shin HS, Shim KH, Suh EK (2008) A study on the structure/phase transformation of titanate nanotubes synthesized at various hydrothermal temperatures. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 92:1533–1539
Sreekantan S, Wei LC (2010) Study on the formation and photocatalytic activity of titanate nanotubes synthesized via hydrothermal method. J Alloys Compd 490:436–442
Xiao Q, Ouyang LL, Gao L, Yao C (2011) Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous N,S-codoped TiO2(B) nanobelts. Appl Surf Sci 257:3652–3656
Yang DJ, Liu HW, Zheng ZF, Yuan Y, Zhao JC, Waclawik ER, Ke XB, Zhu HY (2009) An efficient photocatalyst structure: TiO2(B) nanofibers with a shell of anatase nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 131:17885–17893
Yang Y, Luo LJ, Xiao M, Li H, Pan XJ, Jiang FZ (2015) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of surface fluorinated TiO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of estrogens. Mater Sci Semicond Process 40:183–193
Zhang YW, Xu JF, Feng JY, Yang A, Liu Y, Zhi MJ, Hong ZL (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in TiO2(B)@anatase heterostructure nanocomposites prepared by a facile hydrothermal method. Mater Lett 112:173–176
Zhang L, Jing DW, She XL, Liu HW, Yang DJ, Lu Y, Li J, Zheng ZF, Guo LJ (2014) Heterojunctions in g-C3N4/TiO2(B) nanofibres with exposed (001) plane and enhanced visible-light photoactivity. J Mater Chem A 2:2071–2078
Zhang Y, Xing Z, Liu X, Li Z, Wu X, Jiang J, Li M, Zhu Q, Zhou W (2016) Ti3+ self-doped blue TiO2(B) single-crystalline nanorods for efficient solar-driven photocatalytic performance. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:26851–26859
Zhang LX, Ni CH, Jiu HF, Chen H, Qi GS (2017a) Preparation of anatase/TiO2(B) TiO2 nanosheet for high performance of photocatalytic reduction of CO2. JMater Sci: Mater Electron 28:6601–6606
Zhang XF, Wang Y, Liu BS, Sang YH, Liu H (2017b) Heterostructures construction on TiO2 nanobelts: a powerful tool for building high-performance photocatalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 202:620–641
Zhao B, Chen F, Liu HQ, Zhang JL (2011) Mesoporous TiO2-B nanowires synthesized from tetrabutyl titanate. J Phys Chem Solids 72:201–206
Zheng ZF, Liu HW, Ye JP, Zhao JC, Waclawik ER, Zhu HY (2010) Structure and contribution to photocatalytic activity of the interfaces in nanofibers with mixed anatase and TiO2(B) phases. J Mol Catal A Chem 316:75–82
Zhou WJ, Gai LG, Hu PG, Cui JJ, Liu XY, Wang DZ, Li GH, Jiang HD, Liu D, Liu H, Wang JY (2011a) Phase transformation of TiO2 nanobelts and TiO2(B)/anatase interface heterostructure nanobelts with enhanced photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 13:6643
Zhou W, Sun F, Pan K, Tian G, Jiang B, Ren Z, Tian C, Fu H (2011b) Well-ordered large-pore mesoporous anatase TiO2 with remarkably high thermal stability and improved crystallinity: preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic performance. Adv Funct Mater 21:1922–1930
Zhou Y, Zha JM, Wang ZJ (2012) Occurrence and fate of steroid estrogens in the largest wastewater treatment plant in Beijing, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:6799–6813
Zhou W, Li W, Wang JQ, Qu Y, Yang Y, Xie Y, Zhang K, Wang L, Fu H, Zhao D (2014) Ordered mesoporous black TiO2 as highly efficient hydrogen evolution photocatalyst. J Am Chem Soc 136:9280–9283
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21767030), Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (2016FB014), and Foundation of Education Bureau of Yunnan Province (2017ZZX087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L., Xia, L., Tan, W. et al. The TiO2 (B) nano-belts with excellent performance prepared via alkaline stirring hydrothermal method and its application to remove 17α-ethynylestradiol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34018–34026 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3122-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3122-8