Abstract
Purpose
Heavy metals often occur as co-contaminants with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and reportedly have adverse effects on biodegradation. In this study, the development of 14C-phenanthrene mineralisation in soil co-contaminated with aged or freshly added Al or Fe amendment was assessed.
Materials and methods
14C-phenanthrene mineralisation was assessed using respirometry; respirometers incorporated a Teflon-lined screw-capped CO2 trap containing 1-M NaOH within a glass scintillation vial. The production of 14CO2 was assessed by the addition of Ultima Gold liquid scintillation fluid to the CO2 traps and subsequent liquid scintillation counting. Enumeration of phenanthrene-degrading bacteria was achieved by counting the colony forming unit count using the spread plate method.
Results and discussion
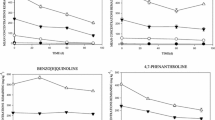
This investigation considered the effects of Al and Fe (50, 100, 250 and 500 mg/kg) on 14C-phenanthrene biodegradation in soil over 63-day contact time. Fresh Al amendments at lower concentrations (50 and 100 mg/kg) stimulated phenanthrene catabolism (p <0.05) at t = 21 and 42 days which may reflect an ‘Arndt–Schulz’ effect, but phenanthrene catabolism was significantly reduced (p <0.05) in 500 mg/kg aged Al this could be due to Al toxicity to phenanthrene degraders. Phenanthrene mineralisation was stimulated in the highest Fe concentration (500 mg/kg) in aged and fresh Fe amendments at t = 21 days. This could be because Fe is an essential requirement for microbial growth.
Conclusions
The impact of Al or Fe on the catabolism of 14C-phenanthrene was dependent on incubation time and Al was more toxic than Fe to soil PAH catabolic activity. This could be because Al is a non-essential microbial requirement. Bioremediation of soils co-contaminated with PAH and heavy metal is a complex problem; therefore, studies on the impact of metals on PAHs biodegradation highlight the risks and biodegradation potential in contaminated soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezcua-Allieri MA, Lead JR, Rodriguez-Vazquez R (2005) Impact of microbial activity on copper, lead and nickel mobilization during the bioremediation of soil PAHs. Chemosphere 61:484–491
Amor L, Kennes C, Veiga MC (2001) Kinetics of inhibition in the biodegradation of monoaromatic hydrocarbons in presence of heavy metals. Bioresource Technol 78:181–185
Baldrin P, Wiesche C, Gabriel J, Nerud F, Zadrazil F (2000) Influence of cadmium and mercury on activities of ligninolytic enzymes and degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pleurotus osreatus in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2471–2478
Cao L, Shen G, Lu Y (2008) Combined effects of heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on soil microorganisms communities. Environ Geol 54:1531–1536
Chaperon S, Sauve S (2007) Toxicity interaction of metals (Ag, Cu, Hg, Zn) to urease and dehydrogenase activities. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2329–2338
Couling NR, Towell MG, Semple KT (2010) Biodegradation of PAHs in soil: influence of chemical structure, concentration and multiple amendment. Environ Pollut 158:3411–3420
Dahlin S, Witter E (1998) Can the low microbial biomass C-to-organic C ratio in an acid and a metal contaminated soil be explained by differences in the substrate utilization efficiency and maintenance requirement? Soil Biol Biochem 30:633–641
Dai J, Li S, Zhang Y, Wang R, Yu Y (2008) Distribution, sources and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in topsoil at Ji’nan city, China. Environ Monit Assess 147:317–326
Dinkla IT, Gabor EM, Janssen DB (2001) Effects of iron limitation on the degradation of toluene by pseudomonas strains carrying the TOL (Pwwo) plasmid. Appl Environ Microb 67:3406–3412
Doick KJ, Lee PH, Semple KT (2003) Assessment of spiking procedures for the introduction of a phenanthrene-LNAPL mixture into field-wet soil. Environ Pollut 126:399–406
Flis SE, Glenn AR, Dilworth MJ (1993) The interaction between aluminium and root nodule bacteria. Soil Biol Biochem 25:403–417
Freeman DJ, Cattell CR (1990) Woodburning as a source of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Technol 24:1581–1585
Giller KE, Witter E, Mcgrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414
Gogolev A, Wilke BM (1997) Combination effects of heavy metals and fluoranthene on soil bacteria. Biol Fert Soils 25:274–278
Haanstra L, Doelman P (1984) Glutamic acid decomposition as a sensitive measure of heavy metal pollution in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 16:595–600
Hoffman DR, Okon JL, Sandrin TR (2005) Medium composition affects the degree and pattern of cadmium inhibition of naphthalene biodegradation. Chemosphere 59:919–927
Hong JW, Park JY, Gadd GM (2010) Pyrene degradation and copper and zinc uptake by Fusarium solani and Hypocrea lixii isolated from petrol station soil. J Appl Microbiol 108:2030–2040
Ibarrolaza A, Coppotelli RM, Del Panno MT, Donati ER, Morelli IS (2009) Dynamics of microbial community during bioremediation of phenanthrene and chromium(VI)-contaminated soil microcosms. Biodegradation 20:95–107
Illmer P, Buttinger R (2006) Interactions between iron availability, aluminium toxicity and fungal siderophores. Biometals 19:367–377
Irha N, Slet J, Petersell V (2003) Effects of heavy metals and PAH on soil assessed via dehydrogenase assay. Environ Int 28:779–782
Ke L, Luo L, Wang P, Luan T, Tam NF-Y (2010) Effects of metals on biosorption and biodegradation of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a freshwater green alga Selenastrum capricornutum. Bioresource Technol 101:6950–6961
Lakzian A, Murphy P, Turner A, Beynon JL, Giller KE (2002) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. Viciae populations in soils with increasing heavy metal contamination: abundance, plasmid profiles, diversity and metal tolerance. Soil Biol Biochem 34:519–529
Lee PH, Doick KJ, Semple KT (2003) The development of phenanthrene catabolism in soil amended with transformer oil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 228:217–223
Macleod CJA, Semple KT (2002) The adaptation of two similar soils to pyrene catabolism. Environ Pollut 119:357–364
Macleod CJA, Semple KT (2006) The influence of single and multiple applications of pyrene on the evolution of pyrene catabolism in soil. Environ Pollut 139:455–460
Malakul P, Srinivasan KR, Wang HY (1998) Metal toxicity reduction in naphthalene biodegradation by use of metal chelating adsorbents. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4610–4613
Maliszewka-Kordybach B, Smereczak B (2003) Habitat function of agricultural soils as affected by heavy metals and polyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination. Environ Int 28:719–728
Moreno JL, Bastida F, Ros M, Hernandez T, Garcia C (2009) Soil organic carbon buffers heavy metal contamination on semiarid soils: Effects of different metal threshold levels on soil microbial activity. Eur J Soil Biol 45:220–228
Nakatsu CH, Carmosini N, Baldwin B, Beasley PK, Konopka A (2005) Soil microbial community responses to additions of organic carbon substrates and heavy metals (Pb and Cr). Appl Environ Microb 71:7679–7689
Oliveira A, Pampulha ME (2006) Effects of long-term heavy metal contamination on soil microbial characteristics. J Biosci Bioeng 102:157–161
Peng WY, JiYan S, Hui W, Qi L, XinCai C, YingXu C (2007) The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotox Environ Safe 67:75–81
Pepper IL, Gentry TJ, Newby DT, Roane TM, Josephson KL (2002) The role of cell bioaugmentation and gene bioaugmentation in the remediation of co-contaminated soils. Environ Health Perspect 110:943–946
Pereira P, Lopes WA, Carvalho LS, da Rocha GO, Bahia NC, Loyola J, Quiterio SL, Escaleria V, Arbilla G, de Andrade JB (2007) Atmospheric concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of particulate trace metals in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Atmos Environ 41:7837–7850
Perez Silva R, Rodriguez A, Montes De Oca J, Moreno D (2009) Biosorption of chromium, copper, manganese and zinc by Pseudomonas aeroginosa AT 18 isolated from a site contaminated with petroleum. Bioresour Technol 100:1533–1538
Pina RG, Cervantes C (1996) Microbial interactions with aluminium. Biometals 9:311–316
Post RD, Beeby N (1996) Activity of the microbial decomposer community in metal-contaminated roadside soils. J Appl Ecol 33:703–709
Rajapaksha RMCP, Tobor-Kaplon MAM, Baath E (2004) Metal toxicity affects fungal and bacterial activities in soil differently. Appl Environ Microb 70:2966–2973
Reid BJ, Macleod CJA, Lee PH, Morriss AWJ, Stokes JD, Semple KT (2001) A simple 14C-respirometric method for assessing microbial catabolic potential and contaminant bioavailability. FEMS Microbiol Lett 196:141–146
Rhodes AH, McAllister LE, Chen R, Semple KT (2010) Impact of activated charcoal on the mineralisation of 14C-phenanthrene in soils. Chemosphere 79:463–469
Riis V, Babel W, Pucci OH (2002) Influence of heavy metals on the microbial degradation of diesel fuel. Chemosphere 49:559–568
Roane TM, Pepper IL (2000) Microbial responses to environmentally toxic cadmium. Microbial Ecol 38:358–364
Said WA, Lewis DL (1991) Quantitative assessment of the effects of metals on microbial degradation of organic chemicals. Appl Environ Microb 57:1498–1503
Sandrin TR, Maier RM (2003) Impact of metals on the biodegradation of organic pollutants. Environ Health Perspect 111:1093–1101
Sandrin TR, Chech AM, Maier RM (2000) A rhamnolipid biosurfactant reduces cadmium toxicity during naphthalene biodegradation. Appl Environ Microb 66:4585–4588
Santos EC, Jacques RJS, Bento FM, Peralba MR, Selbach PA, Sa ELS, Camargo AO (2008) Anthracene biodegradation and surface activity by iron-stimulated Pseudomonas sp. Bioresource Technol 99:2644–2649
Shen G, Cao L, Yitong L, Hong J (2005) Influence of phenanthrene on cadmium toxicity to soil enzymes and microbial growth. Environ Sci Pollut R 12:259–263
Shen G, Lu Y, Hong J (2006) Combined effect of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on urease activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 63:474–480
Sikkema J, de Bont JAM, Poolman B (1994) Interactions of cyclic hydrocarbons with biological membranes. Biol Chem 269:8022–8028
Simarro R, Gonzalez N, Bautista L, Sanz R, Molina MC (2011) Optimisation of key abiotic factors of PAH (naphthalene, phenanthrene and anthracene) biodegradation process by a bacterial consortium. Water Air Soil Pollut 217:365–374
Sokhn J, De Leij FAAM, Hart TD, Lynch JM (2001) Effect of copper on the degradation of phenanthrene by soil microorganisms. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:164–168
Tani A, Inoue C, Tanaka Y, Yamamoto Y, Kondo H, Hiradate S, Kimbara K, Kawai F (2008) The crucial role of mitochondrial regulation in adaptive aluminium resistance in Rhodotoruls glutinis. Microbiology 154:3437–3446
Thavamani P, Megharaj M, Krishnamurti GSR, Mcfarland R, Naidu R (2011) Finger printing of mixed contaminants from former manufactured gas plant (MGP) site soils: implications to bioremediation. Environ Int 37:184–189
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (2008) Available: http://www.epa.gov/wastes/hazard/Wastemin/minimize/factshts/pahs.pdf. Accessed 8 Dec 2011
Wild SR, Jones KC (1995) polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in the United Kingdom environment: a preliminary source inventory and budget. Environ Pollut 88:91–108
Wong KW, Toh BA, Ting YP, Obbard JP (2005) Biodegradation of phenanthrene by the indigenous microbial biomass in a zinc-amended soil. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:50–55
Yunker MB, Lachmuth CL, Cretney WJ, Fowler BR, Dangerfield N, White L, Ross PS (2011) Biota-sediment partitioning of aluminium smelter related PAHs and pulp mill related diterpenes by intertidal clams at Kitimat British Columbia. Mar Environ Res 72:105–126
Zhang X, Liu P, Yang YS, Xu G (2007) Effect of Al in soil on photosynthesis and related morphological and physiological characteristics of two soybean genotypes. Bot Stud 48:435–444
Zukauskaite A, Jakubauskaite V, Belous O, Ambrazaitiene D, Stasiskiene Z (2008) Impact of heavy metals on oil products biodegradation process. Waste Manage Res 26:500–507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Willie Peijnenburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obuekwe, I.S., Semple, K.T. Impact of Al and Fe on the development of phenanthrene catabolism in soil. J Soils Sediments 13, 1589–1599 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0759-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0759-2