Abstract
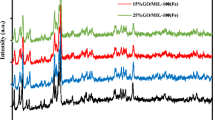
In this study, MIL-101(Fe), MIL-101(Fe,Cu), and graphene oxide (GO)/MIL-101(Fe,Cu) were synthesized to compose a novel sorbent. The adsorption properties of these three MOF-based composites were compared toward the removal of phosphate. Furthermore, the influencing factors including adsorption time, pH, temperature, and initial concentration on the adsorption capacity of phosphate on these materials as well as the reusability of the material were discussed. The structure of fabricated materials and the removal mechanism of phosphate on the composite material were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), nitrogen adsorption-desorption analysis, and zeta potential. The results show that the maximum adsorption capacity of phosphate by the composite GO/MIL-101(Fe,Cu)-2% was 204.60 mg·g−1, which is higher than that of MIL-101(Fe,Cu) and MIL-101(Fe). likewise the specific surface area of GO/MIL-101(Fe,Cu)-2% is 778.11 m2/g is higher than that of MIL-101(Fe,Cuand MIL-101(Fe),which are 747.75 and 510.66 m2/g, respectively. The adsorption mechanism of phosphate is electrostatic attraction, forming coordination bonds and hydrogen bonds. The fabricated material is a promising adsorbent for the removal of phosphate with good reusability.
Graphical abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15526-6
References
Adegoke KA, Bello OS (2015) Dye sequestration using agricultural wastes as adsorbents. Water Resour Ind 12:8–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2015.09.002
Al-Alwani MAM, Ludin NA, Mohamad AB, Kadhum AAH, Mukhlus A (2018) Application of dyes extracted from Alternanthera dentata leaves and Musa acuminata bracts as natural sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Spectrochim Acta A 192:487–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.11.018
Amini A, Khajeh M, Oveisi AR, Daliran S, Ghaffari-Moghaddam M, Delarami HS (2020) A porous multifunctional and magnetic layered graphene oxide/3D mesoporous MOF nanocomposite for rapid adsorption of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions. J Ind Eng Chem 93:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.10.008
Bacelo H, Pintor AMA, Santos SCR, Boaventura RAR, Botelho CMS (2020) Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem Eng J 381:122566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122566
Barbosa ADS, Julião D, Fernandes DM, Peixoto AF, Freire C, de Castro B, Granadeiro CM, Balula SS, Cunha-Silva L (2017) Catalytic performance and electrochemical behaviour of metal–organic frameworks: MIL-101(Fe) versus NH2-MIL-101(Fe). Polyhedron 127:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2016.10.032
Bu JQ, Yuan L, Ren YL, Liu YX, Meng Y, Peng X (2019) Enhanced removal of Eriochrome Black T in wastewater by Zirconium-based MOF/graphite oxide. Can J Chem:98. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2019-0368
Buhmann A, Papenbrock J (2013) Biofiltering of aquaculture effluents by halophytic plants: basic principles, current uses and future perspectives. Environ Exp Bot 92:122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.07.005
Burakov AE, Galunin EV, Burakova IV, Kucherova AE, Agarwal S, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Chen H, Liu TL, Meng Y, Cheng Y, Lu J, Wang HS (2020) Novel graphene oxide/aminated lignin aerogels for enhanced adsorption of malachite green in wastewater. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 603:125281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125281
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
Dapaah MF, Liu BJ, Cheng L (2021) Adsorption of organic compounds from aqueous solution by pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde grafted MIL-101(Cr)-NH2 metal-organic frameworks. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105275
Deletic A, Wang HT (2019) Water pollution control for sustainable development. Engineering 5:839–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2019.07.013
Dollimore D, Spooner P, Turner A (1976) The bet method of analysis of gas adsorption data and its relevance to the calculation of surface areas. Surf Technol 4:121–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-4583(76)90024-8
Dong Q, Shi SY, Xie YS, Wang YP, Zhang XQ, Wang XQ, Guo SY, Zhu LY, Zhang GH, Xu D (2020) Preparation of mesoporous zirconia ceramic fibers modified by dual surfactants and their phosphate adsorption characteristics. Ceram Int 46:14019–14029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.201
Drenkova-Tuhtan A, Schneider M, Franzreb M, Meyer C, Gellermann C, Sextl G, Mandel K, Steinmetz H (2017) Pilot-scale removal and recovery of dissolved phosphate from secondary wastewater effluents with reusable ZnFeZr adsorbent @ Fe3O4/SiO2 particles with magnetic harvesting. Water Res 109:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.039
Eltaweil AS, Elshishini HM, Ghatass ZF, Elsubruiti GM (2020) Ultra-high adsorption capacity and selective removal of Congo red over aminated graphene oxide modified Mn-doped UiO-66 MOF. Powder Technol 379:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.084
El-Yazeed WSA, El-Reash YGA, Elatwy LA, Ahmed AI (2020) Novel bimetallic Ag-Fe MOF for exceptional Cd and Cu removal and 3,4-dihydropyrimidinone synthesis. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 114:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.09.028
Emam HE, Abdelhameed RM, Ahmed HB (2020) Adsorptive performance of MOFs and MOF containing composites for clean energy and safe environment. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104386
Fakhri H, Farzadkia M, Boukherroub R, Srivastava V, Sillanpää M (2020) Design and preparation of core-shell structured magnetic graphene oxide@MIL-101(Fe): photocatalysis under shell to remove diazinon and atrazine pesticides. Sol Energy 208:990–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.08.050
Fu CC, Tran HN, Chen XH, Juang RS (2020) Preparation of polyaminated Fe3O4@chitosan core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for efficient adsorption of phosphate in aqueous solutions. J Ind Eng Chem 83:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.11.033
Gu Y, Xie DH, Wang YC, Qin WX, Zhang HM, Wang GZ, Zhang YX, Zhao HJ (2019) Facile fabrication of composition-tunable Fe/Mg bimetal-organic frameworks for exceptional arsenate removal. Chem Eng J 357:579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.174
Gupta NK, Saifuddin M, Kim S, Kim KS (2020) Microscopic, spectroscopic, and experimental approach towards understanding the phosphate adsorption onto Zn–Fe layered double hydroxide. J Mol Liq 297:111935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111935
He L, Dong YN, Zheng YN, Jia QM, Shan SY, Zhang YQ (2019) A novel magnetic MIL-101(Fe)/TiO2 composite for photo degradation of tetracycline under solar light. J Hazard Mater 361:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.079
He JJ, Xu YH, Wang W, Hu B, Wang ZJ, Yang X, Wang Y, Yang LW (2020) Ce(III) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range. Chem Eng J 379:122431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122431
Hou YB, Xu ZM, Yuan Y, Liu LX, Ma SC, Wang W, Hu Y, Hu WZ, Gui Z (2019) Nanosized bimetal-organic frameworks as robust coating for multi-functional flexible polyurethane foam: rapid oil-absorption and excellent fire safety. Compos Sci Technol 177:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.04.018
Huang WY, Zhang YM, Li D (2017) Adsorptive removal of phosphate from water using mesoporous materials: A review. J Environ Manag 193:470–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.02.030
Isiuku BO, Enyoh CE (2020) Pollution and health risks assessment of nitrate and phosphate concentrations in water bodies in South Eastern, Nigeria. Environ Adv 2:100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2020.100018
Kyzas GZ, Deliyanni EA, Bikiaris DN, Athanasios CM (2018) Graphene composites as dye adsorbents: review. Chem Eng Res Des 129:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.006
Lai KC, Lee LY, Hiew BYZ, Gopakumar ST, Gan SY (2018) Environmental application of three-dimensional graphene materials as adsorbents for dyes and heavy metals: review on ice-templating method and adsorption mechanisms. J Environ Sci 79:174–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.11.023
Langer M, Väänänen J, Boulestreau M, Miehe U, Bourdon C, Lesjean B (2017) Advanced phosphorus removal via coagulation, flocculation and microsieve filtration in tertiary treatment. Water Sci Technol 75:2875–2882. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.166
Lebron YAR, Moreira VR, Drumond GP, Gomes GCF, da Silva MM, de Oliveira BR, Jacob RS, Viana MM, de Vasconcelos CKB, de Souza Santos LV (2020) Statistical physics modeling and optimization of norfloxacin adsorption onto graphene oxide. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 606:125534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125534
Leo CP, Chai WK, Mohammad AW, Qi Y, Hoedley AF, Chai SP (2011) Phosphorus removal using nanofiltration membranes. Water Sci Technol 64:199–205. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.598
Li ZC, Liu XM, Jin W, Hu QS, Zhao YP (2019) Adsorption behavior of arsenicals on MIL-101(Fe): the role of arsenic chemical structures. J Colloid Interface Sci 554:692–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.046
Li YT, Ju WM, Yang L, Zhang LL, Sun YJ (2020) Adsorption behaviors and mechanism of graphene oxide for silver complex anion removal. Appl Surf Sci 529:147112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147112
Lin JL, Hu H, Gao NY, Ye JS, Chen YJ, Ou H (2020) Fabrication of GO@MIL-101(Fe) for enhanced visible-light photocatalysis degradation of organophosphorus contaminant. J Water Process Eng 33:101010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101010
Liu RT, Chi LN, Wang XZ, Sui YM, Wang Y, Arandiyan H (2018) Review of metal (hydr)oxide and other adsorptive materials for phosphate removal from water. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5269–5286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.008
Liu ZN, Fan AP, Han XG, Shapour H, Zhang QY (2020a) PEI-modified chromium-based metal organic framework for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 184:139–149. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24992
Liu ZN, Fan AP, Ho CH (2020b) Preparation of AC/Cu-BTC composite and its adsorption mechanisms. J Environ Eng 146:04020018. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001678
Liu YX, Li S, Wang C, Guo L, Wang YZ (2020c) Accordion-like bimetal-organic framework anchoring on the partially-exfoliated graphite paper for high-performance supercapacitors. Appl Surf Sci 528:146954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146954
Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Bolan NS (2014) Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:847–907. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2012.741311
Nebol'sin VA, Galstyan V, Silina YE (2020) Graphene oxide and its chemical nature: multi-stage interactions between the oxygen and graphene. Surf Interfaces 21:100763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100763
Ogata F, Uematsu Y, Fukuda M, Saenjum C, Kabayama M, Nakamura T, Kawasaki N (2020) Changes in the mechanism of the reaction between phosphate and magnesium ions: effect of initial concentration and contact time on removal of phosphate ions from aqueous media. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104385
Rego RM, Kuriya G, Kurkuri MD, Kigga M (2021) MOF based engineered materials in water remediation: recent trends. J Hazard Mater 403:123605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123605
Santana CS, Olivares DMM, Silva VHC, Luzardo FHM, Velasco FG, de Jesus RM (2020) Assessment of water resources pollution associated with mining activity in a semi-arid region. J Environ Manag 273:111148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111148
Sarma VVSS, Vivek R, Rao DN, Ghosh VRD (2020) Severe phosphate limitation on nitrogen fixation in the Bay of Bengal. Cont Shelf Res 205:104199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2020.104199
Srinivasan A, Viraraghavan T (2010) Decolorization of dye wastewaters by biosorbents: a review. J Environ Manag 91:1915–1929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.05.003
Strokal M, Kroeze C (2020) Water, society and pollution in an urbanizing world: recent developments and future challenges. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 46:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2020.10.003
Sun XB, Zhou YL, Zheng XG (2020) Comparison of adsorption behaviors of Fe-La oxides co-loaded MgO nanosheets for the removal of methyl orange and phosphate in single and binary systems. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104252
Tian YH, Yu ZC, Cao LY, Zhang XL, Sun CH, Wang DW (2021) Graphene oxide: an emerging electromaterial for energy storage and conversion. J Energy Chem 55:323–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.07.006
Wang L, Wang JY, He C, Lyu W, Zhang WL, Yan W, Yang L (2019) Development of rare earth element doped magnetic biochars with enhanced phosphate adsorption performance. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 561:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.10.082
Wang YT, Wang KQ, Lin J, Xiao LQ, Wang XL (2020a) The preparation of nano-MIL-101(Fe)@chitosan hybrid sponge and its rapid and efficient adsorption to anionic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 165(B):684–2692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.073
Wang YF, Zhao W, Qi ZY, Zhang L, Zhang YN, Huang HO, Peng YZ (2020b) Designing ZIF-8/hydroxylated MWCNT nanocomposites for phosphate adsorption from water: capability and mechanism. Chem Eng J 394:124992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124992
Zhang Y, Li HJ, Li MC, Li MH (2020) Adsorption of aniline on aminated chitosan/graphene oxide composite material. J Mol Struct 1209:127973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127973
Zheng YQ, Cheng B, You W, Yu JG, Ho WK (2019) 3D hierarchical graphene oxide-NiFe LDH composite with enhanced adsorption affinity to Congo red, methyl orange and Cr(VI) ions. J Hazard Mater 369:214–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.013
Zhou X, Huang WY, Shi J, Zhao ZX, Xia QB, Li YW, Wang HH, Li Z (2014) A novel MOF/graphene oxide composite GrO@MIL-101 with high adsorption capacity of acetone. J Mater Chem A 2:4722–4730. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA15086K
Availability of data and materials
All authors agreed to state that required data and materials relevant will be available for further validity of the results presented.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51278418).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
You Wu designed the materials, conducted major adsorption experiments, and wrote the manuscript of the paper. Zhuannian Liu provided guidance of the research, reviewed the manuscript, and provided experimental resources. Bakhtari Mohammad Fahim conducted data processing and grammar review. Junnan Luo did the characterization experiment. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We assured that this manuscript is original work and this work neither accepted nor submitted simultaneously to any other journals.
Consent to participate
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript.
Consent for publication
This manuscript is approved by all authors for publication in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The correct name of the 2nd Author is presented in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Liu, Z., Bakhtari, M.F. et al. Preparation of GO/MIL-101(Fe,Cu) composite and its adsorption mechanisms for phosphate in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51391–51403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14206-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14206-9